标签:style blog http io color ar os 使用 sp
在STL中,容器是其中的重中之重,基本的STL中的算法,仿函数等都是围绕着容器实现的功能。而,内存配置器,是容器的实现的基础。所以,我第一次要去编写便是内存配置器的实现。在STL中,内存配置器的实现是在stl_alloc.h中。
在SGI STL中配置分为两级,第一级配置器和第二级配置器。两者关系如下:
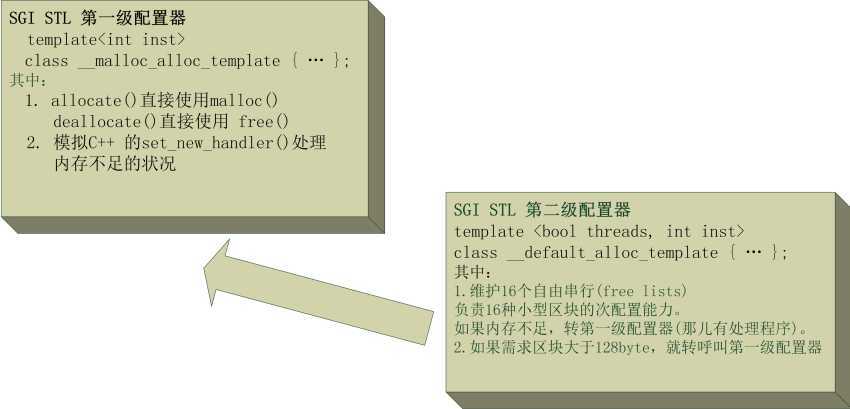
图1:第一级配置器和第二级配置器
在SGI STL中内存的配置器分为两级,第一级配置器和第二级配置器。第一级配置器就是,直接调用系统的malloc分配内存。对于小于128byte的内存分配请求,我们使用第二级内存配置器。第二级内存配置器是一个内存池,其中共有16个已分配好的区块形成的链表。这16个链表的中区块的大小依次是8,16,24....128byte,都8的倍数。每次请求小于等于128byte时,把请求的大小上调到最接近的8的倍数,比如,7就上调为8,30就上调为32,然后找到对应大小区块的链表,从中取下一个区块返回给请求。
第二级配置器使用内存池的好处就是,可以避免太多小额区块造成的内存破碎。同时,每次分配内存都需要调用malloc去分配,malloc调用的消耗的时间等资源是一定的,对于大区块的分配这样的消耗的时间等资源,是没有什么的。但是对于小额区块的,它的消耗就显得太不值的了。我们可以采用一次预分配一块连续的大区块,把它串成一个定额大小的区块链表,(8的倍数字节),下次使用的时候,从对应预分配的区块链表中找一个能够满足大小的,最接近的区块直接返回给请求,这样就可以避免对于小区块的malloc调用。同时对于小区块的释放,可以直接把它加入到内存池中对应大小的链表中即可。
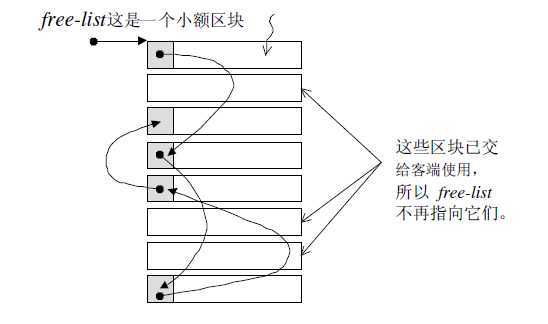
图2:把连续大区块串成小额区块
在第二级配置器中维持一个free_list[16]数组,其中存储着8-128byte各种大小区块的链表的头节点地址。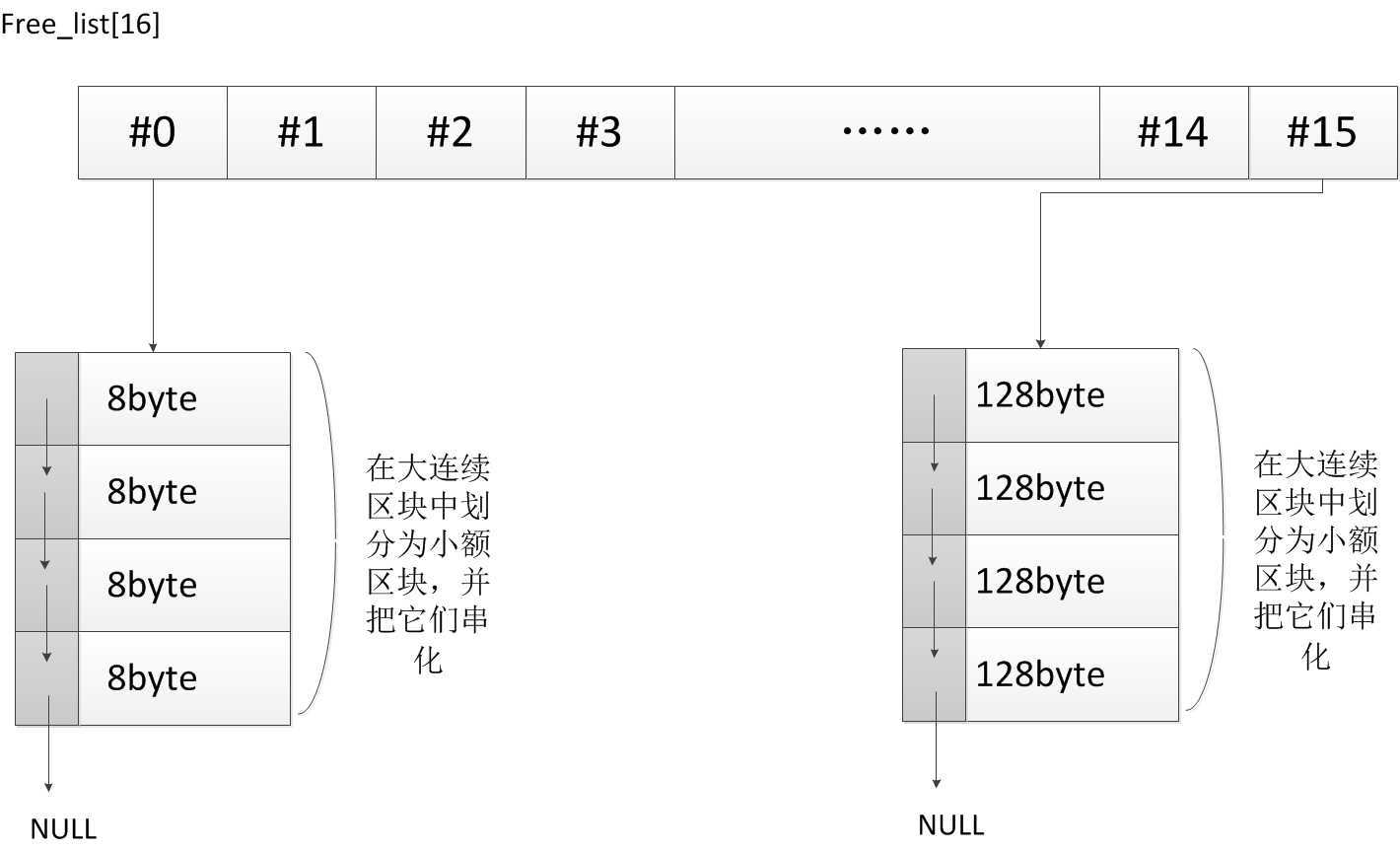
图3:free_list[16]结构
每次分配只要从适当大小的链表中取出第一个节点,返回给请求,让free_list对应的位置的保存链表的下一个节点地址。释放的时候,对于小于等于128byte的区块,只要把它插入对应大小区块链表的头,然后调整保存的链表头结点的地址就可以了。当需求大小区块的使用完了的时候,可以利用malloc一次分配适当大小的大区块,然后把它分割为对应大小的小区块,在把它们串联起来形成链表,把第一个节点地址存入对应的free_list的位置中。
上面只是配置器的简介,在源码中有详细的注释。源码如下:

1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: stl_alloc_wjzh.h 3 > Author: wjzh 4 > Mail: wangjzh_1@163.com 5 > Created Time: 2014年10月31日 星期五 16时06分23秒 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 8 #ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALLOC_WJZH_H 9 #define __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALLOC_WJZH_H 10 11 #ifdef __SUNPRO_CC 12 # define __PRIVATE public 13 #else 14 # define __PRIVATE private 15 #endif 16 17 #ifdef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG 18 # define __USE_MALLOC 19 #endif 20 21 #if 0 22 # include <new> 23 # define __THROW_BAD_ALLOC throw bad_alloc 24 #elif !defined(__THROW_BAD_ALLOC) 25 //# include <iostream.h> 26 #include <iostream> 27 # define __THROW_BAD_ALLOC std::cerr << "out of memory" << std::endl; exit(1) 28 #endif 29 30 #ifndef __ALLOC 31 # define __ALLOC alloc 32 #endif 33 #ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS 34 # include <windows.h> 35 #endif 36 37 #include <stddef.h> 38 #include <stdlib.h> 39 #include <string.h> 40 #include <assert.h> 41 #ifndef __RESTRICT 42 # define __RESTRICT 43 #endif 44 45 #if !defined(__STL_PTHREADS) && !defined(_NOTHREADS) 46 && !defined(__STL_SGI_THREADS) && !defined(__STL_WIN32THREADS) 47 # define _NOTHREADS 48 #endif 49 50 #ifdef __STL_PTHREADS 51 # include <pthread.h> 52 # define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK 53 if (threads) pthread_mutex_lock(&__node_allocator_lock) 54 # define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK 55 if (threads) pthread_mutex_unlock(&__node_allocator_lock) 56 # define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS true 57 # define __VOLATILE volatile 58 # endif 59 # ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS 60 # define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK 61 EnterCriticalSection(&__node_allocator_lock) 62 # define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK 63 LeaveCriticalSection(&__node_allocator_lock) 64 # define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS true 65 # define __VOLATILE volatile 66 # endif 67 68 # ifdef __STL_SGI_THREADS 69 extern "C" { 70 extern int __us_rsthread_malloc; 71 } 72 # define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK if (threads && __us_rsthread_malloc) 73 { __lock(&__node_allocator_lock); } 74 # define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK if(threads && __us_rsthread_malloc) 75 { __unlcok(&__node_allocator_lock); } 76 # define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS true 77 # define __VOLATILE volatile 78 # endif 79 80 # ifdef _NOTHREADS 81 # define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK 82 # define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK 83 # define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS false 84 # define __VOLATILE 85 # endif 86 87 __STL_BEGIN_NAMESPACE 88 89 #if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32) 90 #pragma set woff 1174 91 #endif 92 93 #ifdef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG 94 # ifdef __DECLARE_GLOBALS_HERE 95 void (* __malloc_alloc_oom_handler)() = 0; 96 #else 97 extern void (* __malloc_alloc_oom_handler)(); 98 # endif 99 #endif 100 101 template <int inst> 102 class __malloc_alloc_template { 103 private: 104 static void *oom_malloc(size_t); 105 static void *oom_realloc(void *, size_t); 106 #ifndef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG 107 static void (* __malloc_alloc_oom_handler)(); 108 #endif 109 public: 110 static void* allocate(size_t n) 111 { 112 void *result = malloc(n); 113 if (0 == result) result = oom_malloc(n); 114 return result; 115 } 116 117 static void deallocate(void *p, size_t) 118 { 119 free(p); 120 } 121 122 static void * reallocate(void *p, size_t , size_t new_sz) 123 { 124 void *result = realloc(p, new_sz); 125 if (0 == result) result = oom_realloc(p, new_sz); 126 return result; 127 } 128 129 static void (* set_malloc_handler(void (*f)()))() 130 { 131 void (* old)() = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler; 132 __malloc_alloc_oom_handler = f; 133 return(old); 134 } 135 136 }; 137 138 // malloc_alloc out-of-memory handling 139 // 分配内存时,没有内存时的处理 140 141 #ifndef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG 142 template <int inst> 143 void (* __malloc_alloc_template<inst>::__malloc_alloc_oom_handler)() = 0; 144 #endif 145 146 template <int inst> 147 void * __malloc_alloc_template<inst>::oom_malloc(size_t n) 148 { 149 void (* my_malloc_handler)(); 150 void *result; 151 for (;;) 152 { 153 my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler; 154 if (0 == my_malloc_handler) { __THROW_BAD_ALLOC; } 155 (*my_malloc_handler)(); 156 result = malloc(n); 157 if (result) return (result); 158 } 159 } 160 161 template <int inst> 162 void * __malloc_alloc_template<inst>::oom_realloc(void *p, size_t n) 163 { 164 void (* my_malloc_handler)(); 165 void *result; 166 167 for (;;) 168 { 169 my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler; 170 if (0 == my_malloc_handler) { __THROW_BAD_ALLOC; } 171 (*my_malloc_handler)(); 172 result = realloc(p, n); 173 if (result) return (result); 174 } 175 } 176 177 typedef __malloc_alloc_template<0> malloc_alloc; 178 179 template<class T, class Alloc> 180 class simple_alloc 181 { 182 public: 183 static T *allocate(size_t n) 184 { 185 return 0 == n ? 0 : (T*) Alloc::allocate(n * sizeof(T)); 186 } 187 static T *allocate(void) 188 { 189 return (T*) Alloc::allocate(sizeof(T)); 190 } 191 static void deallocate(T *p, size_t n) 192 { 193 if (0 != n) Alloc::deallocate(p, n * sizeof(T)); 194 } 195 static void deallocate(T *p) 196 { 197 Alloc::deallocate(p, sizeof(T)); 198 } 199 }; 200 201 // Allocator adaptor to check size arguments for debugging. 202 template <class Alloc> 203 class debug_alloc 204 { 205 private: 206 enum { extra = 8}; // Size of space used to store size. Note 207 // that this must be large enough to preserve 208 // alignment. 209 210 public: 211 static void * allocate(size_t n) 212 { 213 char *result = (char *)Alloc::allocate(n + extra); 214 *(size_t *)result = n; //前size_t大小用来记录result的大小,实际预分配了extra个字节,用来存储大小, 215 //但是只用size_t字节,因为不同系统size_t大小不同,8个字节足够满足所有系统了 216 return result + extra; 217 } 218 219 static void deallocate(void *p, size_t n) 220 { 221 char * real_p = (char *)p - extra; 222 assert(*(size_t *)real_p == n); 223 Alloc::deallocate(real_p, n + extra); 224 } 225 226 static void * reallocate(void *p, size_t old_sz, size_t new_sz) 227 { 228 char * real_p = (char *)p - extra; 229 assert(*(size_t *)real_p == old_sz); 230 char * result = (char *) 231 Alloc::reallocate(real_p, old_sz + extra, new_sz+ extra); 232 *(size_t *)result = new_sz; 233 return result + extra; 234 } 235 236 }; 237 238 #ifdef __USE_MALLOC 239 240 typedef malloc_alloc alloc; 241 typedef malloc_alloc single_client_alloc; 242 243 #else 244 245 //下面是第二级配置器 246 //主要是维护一个内存池,用来小于128byte的小型区块内存的分配 247 //其中,有多个链表,各链表中的node大小从8-128byte,都是8的倍数 248 //分配时,不是8的倍数,上调至最近的8的倍数, 249 //然后从相应链表中取下一个对应大小的node分配给请求 250 #ifdef __SUNPRO_CC 251 enum {__ALIGN = 8}; //小型区块的上调边界 252 enum {__MAX_BYTES = 128}; //小型区块的上限 253 enum {__NFREELISTS = __MAX_BYTES/__ALIGN}; 254 #endif 255 256 //第二级配置器 257 template <bool threads, int inst> 258 class __default_alloc_template 259 { 260 private: 261 # ifndef __SUNPRO_CC 262 enum {__ALIGN = 8}; //小型区块的上调边界 263 enum {__MAX_BYTES = 128}; //小型区块的上限 264 enum {__NFREELISTS = __MAX_BYTES/__ALIGN}; 265 # endif 266 //大小上调至8的倍数 267 static size_t ROUND_UP(size_t bytes) 268 { 269 return (((bytes) + __ALIGN-1) & ~(__ALIGN - 1)); 270 } 271 __PRIVATE: 272 union obj 273 { 274 union obj * free_list_link; //用于在链表中指向下一个节点 275 char client_data[1]; //用于存储实际区块的内存地址,由于这是一个union,很好的节约了这个数据的内存 276 }; 277 private: 278 # ifdef __SUNPRO_CC 279 static obj * __VOLATILE free_list[]; 280 # else 281 static obj * __VOLATILE free_list[__NFREELISTS]; 282 # endif 283 static size_t FREELIST_INDEX(size_t bytes) 284 { 285 return (((bytes) + __ALIGN-1)/__ALIGN - 1); 286 } 287 288 //返回大小为n的对象,并可能加入大小为n的其他区块到free list 289 static void *refill(size_t n); 290 //配置一块空间,可容纳nobjs个大小为"size"的区块 291 //如果配置nobjs个区块有所不便,nobjs可能会降低 292 static char *chunk_alloc(size_t size, int &nobjs); 293 294 //chunk 分配、配置的状态 295 static char *start_free; //内存池起始位置。只在chunk_alloc()中变化 296 static char *end_free; //内存池结束位置。只在chunk_alloc()中变化 297 static size_t heap_size; 298 /* 299 # ifdef __STL_SGI_THREADS 300 static volatile unsigned long __node_allocator_lock; 301 static void __lock(volatile unsigned long *); 302 static inline void __unlock(volatile unsigned long *); 303 # endif 304 */ 305 306 # ifdef __STL_PTHREADS 307 static pthread_mutex_t __node_allocator_lock; 308 # endif 309 310 # ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS 311 static CRITICAL_SECTION __node_allocator_lock; 312 static bool __node_allocator_lock_initialized; 313 314 public: 315 __default_alloc_template() 316 { 317 //假定第一个构造函数的调用在线程启动起 318 if (!__node_allocator_lock_initialized) 319 { 320 InitializedCriticalSection(&__node_allocator_lock); 321 __node_allocator_lock_initialized = true; 322 } 323 } 324 private: 325 # endif 326 327 class lock 328 { 329 public: 330 lock() { __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK; } 331 ~lock() { __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK; } 332 }; 333 friend class lock; 334 public: 335 //n必须大于0 336 static void * allocate(size_t n) 337 { 338 obj * __VOLATILE * my_free_list; 339 obj * __RESTRICT result; 340 341 //需要分配的大小大于二级配置器的__MAX_BYTES,直接使用第一级配置器 342 if (n > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES) 343 { 344 return(malloc_alloc::allocate(n)); 345 } 346 my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n); //找到比需要分配的大小大,且最接近的大小块所在的链表所在free_list数组中的位置 347 348 //如果支持线程,定义lock 349 # ifndef _NOTHREADS 350 lock lock_instance; 351 # endif 352 result = *my_free_list; //取出找的对应链表的指向第一个节点的指针 353 if (result == 0) //对应的链表中没有剩余未分配的节点区块 354 { 355 void *r = refill(ROUND_UP(n)); //再从内存池中分配一批,需求大小的区块(实际大小是请求大小上调至8的倍数后的数值), 356 //然后,放入对应链表,待分配给请求 357 return r; 358 } 359 //如果对应大小区块的链表中不为空,还有待分配的区块,取出第一个节点 360 *my_free_list = result -> free_list_link; 361 return (result); 362 }; 363 364 //p不可以是0 365 static void deallocate(void *p, size_t n) 366 { 367 obj *q = (obj *)p; 368 obj * __VOLATILE * my_free_list; 369 370 //大于区块大小上限的,直接调用第一级配置器释放 371 if (n > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES) 372 { 373 malloc_alloc::deallocate(p, n); 374 return; 375 } 376 my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n); 377 //需要修改my_free_list,如果支持线程,那么需要加上互斥锁 378 # ifndef _NOTHREADS 379 lock lock_instance; 380 # endif 381 382 //头插法,插入对应大小的区块链表 383 q -> free_list_link = *my_free_list; 384 *my_free_list = q; 385 //lock是静态对象,到此,将自动析构销毁,在其析构函数中,会释放锁 386 } 387 388 static void *reallocate(void *p, size_t old_sz, size_t new_sz); 389 390 }; 391 392 typedef __default_alloc_template<__NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS, 0> alloc; 393 typedef __default_alloc_template<false, 0> single_client_alloc; 394 395 396 // 我们从大的chunks中分配内存,是为了避免使用malloc太频繁了 397 // 假设size已经适当上调至8的倍数 398 // 我持有allocation lock 399 // 注意参数objs 是pass by reference 400 template <bool threads, int inst> 401 char * 402 __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::chunk_alloc(size_t size, int& nobjs) 403 { 404 char * result; 405 size_t total_bytes = size * nobjs; 406 size_t bytes_left = end_free - start_free; //内存池剩余空间 407 408 if (bytes_left >= total_bytes) 409 { 410 //内存池中剩余的空间足够满足需求量 411 result = start_free; 412 start_free += total_bytes; 413 return(result); 414 } 415 else if (bytes_left >= size) 416 { 417 //内存池剩余空间不能完全满足需求量,但足够供应一个及以上的区块 418 nobjs = bytes_left/size; 419 total_bytes = size * nobjs; 420 result = start_free; 421 start_free += total_bytes; 422 return (result); 423 } 424 else 425 { 426 //内存池连一个区块的大小都无法满足 427 size_t bytes_to_get = 2 * total_bytes + ROUND_UP(heap_size >> 4); 428 //以下试着让内存池中的残余零头还有利用价值 429 if (bytes_left > 0) 430 { 431 //内存池中内还有一些零头,先配给适当的free list 432 //首先寻找适当的free list 433 obj * __VOLATILE * my_free_list = 434 free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(bytes_left); 435 436 //调整free list,将内存池中残余的空间编入 437 ((obj *)start_free) -> free_list_link = *my_free_list; 438 *my_free_list = (obj *)start_free; 439 } 440 441 //配置heap空间,用来补充内存池 442 start_free = (char *)malloc(bytes_to_get); 443 if (0 == start_free) 444 { 445 //如果heap空间不足,malloc()失败 446 int i; 447 obj * __VOLATILE *my_free_list, *p; 448 //试着检视我们手上的东西。这不会造成伤害。我们不打算尝试配置 449 //较小的区块,因为那在多线程机器上容易导致灾难 450 //以下搜索适当的free list 451 //所谓适当是指“尚有未用区块,且区块够大”之free list 452 for (i = size; i <= __MAX_BYTES; i += __ALIGN) 453 { 454 my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(i); 455 p = *my_free_list; 456 if (0 != p) 457 { 458 //free list内尚有未用区块 459 //调整free list以释放出未用的区块到内存池 460 *my_free_list = p -> free_list_link; 461 start_free = (char *)p; 462 end_free = start_free + i; 463 // 此时内存池已经有内存了 464 // 递归调用自己,为了修正objs 465 return chunk_alloc(size, nobjs); 466 //注意,任何残余的零头终将被编入适当的free list中备用 467 468 } 469 } 470 end_free = 0; //如果出现意外(山穷水尽,到处都没有内存可用了) 471 //调用第一级配置器,看看out-of-memory机制能否尽点力 472 start_free = (char *)malloc_alloc::allocate(bytes_to_get); 473 //这会导致抛出异常,或内存不足的情况获得改善 474 } 475 heap_size += bytes_to_get; 476 end_free = start_free + bytes_to_get; 477 //递归调用自己,为了修正objs 478 return chunk_alloc(size, nobjs); 479 } 480 } 481 482 483 484 // 返回一个大小为n的对象,并且有时候会为适当的free list 增加节点 485 // 假设n已经适当上调至8的倍数 486 // 我们持有allocation lock 487 template <bool threads, int inst> 488 void* __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::refill(size_t n) 489 { 490 int nobjs = 20; //默认一次分配20个需求大小的区块 491 char * chunk = chunk_alloc(n, nobjs); //chunk是分配的空间的开始地址,令其类型为char *,主要是因为一个char的大小正好是一个byte 492 obj * __VOLATILE *my_free_list; 493 obj * result; 494 obj * current_obj, * next_obj; 495 int i; 496 497 //如果只获得一个区块,这个区块就分配给调用者,free list 无新节点 498 if (1 == nobjs) return chunk; 499 //否则准备调整free list,纳入新节点 500 my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n); 501 502 //以下在chunk空间内建立free list 503 result = (obj *)chunk; //这一块准备返回给客端 504 // 以下导引free list 指向新配置的空间(取自内存池) 505 506 //由于chunk是char*,所以加上n,就表示走过n个char, 507 //一个char正好是一个byte,所以chunk+n现在指向第二个区块 508 *my_free_list = next_obj = (obj *)(chunk + n); 509 for (i = 1; ; ++i) 510 { 511 // 从1开始,因为第0个将返回给客端 512 current_obj = next_obj; 513 // 每次移动n个char,正好是n个byte,所以正好指向下个区块 514 next_obj = (obj *)((char *)next_obj + n); 515 if (nobjs - 1 == i) 516 { 517 // 已经遍历完,此时next_obj指向的内存已经超出我们分配的大小了 518 // 不属于我们的内存 519 current_obj -> free_list_link = 0; 520 break; 521 } 522 else 523 { 524 current_obj -> free_list_link = next_obj; 525 } 526 } 527 return result; 528 } 529 530 531 template<bool threads, int inst> 532 void* 533 __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::reallocate(void *p, 534 size_t old_sz, 535 size_t new_sz) 536 { 537 void * result; 538 size_t copy_sz; 539 540 if (old_sz > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES && new_sz > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES) 541 { 542 return realloc(p, new_sz); 543 } 544 if (ROUND_UP(old_sz) == ROUND_UP(new_sz)) return p; 545 result = allocate(new_sz); 546 copy_sz = new_sz > old_sz ? old_sz : new_sz; 547 memcpy(result, p, copy_sz); 548 deallocate(p, old_sz); 549 return result; 550 551 } 552 553 #ifdef __STL_PTHREADS 554 template <bool threads,int inst> 555 pthread_mutex_t 556 __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__node_allocator_lock 557 = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; 558 #endif 559 560 #ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS 561 template <bool threads, int inst> CRITICAL_SECTION 562 __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__node_allocator_lock; 563 564 template <bool threads, int inst> bool 565 __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__node_allocator_lock_initialized 566 = false; 567 #endif 568 569 //省略了通用lock的实现(即不使用pthread,也没有win32thread) 570 571 template <bool threads, int inst> 572 char *__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::start_free = 0; //设置初始值 573 574 template <bool threads, int inst> 575 char *__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::end_free = 0; //设置初始值 576 577 template <bool threads, int inst> 578 size_t __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::heap_size = 0; //设置初始值 579 580 //初始化16种大小的区块链表为空 581 template <bool threads, int inst> 582 typename __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::obj * __VOLATILE 583 __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::free_list[ 584 # ifdef __SUNPRO_CC 585 __NFREELISTS 586 # else 587 __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__NFREELISTS 588 # endif 589 ] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, }; 590 591 # ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS 592 // Create one to get critical section initialized. 593 // We do this onece per file, but only the first constructor 594 // does anything. 595 static alloc __node_allocator_dummy_instance; 596 # endif 597 598 # endif /* ! __USE_MALLOC */ 599 600 #if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32) 601 #pragma reset woff 1174 602 #endif 603 604 __STL_END_NAMESPACE 605 606 #undef __PRIVATE 607 608 #endif /* __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALLOC_WJZH_H */ 609 610 //End
自己动手实现STL 01:内存配置器的实现(stl_alloc.h)
标签:style blog http io color ar os 使用 sp
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wangjzh/p/4097355.html