标签:des android style blog http io ar color os
Service是Android系统中的一种组件,它跟Activity的级别差不多,但是它不能自己运行,只能后台运行,并且可以和其他组件进行交互。Service是没有界面的长生命周期的代码。Service是一种程序,它可以运行很长时间,但是它却没有用户界面。这么说有点枯燥,来看个例子,打开一个音乐播放器的程序,这个时候若想上网了,那么,我们打开Android浏览器,这个时候虽然我们已经进入了浏览器程序,但是,歌曲播放并没有停止,而是在后台继续一首接着一首地播放。其实这个播放就是由播放音乐的Service进行控制的。
当然这个播放音乐的Service也可以停止,例如,当播放列表里边的歌曲都结束,或者用户按下了停止音乐播放的快捷键等。Service可以在很多场合的应用中使用,比如播放多媒体的时候用户启动了其他Activity,这个时候程序要在后台继续播放,比如检测SD卡上文件的变化,再或者在后台记录用户地理信息位置的改变等等。总之服务嘛,总是藏在后头的。
service的注册跟activity的注册类似,同样是要在AndroidManifest.xml的文件里注册。

<service android:name=".MyService"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.guo.service.playmusic.MyService"/> </intent-filter> </service>
service有两种模式,本地服务和远程服务。我们一般开发应用都是用的本地服务,而远程服务经常在做系统开发时被用到。所以今天我会主要讲本地的服务,远程服务放着以后再讲吧(其实UP主也没用过远程服务就是了==)
| 类别 | 区别 | 优点 | 缺点 | 应用 |
| 本地服务(Local) | 该服务依附在主进程上, | 服务依附在主进程上而不是独立的进程,这样在一定程度上节约了资源,另外Local服务因为是在同一进程因此不需要IPC,也不需要AIDL。相应bindService会方便很多。 | 主进程被Kill后,服务便会终止。 | 非常常见的应用如:HTC的音乐播放服务,天天动听音乐播放服务。 |
| 远程服务(Remote) | 该服务是独立的进程, | 服务为独立的进程,对应进程名格式为所在包名加上你指定的android:process字符串。由于是独立的进程,因此在Activity所在进程被Kill的时候,该服务依然在运行,不受其他进程影响,有利于为多个进程提供服务具有较高的灵活性。 | 该服务是独立的进程,会占用一定资源,并且使用AIDL进行IPC稍微麻烦一点。 | 一些提供系统服务的Service,这种Service是常驻的。 |
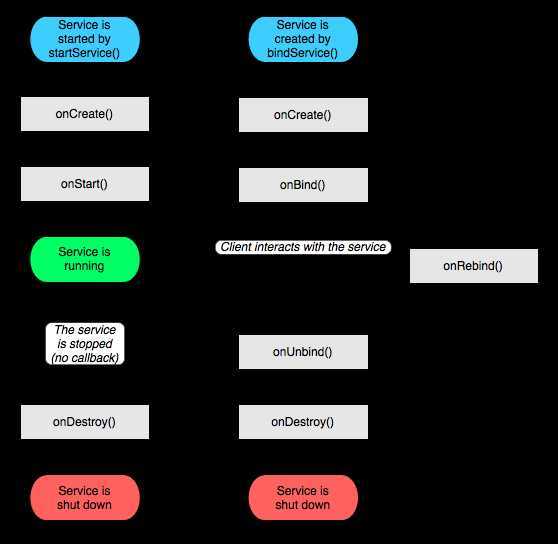
service的生命周期比activity简单多了,原因是service是在后台运行的,它是一直运行的,所以不需要那么多的状态判断。它只继承了onCreate()、onStart()或者说是onStartCommand()、 // 2.0 API level之后,实现onStart等同于重写onStartCommand并返回 关于onStartCommon()的详解:http://blog.csdn.net/lizzy115/article/details/7001731
onDestroy()三个方法。 服务不能自己运行,需要通过调用Context.startService()或Context.bindService()方法启动服务。这两个方法都可以启动Service,但是它们的使用场合有所不同。
四、Service实例
ServiceActivity.java:

package com.example.helloandroid; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; public class ServiceActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_service); Button btnStartService = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.btnStartService); Button btnStopService = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.btnStopService); btnStartService.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){ @Override public void onClick(View v) { startService(new Intent(ServiceActivity.this, MyService.class)); } }); btnStopService.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){ @Override public void onClick(View v) { stopService(new Intent(ServiceActivity.this, MyService.class)); } }); } @Override protected void onStart() { super.onStart(); } @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); } @Override protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); } @Override protected void onStop() { super.onStop(); } @Override protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); } }
activicy_service.xml:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="服务" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btnStartService" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="启动服务" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btnStopService" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="停止服务" /> </LinearLayout>
MyService.java:

package com.example.helloandroid; import android.app.Service; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.IBinder; import android.util.Log; import android.widget.Toast; public class MyService extends Service{ private final String STR_TAG ="TAG"; @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public void onCreate(){ Log.v(STR_TAG, "My Service Create"); } @Override public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) { Log.v(STR_TAG, "My Service Started"); } @Override public void onDestroy(){ Log.v(STR_TAG, "My Service Destroy"); } }
启动Service过程如下:
context.startService() ->onCreate()- >onStart()->Service running
其中onCreate()可以进行一些服务的初始化工作.
停止Service过程如下:
context.stopService() | ->onDestroy() ->Service stop
标签:des android style blog http io ar color os
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/engine1984/p/4128453.html