标签:des style blog http io ar color os 使用
2014.10.15日以来的一个月,挤破了头、跑断了腿、伤透了心、吃够了全国最大餐饮连锁店——沙县小吃。其中酸甜苦辣,绝不是三言两语能够说得清道的明的。校招的兄弟姐妹们,你们懂得……
体会最深的一句话还是:出来混,迟早要还的。
一个月过去了,迷茫之际有太多无奈,无奈中又夹杂些许庆幸,岁月匆匆,人生不息,奋斗不止。
遵守最初的诺言,继续走我可视化的道路:
上集摘要:一个月博文中大概介绍了可视化的一些常用工具,从可操作性、实用性、交互性等各方面进行了简单的对比和总结,具体参见http://www.cnblogs.com/bigdataZJ/p/VisualizationSoloShow.html,结合自己的需求,挑出了Prefuse和Processing两员大将出来露了一手,详情请见http://www.cnblogs.com/bigdataZJ/p/VisualizationSoloShow2.html
一番角逐之后,Prefuse工具集脱颖而出,其强大的展示效果、开发者友好的API说明文档、丰富的自带Demo无一不让我对其欲罢不能。下面我们来好好分析下Prefuse的强大之处:
1.Prefuse主要特征:
(1)任意数据类型的表格、图和树形数据结构,数据索引、选择查询,有效的内存占用
(2)具有布局、着色、大小、图形编码、扭曲、动画等多个组件
(3)具有交互控制库
(4)支持动画过渡,通过一系列的活动调度机制
(5)支持平移、缩放等视图变换
(6)对于交互过滤数据的动态查询
(7)能够使用可用的搜索引擎进行文本检索
(8)具有布局和动画的力导向模拟引擎
(9)灵活的多视图展现,包括“概述+细节”和“小倍数”显示
(10)内置类SQL语句查询,可以用于编写查询语句实现查询指定字段的数据
(11)提供查询语句到Prefuse数据结构的数据映射的SQL查询
(12)简单、开发者友好的APIs文档
2.Prefuse模型:
(1)prefuse.data包提供了 Table, Graph, Tree等数据结构;提供了一个data tables,他的行使用一个类 Tuple来表示;这个包中,Node和Edge来表示图或者树的一些成员。
作为一种高级特征的工具集,Prefuse提供了一种解释性的表达式语言,该语言可以用来请求Prefuse中的数据结构并根据已有的数据列创建衍生的列数据。表达式语言的功能实现类在prefuse.data.expression包中,文本表达式解析类在ExpressionParser类中。
(2)prefuse.data.io包提供了文件的读写,包括表,图和树的结构,其中,表的格式:CSV和任意分割的文本文件,对于网络,有 GraphML和 TreeML(XML也能);prefuse.data.io.sql包提供了对SQL数据库的查询,并返回一个prefuse表
(3)可视化抽象是通过将数据添加到Visulization实例中来得到的,它除了包含原始数据外,还建立了一套完整的可视化体系,包括x、y的坐标轴,颜色,大小字体等值,任意的Tuple, Node, 或者 Edge被添加到Visulization实例中时候,相关的VisualItems实例就建立好了,如NodeItem和 EdgeItem就是VisualItems的实例。(也就是说,可视化抽象实现了添加的数据元素与VisualItems之间的映射)
(4)可视化映射工作由Action模块来完成,它是有一系列独立的处理模块组成的,这些模块来完成可视性、布局计算、颜色设定以及任何其他的可视化工作。prefuse.action包以及其子包会提供一系列布局,形变,动画以及可视化编码的工作。
(5)Renderer模块决定了VisualItems的出现情况,Renderers模块负责计算显示区域,即如何将可视化图形绘制在屏幕上。RendererFactory用来对Renderer进行管理,体现在给VisualItems分配适当的Renderer上。
(6)交互工作,Display组建负责完成交互方面的工作,起到一个类似于摄像机的功能,对显示的区域进行选取,缩放。它直接与用户相关。
一个Visualization可以与多个Display实例关联,以实现多视图参数配置,比如“概述+详细”以及小倍数显示视图等。
(7)每个Display实例都支持若干个Controls,他们负责处理Display上鼠标和键盘的action。prefuse.controls包提供了一个预处理的控制器可以用来完成旋转缩放Display的工作,通过prefuse.controls包的子类ControlAdapter可以实现对Display的控制。
(8)最后,prefuse.data.query 包提供了动态查询绑定(?)的功能,这些绑定能够生成合适的用户界面组建,来直接操作这些查询。
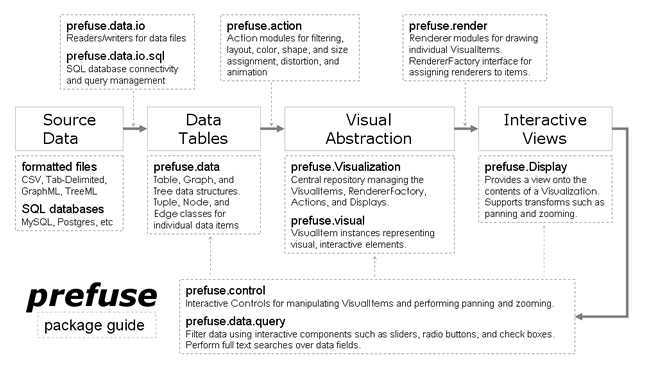
3.Prefuse自带Demo---GraphView.java详解
下面是自己在研读Prefuse源码文件夹demos下的GraphView加的一些注释:
1 //start of class GraphView 2 3 public class GraphView extends JPanel { 4 5 private static final String graph = "graph"; 6 7 private static final String nodes = "graph.nodes"; 8 9 private static final String edges = "graph.edges"; 10 11 private Visualization m_vis; 12 13 14 15 public GraphView(Graph g, String label) { 16 17 super(new BorderLayout());//在GraphView的构造函数中调用超类的构造方法,并创建布局BorderLayout对象。 18 19 // create a new, empty visualization for our data 20 21 m_vis = new Visualization();//创建Visualization对象,使用默认的渲染工厂(DefaultRendererFactory)。Visualization类负责管理源数据与可视化组件之间的映射。 22 23 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 24 25 // set up the renderers 26 27 LabelRenderer tr = new LabelRenderer(); 28 29 tr.setRoundedCorner(8, 8); 30 31 m_vis.setRendererFactory(new efaultRendererFactory(tr));//新建标签渲染器并注册到Visualization上,使用的还是DefaultRendererFactory。 32 33 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 34 // register the data with a visualization 35 36 // adds graph to visualization and sets renderer label field 37 38 setGraph(g, label);// 向Visualization添加图形Graph并为标签域赋值。 39 40 41 42 // fix selected focus nodes 声明一个数据元组集合,并为该集合添加一个数据元组的监听器 43 44 TupleSet focusGroup = m_vis.getGroup(Visualization.FOCUS_ITEMS); 45 46 focusGroup.addTupleSetListener(new TupleSetListener() { 47 48 public void tupleSetChanged(TupleSet ts, Tuple[] add, Tuple[] rem) 49 50 { 51 52 for ( int i=0; i<rem.length; ++i ) 53 54 ((VisualItem)rem[i]).setFixed(false); 55 56 for ( int i=0; i<add.length; ++i ) { 57 58 ((VisualItem)add[i]).setFixed(false); 59 60 ((VisualItem)add[i]).setFixed(true); 61 62 } 63 64 if ( ts.getTupleCount() == 0 ) { 65 66 ts.addTuple(rem[0]); 67 68 ((VisualItem)rem[0]).setFixed(false); 69 70 } 71 72 m_vis.run("draw"); 73 74 } 75 76 });//声明一个数据元组集合,并通过匿名内部类的形式为该集合添加一个数据元组的监听器(TupleSetListener),其中ts:变化的数据元组;add:已经加入的元组数组集合;rem:移除的数据集合。 77 78 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 79 80 // create actions to process the visual data 81 82 83 84 int hops = 30; 85 86 final GraphDistanceFilter filter = new GraphDistanceFilter(graph, hops); 87 88 89 90 ColorAction fill = new ColorAction(nodes, 91 92 VisualItem.FILLCOLOR, ColorLib.rgb(200,200,255)); 93 94 fill.add(VisualItem.FIXED, ColorLib.rgb(255,100,100)); 95 96 fill.add(VisualItem.HIGHLIGHT, ColorLib.rgb(255,200,125)); 97 98 99 100 ActionList draw = new ActionList(); 101 102 draw.add(filter); 103 104 draw.add(fill); 105 106 draw.add(new ColorAction(nodes, VisualItem.STROKECOLOR, 0)); 107 108 draw.add(new ColorAction(nodes, VisualItem.TEXTCOLOR, ColorLib.rgb(0,0,0))); 109 110 draw.add(new ColorAction(edges, VisualItem.FILLCOLOR, ColorLib.gray(200))); 111 112 draw.add(new ColorAction(edges, VisualItem.STROKECOLOR, ColorLib.gray(200)));// 根据设定距离hops新建一个图形距离过滤器类;针对nodes,采取完全填充颜色的方式(FILLCOLOR),并对聚焦点(fixed )、高亮点(与fixed node相邻的点即highlight)以及剩余点分别赋予不同的颜色表现.将GraphDistanceFilter和ColorAction都注册到声明的ActionList对象上,并同时添加点与边的描边颜色以及填充颜色的ColorAction。 113 114 ActionList animate = new ActionList(Activity.INFINITY); 115 116 animate.add(new ForceDirectedLayout(graph)); 117 118 animate.add(fill); 119 120 animate.add(new RepaintAction());//声明一个ActionList的animate对象,在该对象上添加布局方式(这里采用力导向布局方法ForceDirectedLayout),并添加上面的ColorAction类的fill对象以及一个重绘图形Action。 121 // finally, we register our ActionList with the Visualization. 122 123 // we can later execute our Actions by invoking a method on our 124 125 // Visualization, using the name we‘ve chosen below. 126 127 m_vis.putAction("draw", draw); 128 129 m_vis.putAction("layout", animate); 130 131 m_vis.runAfter("draw", "layout");//将draw和animate注册到m_vis上,后面通过Visualization的方法触发执行每个注册的Action。 132 133 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 134 135 // set up a display to show the visualization 136 Display display = new Display(m_vis); 137 display.setSize(700,700); 138 display.pan(350, 350); 139 display.setForeground(Color.GRAY); 140 display.setBackground(Color.WHITE); 141 142 143 144 // main display controls 145 display.addControlListener(new FocusControl(1)); 146 display.addControlListener(new DragControl()); 147 display.addControlListener(new PanControl()); 148 display.addControlListener(new ZoomControl()); 149 display.addControlListener(new WheelZoomControl()); 150 display.addControlListener(new ZoomToFitControl()); 151 display.addControlListener(new NeighborHighlightControl());//通过Display展现Visualization包括:设置画布大小,平移范围,前景背景颜色以及添加聚焦、拖拽、平移、缩放、滑轮、缩放至适合显示、紧邻高亮监听器。 152 153 154 155 // overview display 156 157 // Display overview = new Display(vis); 158 159 // overview.setSize(290,290); 160 161 // overview.addItemBoundsListener(new FitOverviewListener()); 162 163 164 165 display.setForeground(Color.GRAY); 166 167 display.setBackground(Color.WHITE); 168 169 170 171 // -------------------------------------------------------------------- 172 173 // launch the visualization 174 175 176 177 // create a panel for editing force values 178 179 ForceSimulator fsim = ((ForceDirectedLayout)animate.get(0)).getForceSimulator(); 180 181 JForcePanel fpanel = new JForcePanel(fsim); 182 183 184 185 final JValueSlider slider = new JValueSlider("Distance", 0, hops, hops); 186 187 slider.addChangeListener(new ChangeListener() { 188 189 public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent e) { 190 191 filter.setDistance(slider.getValue().intValue());//只要调节面板上的值有变动就执行下面的run函数,重新布局界面 192 193 m_vis.run("draw"); 194 195 } 196 197 }); 198 199 slider.setBackground(Color.WHITE); 200 201 slider.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(300,30)); 202 203 slider.setMaximumSize(new Dimension(300,30));//设置调节面板的背景颜色、大小 204 205 206 207 208 209 Box cf = new Box(BoxLayout.Y_AXIS); 210 211 cf.add(slider); 212 213 cf.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("Connectivity Filter")); 214 215 fpanel.add(cf); 216 217 //fpanel.add(opanel); 218 219 fpanel.add(Box.createVerticalGlue()); 220 221 222 223 // create a new JSplitPane to present the interface 224 225 JSplitPane split = new JSplitPane(); 226 227 split.setLeftComponent(display); 228 229 split.setRightComponent(fpanel); 230 231 split.setOneTouchExpandable(true); 232 233 split.setContinuousLayout(false); 234 235 split.setDividerLocation(700);//为整张画布布局,包括左边、右边应该呈现什么内容等 236 237 // now we run our action list 238 239 //m_vis.run("draw"); 240 241 add(split); 242 243 } 244 245 246 247 public void setGraph(Graph g, String label) { 248 249 // update labeling 250 251 DefaultRendererFactory drf = (DefaultRendererFactory) 252 253 m_vis.getRendererFactory(); 254 255 ((LabelRenderer)drf.getDefaultRenderer()).setTextField(label); 256 257 // update graph 258 259 m_vis.removeGroup(graph); 260 261 VisualGraph vg = m_vis.addGraph(graph, g); 262 263 m_vis.setValue(edges, null, VisualItem.INTERACTIVE, Boolean.FALSE); 264 265 VisualItem f = (VisualItem)vg.getNode(0); 266 267 m_vis.getGroup(Visualization.FOCUS_ITEMS).setTuple(f); 268 269 f.setFixed(false); 270 271 } 272 273 274 275 // ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 276 277 // Main and demo methods 278 279 280 281 public static void main(String[] args) { 282 283 UILib.setPlatformLookAndFeel(); 284 285 286 287 // create graphview 288 289 String datafile = null; 290 291 String label = "label"; 292 293 if ( args.length > 1 ) {//如果用户在运行时有参数传值则分别赋值给datafile和label 294 295 datafile = args[0]; 296 297 label = args[1]; 298 299 } 300 301 JFrame frame = demo(datafile, label); //通过调用demo函数完成整个界面的设计布局等,最终呈现一个JFrame 302 303 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); // 关闭按钮的动作为退出 304 } 305 306 307 308 public static JFrame demo() { 309 310 return demo((String)null, "label"); 311 312 } 313 314 315 316 public static JFrame demo(String datafile, String label) { 317 318 Graph g = null; 319 320 if ( datafile == null ) { 321 322 g = GraphLib.getGrid(15,15);//如果datafile为空,则通过调用图形库GraphLib中的getGrid得到15*15的网状图形,如下图所示 323 label = "label"; 324 325 } else { 326 327 try { 328 329 g = new GraphMLReader().readGraph(datafile);//否则通过指定路径读取datafile文件并转换为图形 330 331 } catch ( Exception e ) { 332 333 e.printStackTrace(); 334 335 System.exit(1); 336 337 } 338 339 } 340 341 return demo(g, label); 342 343 } 344 345 346 347 public static JFrame demo(Graph g, String label) { 348 349 final GraphView view = new GraphView(g, label); 350 351 352 353 // set up menu 354 355 JMenu dataMenu = new JMenu("Data");//新建菜单栏 356 357 dataMenu.add(new OpenGraphAction(view));//注册“打开文件”选项卡 358 359 dataMenu.add(new GraphMenuAction("Grid","ctrl 1",view) {//添加网状布局选项卡 360 361 protected Graph getGraph() { 362 363 return GraphLib.getGrid(15,15); 364 365 } 366 367 }); 368 369 dataMenu.add(new GraphMenuAction("Clique","ctrl 2",view) {//添加团状布局选项卡 370 371 protected Graph getGraph() { 372 373 return GraphLib.getClique(10); 374 375 } 376 377 }); 378 379 dataMenu.add(new GraphMenuAction("Honeycomb","ctrl 3",view) {//添加蜂窝状布局选项卡 380 381 protected Graph getGraph() { 382 383 return GraphLib.getHoneycomb(5); 384 385 } 386 387 }); 388 389 dataMenu.add(new GraphMenuAction("Balanced Tree","ctrl 4",view) {//添加平衡树布局选项卡 390 391 protected Graph getGraph() { 392 393 return GraphLib.getBalancedTree(3,5); 394 395 } 396 397 }); 398 399 dataMenu.add(new GraphMenuAction("Diamond Tree","ctrl 5",view) { 400 401 protected Graph getGraph() { 402 403 return GraphLib.getDiamondTree(3,3,3); //添加钻石树形图布局选项卡 404 405 } 406 407 }); 408 409 JMenuBar menubar = new JMenuBar(); 410 411 menubar.add(dataMenu);//将以上菜单选项注册到menubar菜单栏上 412 413 414 415 // launch window 416 417 JFrame frame = new JFrame("p r e f u s e | g r a p h v i e w"); 418 419 frame.setJMenuBar(menubar); 420 421 frame.setContentPane(view); 422 423 frame.pack(); 424 425 frame.setVisible(true);//添加菜单栏、图形等 426 427 428 429 frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() { 430 431 public void windowActivated(WindowEvent e) { 432 433 view.m_vis.run("layout"); 434 435 } 436 437 public void windowDeactivated(WindowEvent e) { 438 439 view.m_vis.cancel("layout"); 440 441 } 442 443 }); 444 445 446 447 return frame; 448 449 } 450 451 452 // ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 453 454 /** 455 456 * Swing menu action that loads a graph into the graph viewer. 457 458 * 该类主要负责为每一种布局选项配置相应的快捷键 459 460 */ 461 462 public abstract static class GraphMenuAction extends AbstractAction { 463 464 private GraphView m_view; 465 466 public GraphMenuAction(String name, String accel, GraphView view) { 467 468 m_view = view; 469 470 this.putValue(AbstractAction.NAME, name); 471 472 this.putValue(AbstractAction.ACCELERATOR_KEY, 473 474 KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(accel)); 475 476 } 477 478 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { 479 480 m_view.setGraph(getGraph(), "label"); 481 482 } 483 484 protected abstract Graph getGraph(); 485 486 } 487 488 //该类负责对菜单栏的选项卡的响应 489 490 public static class OpenGraphAction extends AbstractAction { 491 492 private GraphView m_view; 493 494 495 496 public OpenGraphAction(GraphView view) { 497 498 m_view = view; 499 500 this.putValue(AbstractAction.NAME, "Open File..."); 501 502 this.putValue(AbstractAction.ACCELERATOR_KEY, 503 504 KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl O")); 505 506 } 507 508 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { 509 510 Graph g = IOLib.getGraphFile(m_view); 511 512 if ( g == null ) return; 513 514 String label = getLabel(m_view, g); 515 516 if ( label != null ) { 517 518 m_view.setGraph(g, label); 519 520 } 521 522 } 523 524 public static String getLabel(Component c, Graph g) { 525 526 // get the column names 527 528 Table t = g.getNodeTable(); 529 530 int cc = t.getColumnCount(); 531 532 String[] names = new String[cc]; 533 534 for ( int i=0; i<cc; ++i ) 535 536 names[i] = t.getColumnName(i); 537 538 539 540 // where to store the result 541 542 final String[] label = new String[1]; 543 544 // -- build the dialog ----- 545 546 // we need to get the enclosing frame first 547 548 while ( c != null && !(c instanceof JFrame) ) { 549 550 c = c.getParent(); 551 } 552 553 final JDialog dialog = new JDialog( 554 555 (JFrame)c, "Choose Label Field", true); 556 557 558 559 // create the ok/cancel buttons 560 561 final JButton ok = new JButton("OK"); 562 563 ok.setEnabled(false); 564 565 ok.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { 566 567 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { 568 569 dialog.setVisible(false); 570 571 } 572 573 }); 574 575 JButton cancel = new JButton("Cancel"); 576 577 cancel.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { 578 579 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { 580 581 label[0] = null; 582 583 dialog.setVisible(false); 584 585 } 586 587 }); 588 589 // build the selection list 590 591 final JList list = new JList(names); 592 list.setSelectionMode(ListSelectionModel.SINGLE_SELECTION); 593 594 list.getSelectionModel().addListSelectionListener( 595 596 new ListSelectionListener() { 597 598 public void valueChanged(ListSelectionEvent e) { 599 600 int sel = list.getSelectedIndex(); 601 602 if ( sel >= 0 ) { 603 604 ok.setEnabled(true); 605 606 label[0] = (String)list.getModel().getElementAt(sel); 607 608 } else { 609 610 ok.setEnabled(false); 611 612 label[0] = null; 613 614 } 615 616 } 617 618 }); 619 620 JScrollPane scrollList = new JScrollPane(list); 621 622 623 624 JLabel title = new JLabel("Choose a field to use for node labels:"); 625 626 627 628 // layout the buttons 629 630 Box bbox = new Box(BoxLayout.X_AXIS); 631 632 bbox.add(Box.createHorizontalStrut(5)); 633 634 bbox.add(Box.createHorizontalGlue()); 635 636 bbox.add(ok); 637 638 bbox.add(Box.createHorizontalStrut(5)); 639 640 bbox.add(cancel); 641 642 bbox.add(Box.createHorizontalStrut(5)); 643 644 645 646 // put everything into a panel 647 648 JPanel panel = new JPanel(new BorderLayout()); 649 650 panel.add(title, BorderLayout.NORTH); 651 652 panel.add(scrollList, BorderLayout.CENTER); 653 654 panel.add(bbox, BorderLayout.SOUTH); 655 656 panel.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(5,2,2,2)); 657 658 659 660 // show the dialog 661 662 dialog.setContentPane(panel); 663 664 dialog.pack(); 665 666 dialog.setLocationRelativeTo(c); 667 668 dialog.setVisible(true); 669 670 dialog.dispose(); 671 672 673 674 // return the label field selection 675 676 return label[0]; 677 678 } 679 680 } 681 682 //该类负责调整至适合屏幕显示 683 684 public static class FitOverviewListener implements ItemBoundsListener { 685 686 private Rectangle2D m_bounds = new Rectangle2D.Double(); 687 688 private Rectangle2D m_temp = new Rectangle2D.Double(); 689 690 private double m_d = 15; 691 692 public void itemBoundsChanged(Display d) { 693 694 d.getItemBounds(m_temp); 695 696 GraphicsLib.expand(m_temp, 25/d.getScale()); 697 698 699 700 double dd = m_d/d.getScale(); 701 702 double xd = Math.abs(m_temp.getMinX()-m_bounds.getMinX()); 703 704 double yd = Math.abs(m_temp.getMinY()-m_bounds.getMinY()); 705 706 double wd = Math.abs(m_temp.getWidth()-m_bounds.getWidth()); 707 708 double hd = Math.abs(m_temp.getHeight()-m_bounds.getHeight()); 709 710 if ( xd>dd || yd>dd || wd>dd || hd>dd ) { 711 712 m_bounds.setFrame(m_temp); 713 714 DisplayLib.fitViewToBounds(d, m_bounds, 0); 715 716 } 717 718 } 719 720 } 721 722 723 724 } 725 726 // end of class GraphView
网格视图:
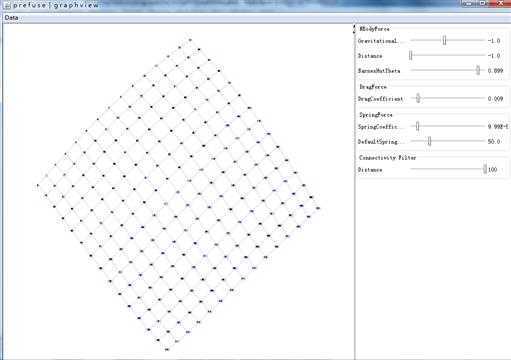
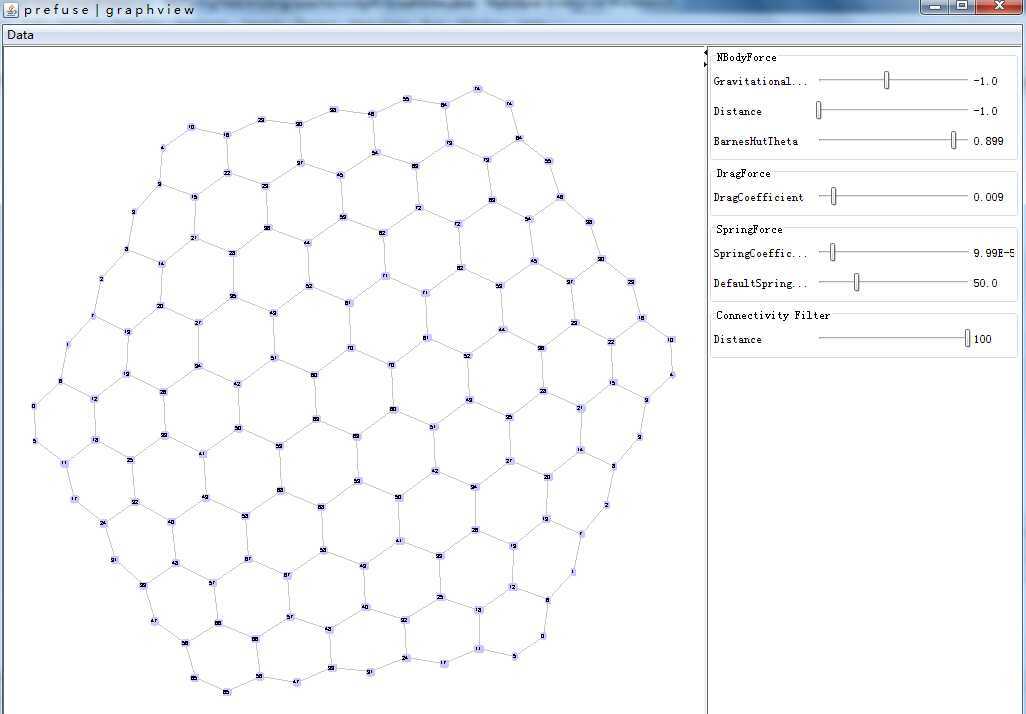
蜂窝状视图:
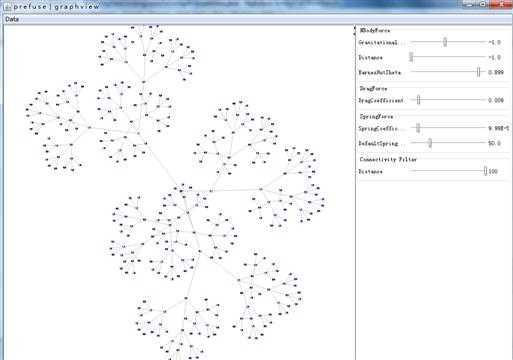
平衡树型视图:
以上介绍了Prefuse的一些特征,模型结构以及自带Demo GraphView.java的理解,后续会继续研究Prefuse的其他Demo以及主要接口。
本文链接http://www.cnblogs.com/bigdataZJ/p/VisualizationSoloShow3.html
可视化工具solo show-----Prefuse自带例子GraphView讲解
标签:des style blog http io ar color os 使用
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/bigdataZJ/p/VisualizationSoloShow3.html