标签:style blog http io color sp strong on 文件
我们知道,刚开始接触C语言编程,一般都是在一个.c或者.cpp(以下只说.c)的文件中编写代码,其中一定会有一个入口函数,
也就是main()函数,你可以将程序代码全部写在main函数里,当然如果你想要程序更加模块化,也可以将一些操作写在一个函数
里,这些函数的声明和定义也都是在main函数中。
想想,随着你的代码量越来越大,实现的功能越来越多,在一个.c文件中,你定义了许许多多的函数,这些函数实现着不同功能,
并且都是混杂在一起,你会不会感觉看着自己写的代码感觉自己的脑子也乱了?在这里我找到了一个方法来将程序变得更加模块化,
更加有条理。总的做法分以下几步:
1.将功能相近的自定义函数的声明写在一个.h文件中(比如:Math.h)
2.将这些函数的具体实现写在.c文件中(比如:Math.c 注意要包含头文件 #include "Math.h" )
3.在你的主程序(支持.c文件格式)中包含头文件(#include "Math.h"),在主程序就可以调用这些自定义函数了
我们现在想要C函数模块,该模块提供数学计算的功能(例如加、减、乘、除等计算功能),自定义函数写在Math.h中,函数的
实现写在Math.c中,在主函数main.c中调用这些函数进行测试。
一、编写Math.h文件
1 #ifndef _MATH_H 2 #define _MATH_H 3 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 6 /* 7 自定义函数的声明 8 */ 9 //加 10 int Add(int a,in b); 11 //减 12 int Sub(int a,int b); 13 //乘 14 int Multi(int a,int b); 15 //除 16 double Dev(int a,int b); 17 // ... 18 #endif
二、编写Math.c文件
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include "Math.h" //必须添加!!! 3 4 int Add(int a,int b) 5 { 6 return a+b; 7 } 8 9 int Sub(int a,int b) 10 { 11 return a-b; 12 } 13 14 int Multi(int a,int b) 15 { 16 return a*b; 17 } 18 19 double Dev(int a,int b) 20 { 21 if(b==0) 22 { 23 printf("\n除数不能为0."); 24 return 0.0; 25 } 26 return (double)a/b; 27 }
三、测试:main.c(支持.c文件格式)调用模块中的函数
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <conio.h> 3 #include "Math.h" //添加自定义函数的头文件 4 5 void main() 6 { 7 int a=15,b=10; 8 9 //调用自定义函数 10 printf("a+b=%d\n", Add(a,b) ); 11 printf("a-b=%d\n", Sub(a,b) ); 12 printf("a*b=%d\n", Multi(a,b) ); 13 printf("a/b=%f\n", Dev(a,b) ); 14 15 getch(); 16 return; 17 }
注意:在VC6.0中添加主程序代码时需要添加.c格式的(main.c),添加.cpp格式的(main.cpp)会报错,
具体原因还不知道,希望知道的可以告知!
程序运行的结果:
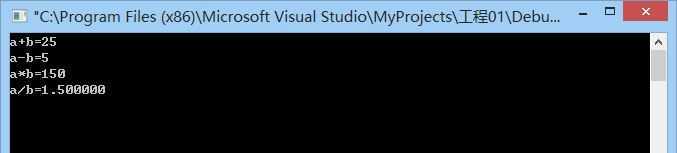
附:以上的内容为本人从《C语言科学与艺术》一书中的学习的总结,供大家学习和分享。
标签:style blog http io color sp strong on 文件
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/miaosha5s/p/4143801.html