标签:组合方法ensemble method adaboost提升方法
组合方法:
我们分类中用到很多经典分类算法如:SVM、logistic 等,我们很自然的想到一个方法,我们是否能够整合多个算法优势到解决某一个特定分类问题中去,答案是肯定的!
通过聚合多个分类器的预测来提高分类的准确率。这种技术称为组合方法(ensemble method) 。组合方法由训练数据构建一组基分类器,然后通过对每个基分类器的预测进行权重控制来进行分类。
考虑25个二元分类组合,每个分类误差是0.35 ,如果所有基分类器都是相互独立的(即误差是不相关的),则在超过一半的基分类器预测错误组合分类器才会作出错误预测。这种情况下的组合分类器的误差率:
下图对角线表示所有基分类器都是等同的情况,实线是基分类器独立时情况。
组合分类器性能优于单个分类器必须满足两个条件:(1)基分类器之间是相互独立的 (2) 基分类器应当好于随机猜测分类器。实践上很难保证基分类器之间完全独立,但是在基分类器轻微相关情况下,组合方法可以提高分类的准确率。
组合方法分为两类:(from http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/ensemble.html)
Two families of ensemble methods are usually distinguished:
In averaging methods, the driving principle is to build several estimators independently and then to average their predictions. On average, the combined estimator is usually better than any of the single base estimator because its variance is reduced.
Examples: Bagging methods, Forests of randomized trees, ...
By contrast, in boosting methods, base estimators are built sequentially and one tries to reduce the bias of the combined estimator. The motivation is to combine several weak models to produce a powerful ensemble.
Examples: AdaBoost, Gradient Tree Boosting, ...
先介绍强可学习与弱可学习,如果存在一个多项式的学习算法能够学习它并且正确率很高,那么就称为强可学习,相反弱可学习就是学习的正确率仅比随机猜测稍好。
提升方法有两个问题:1. 每一轮如何改变训练数据的权重或概率分布 2. 如何将弱分类器整合为强分类器。
很朴素的思想解决提升方法中的两个问题:第1个问题-- 提高被前一轮弱分类器错误分类的权值,而降低那些被正确分类样本权值 ,这样导致结果就是 那些没有得到正确分类的数据,由于权值加重受到后一轮弱分类器的更大关注。 第2个问题 adaboost 采取加权多数表决方法,加大分类误差率小的弱分类器的权值,使其在表决中起到较大的作用,相反较小误差率的弱分类的权值,使其在表决中较小的作用。
具体说来,整个Adaboost 迭代算法就3步:
给定一个训练数据集T={(x1,y1), (x2,y2)…(xN,yN)},其中实例 ,而实例空间
,而实例空间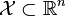 ,yi属于标记集合{-1,+1},Adaboost的目的就是从训练数据中学习一系列弱分类器或基本分类器,然后将这些弱分类器组合成一个强分类器。
,yi属于标记集合{-1,+1},Adaboost的目的就是从训练数据中学习一系列弱分类器或基本分类器,然后将这些弱分类器组合成一个强分类器。
Adaboost的算法流程如下:
a. 使用具有权值分布Dm的训练数据集学习,得到基本分类器:
b. 计算Gm(x)在训练数据集上的分类误差率
由上述式子可知,Gm(x)在训练数据集上的误差率em就是被Gm(x)误分类样本的权值之和。
d. 更新训练数据集的权值分布(目的:得到样本的新的权值分布),用于下一轮迭代由上述式子可知,em <= 1/2时,am >= 0,且am随着em的减小而增大,意味着分类误差率越小的基本分类器在最终分类器中的作用越大。
使得被基本分类器Gm(x)误分类样本的权值增大,而被正确分类样本的权值减小。就这样,通过这样的方式,AdaBoost方法能“聚焦于”那些较难分的样本上。
其中,Zm是规范化因子,使得Dm+1成为一个概率分布:
从而得到最终分类器,如下:
在《统计学习方法》p140页有一个实际计算的例子可以自己计算熟悉算法过程。
通过上面的例子可知,Adaboost在学习的过程中不断减少训练误差e,直到各个弱分类器组合成最终分类器,那这个最终分类器的误差界到底是多少呢
事实上,Adaboost 最终分类器的训练误差的上界为:
下面,咱们来通过推导来证明下上述式子。
当G(xi)≠yi时,yi*f(xi)<0,因而exp(-yi*f(xi))≥1,因此前半部分得证。
关于后半部分,别忘了:
整个的推导过程如下:
这个结果说明,可以在每一轮选取适当的Gm使得Zm最小,从而使训练误差下降最快。接着,咱们来继续求上述结果的上界。
对于二分类而言,有如下结果:
其中,
继续证明下这个结论。
由之前Zm的定义式跟本节最开始得到的结论可知:
而这个不等式
值得一提的是,如果取γ1, γ2… 的最小值,记做γ(显然,γ≥γi>0,i=1,2,...m),则对于所有m,有:
这个结论表明,AdaBoost的训练误差是以指数速率下降的。另外,AdaBoost算法不需要事先知道下界γ,AdaBoost具有自适应性,它能适应弱分类器各自的训练误差率 。在统计学习方法第八章 中有关于这部分比较详细的讲述可以参考!!
在一个简单数据集上的adaboost 的实现(来自机器学习实战)
from numpy import*
def loadSimpData():
datMat = matrix([[ 1. , 2.1],
[ 2. , 1.1],
[ 1.3, 1. ],
[ 1. , 1. ],
[ 2. , 1. ]])
classLabels = [1.0, 1.0, -1.0, -1.0, 1.0]
return datMat,classLabels
def stumpClassify(dataMatrix,dimen,threshVal,threshIneq):
retArray = ones((shape(dataMatrix)[0],1))
if threshIneq =='lt':
retArray[dataMatrix[:,dimen]<= threshVal] = -1.0
else:
retArray[dataMatrix[:,dimen] > threshVal] = -1.0
return retArray
def buildStump(dataArr,classLabels,D):
dataMatrix = mat(dataArr)
labelMat = mat(classLabels).T
m,n = shape(dataMatrix)
numSteps = 10.0 ; bestStump = {} ; bestClasEst = mat(zeros((m,1)))
minError = inf
for i in range(n):
rangeMin = dataMatrix[:,i].min(); rangeMax = dataMatrix[:,i].max()
stepSize = (rangeMax- rangeMin)/numSteps
for j in range(-1,int(numSteps)+1):
for inequal in ['lt','gt']:
threshVal = (rangeMin + float(j)* stepSize)
predictedVals = stumpClassify(dataMatrix, i, threshVal, inequal)
errArr = mat(ones((m,1)))
errArr[predictedVals == labelMat]=0
weightedError = D.T *errArr
# print "split: dim %d, thresh %.2f, thresh ineqal: %s, the weighted error is %.3f" % (i, threshVal, inequal, weightedError)
if weightedError < minError:
minError = weightedError
bestClasEst = predictedVals.copy()
bestStump['dim'] = i
bestStump['thresh'] = threshVal
bestStump['ineq'] = inequal
return bestStump,minError,bestClasEst
def adaBoostTrainDS(dataArr,classLabels,numIt=40):
weakClassArr = []
m = shape(dataArr)[0]
D = mat(ones((m,1))/m) #init D to all equal
aggClassEst = mat(zeros((m,1)))
for i in range(numIt):
bestStump,error,classEst = buildStump(dataArr,classLabels,D)#build Stump
print "D:",D.T
alpha = float(0.5*log((1.0-error)/max(error,1e-16)))#calc alpha, throw in max(error,eps) to account for error=0
bestStump['alpha'] = alpha
weakClassArr.append(bestStump) #store Stump Params in Array
print "classEst: ",classEst.T
expon = multiply(-1*alpha*mat(classLabels).T,classEst) #exponent for D calc, getting messy
D = multiply(D,exp(expon)) #Calc New D for next iteration
D = D/D.sum()
#calc training error of all classifiers, if this is 0 quit for loop early (use break)
aggClassEst += alpha*classEst
print "aggClassEst: ",aggClassEst.T
aggErrors = multiply(sign(aggClassEst) != mat(classLabels).T,ones((m,1)))
errorRate = aggErrors.sum()/m
print "total error: ",errorRate
if errorRate == 0.0: break
return weakClassArr,aggClassEst
if __name__ == "__main__":
D = mat(ones((5,1))/5)
datMat,classLabels = loadSimpData()
buildStump(datMat, classLabels, D)
adaBoostTrainDS(datMat, classLabels, 10)
D: [[ 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2]]
classEst: [[-1. 1. -1. -1. 1.]]
aggClassEst: [[-0.69314718 0.69314718 -0.69314718 -0.69314718 0.69314718]]
total error: 0.2
D: [[ 0.5 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125]]
classEst: [[ 1. 1. -1. -1. -1.]]
aggClassEst: [[ 0.27980789 1.66610226 -1.66610226 -1.66610226 -0.27980789]]
total error: 0.2
D: [[ 0.28571429 0.07142857 0.07142857 0.07142857 0.5 ]]
classEst: [[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
aggClassEst: [[ 1.17568763 2.56198199 -0.77022252 -0.77022252 0.61607184]]
total error: 0.0
参考:统计学习方法、机器学习实战、http://blog.csdn.net/v_july_v/article/details/40718799
组合方法(ensemble method) 与adaboost提升方法
标签:组合方法ensemble method adaboost提升方法
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/huruzun/article/details/41323065