标签:android style blog http io color ar os 使用
当我们想展示一个数组形式的数据的时候,要么是使用列表的形式,要么是使用网格的形式,今天我们介绍一种奇葩的形式,圆圈形式:
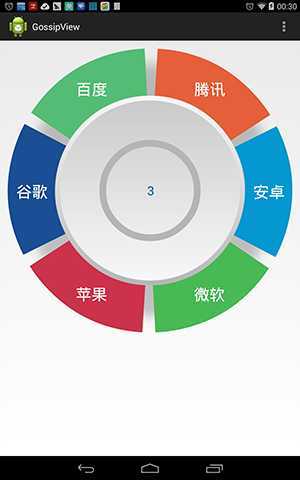
注意,周边的扇形是可以点击的。如果使用现有控件,要实现起来是有难度的,所以我们就采用了自定义View的方式。
下面是原理以及使用方法,整个项目可以到这里下载:https://github.com/jianghejie/GossipView
绘制
主要是外部扇形以及内部圆圈背景的绘制,最里面其实还有个很细的圆圈,那个其实是用在当想显示加载效果的时候,但这不是重点略去不讲。
内部圆圈背景的绘制很简单直接使用Drawable 的draw方法,前提是先设置好bounds(下面会讲到).
mInnerBackGroud.draw(canvas);
而外部扇形的绘制是分别调用drawArc方法(也许应该取别的名字,和canvas的方法冲突了)完成的:
for(int i = 0;i < mPieceNumber ; i++){ drawArc(i , canvas); }
有多少个扇形调用多少次。
drawArc定义如下:
/** 按索引值绘制扇区,第一个扇区的中心位于3点钟方向*/ public void drawArc(int index , Canvas canvas){ int startdegree = mPieceDegree * (index) - (mPieceDegree - mDividerDegree) / 2; if(index == mSelectIndex){ mOuterArcPaint.setColor(0xFFcacccc); }else{ mOuterArcPaint.setColor(outArcColor[index]); } float radious = ((float)mWidth - (float)outArctrokeWidth) / 2 - padding ; float midDegree = startdegree + ( mPieceDegree - mDividerDegree) /2 ; double x = radious * Math.cos(midDegree * Math.PI/180); double y = radious * Math.sin(midDegree * Math.PI/180); x = x + getOriginal().x; y = y + getOriginal().y; canvas.drawArc(mOuterArcRectangle, startdegree, mPieceDegree - mDividerDegree, false, mOuterArcPaint); Rect rect = new Rect(); mOuterTextPaint.getTextBounds(items.get(index).getTitle(), 0, items.get(index).getTitle().length(), rect); int txWidth = rect.width(); int txHeight = rect.height(); canvas.drawText(items.get(index).getTitle(), (int)x - txWidth/2, (int)y + txHeight/2, mOuterTextPaint); }
空间计算:
根据onMeasure方法中的宽和高计算出不同区域的基本参 数,比如外扇形的厚度outArctrokeWidth,外扇形文字的大小mOuterTextPaint,外扇形的半径 mOuterArcRadius,外扇形绘制的矩形区域mOuterArcRectangle;以及内部圆圈mInnerBackGroud的 bounds。
按下效果:
外部扇形的按下效果是根据不同状态下设置画笔的颜色来实现的:
如果某一个扇形的索引刚好等于选中的mSelectIndex,则设置按下的颜色:
if(index == mSelectIndex){ mOuterArcPaint.setColor(0xFFcacccc); }else{ mOuterArcPaint.setColor(outArcColor[index]); }
而内部的圆圈部分则直接采用selector图片的方式:
if(mSelectIndex == -1){ Log.i(TAG,"mSelectIndex = "+mSelectIndex); mInnerBackGroud.setState(PRESSED_FOCUSED_STATE_SET); }else{ mInnerBackGroud.setState(EMPTY_STATE_SET); }
mSelectIndex == -1 表示选中的是最中间的圆圈,若为真设置Drawable mInnerBackGroud的状态为PRESSED_FOCUSED_STATE_SET,反之为EMPTY_STATE_SET,因为 mInnerBackGroud其实是由selector得来的Drawable ,所以只要设置了不同的状态就会绘出不同的图片效果。
另外为了处理扇形和内部圆圈的按下效果,我们必须判断当前到底是点中了那部分
@Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { if(event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) { mSelectIndex = getTouchArea(new Point(event.getX() , event.getY())); this.invalidate(); Log.i(TAG ,"mSelectIndex =" +mSelectIndex); //mSelectIndex = -1; }else if(event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP && event.getAction() != MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL){ int upIndex = getTouchArea(new Point(event.getX() , event.getY())); if(mListener != null){ mListener.onPieceClick(upIndex); } mSelectIndex = -2; this.invalidate(); }else if(event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL){ mSelectIndex = -2; this.invalidate(); } return true; }
在ACTION_DOWN事件中,调用getTouchArea来判断当前选中的是什么,getTouchArea可能返回的有三种值:
-1 选中的是最中间的圆圈
-2 选中的是扇形之间的间隔部分
整数:选中的是某个扇形。
当ACTION_UP事件发生之后我们通知UI重绘,并且调用onPieceClick通知注册的Lisetner我选择了什么。
监听选中了什么
GossipView.OnPieceClickListener
public interface OnPieceClickListener { void onPieceClick(int whitchPiece); }
这个不用解释了吧,最常见的观察者模式。
下面是使用方法:
xml中:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context="com.jcodecraeer.gossipview.MainActivity" > <com.jcodecraeer.gossipview.GossipView android:id="@+id/gossipview" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" /> </RelativeLayout>
Activity中:
... GossipView gossipView = (GossipView)findViewById(R.id.gossipview); String [] strs = {"安卓","微软","苹果","谷歌","百度","腾讯"} ; final List<GossipItem> items =new ArrayList<GossipItem>(); for(int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) { GossipItem item = new GossipItem(strs[i],3); items.add(item); } gossipView.setItems(items); gossipView.setNumber(3); gossipView.setOnPieceClickListener( new GossipView.OnPieceClickListener(){ @Override public void onPieceClick(int index) { if(index != -1 && index != -2) { Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "你选择了" + items.get(index).getTitle(), 300).show(); } } }); ....
GossipItem的定义:
package com.jcodecraeer.gossipview; public class GossipItem { private String title; private int index; public GossipItem (String title,int index){ this.title =title; this.index = index; } public String getTitle() { return title; } public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; } public int getIndex() { return index; } public void setIndex(int index) { this.index = index; } }
转载自:http://www.jcodecraeer.com/a/anzhuokaifa/androidkaifa/2014/1115/1986.html
标签:android style blog http io color ar os 使用
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/noodlesonce/p/4099001.html