标签:blog http io ar os 使用 sp for on
http://www.cnblogs.com/me-sa/archive/2012/11/22/erlang_vm_monitor_text_mode.html
之前介绍过一个Erlang的Web监控工具,如果在字符终端界面呢? Erlang提供了一套监控系统负载情况的模块,可以监控CPU 磁盘 以及内存的使用情况.这些模块组织成为os_mon应用程序,启动os_mon才可以看到采集的系统信息;os_mon依赖sasl应用,我们首先要启动sasl.如果没有运行os_mon,或者系统不支持都会返回无效值;我们先动手试一下:

Eshell V5.9 (abort with ^G)
1> application:start(os_mon).
{error,{not_started,sasl}}
2> application:start(sasl).
ok
3>
...... ...... %% 应用程序启动大量的输出信息被我省略了
=PROGRESS REPORT==== 22-Nov-2012::00:37:33 ===
application: sasl
started_at: nonode@nohost
3> application:start(os_mon).
.............%% 输出信息省略
=PROGRESS REPORT==== 22-Nov-2012::00:37:36 ===
application: os_mon
started_at: nonode@nohost
ok
4>
=PROGRESS REPORT==== 22-Nov-2012::00:37:36 ===
supervisor: {local,kernel_safe_sup}
started: [{pid,<0.56.0>},
{name,timer_server},
{mfargs,{timer,start_link,[]}},
{restart_type,permanent},
{shutdown,1000},
{child_type,worker}]
4> disksup:get_disk_data().
[{"/",18102140,73},
{"/dev/shm",1962120,0},
{"/boot",495844,11}]
5> memsup:get_memory_data().
{4018425856,739979264,{<0.26.0>,284328}}
6> memsup:get_os_wordsize().
64
7>
7> disksup:get_almost_full_threshold().
80
11> disksup:set_almost_full_threshold(0.65).
ok
12> disksup:get_almost_full_threshold().
65
13>
上面查看的是磁盘和内存的使用情况,disksup memsup提供了类似的接口:查看当前状态,查看/设定系统阈值,查看/设定系统数据采样间隔;下面,看看CPU的监控,注意它只支持Unix.cpu_sup提供的接口有:查看当前运行的OS进程数量,获取最近1分钟 5分钟 15分钟的系统平均负载(是不是很熟悉?);
14> cpu_sup:nprocs().
167
15> cpu_sup:avg1().
0
16> cpu_sup:avg5().
0
17> cpu_sup:avg15().
0
18> cpu_sup:util().
0.5439432506552185
20> cpu_sup:util([detailed]).
{[0],
[{soft_irq,0.0020078998462259544},
{hard_irq,1.1279168175796845e-4},
{kernel,0.3190071022063228},
{nice_user,1.6372986061640582e-4},
{user,0.22264870068088854}],
[{steal,0.0},
{idle,99.45393492597752},
{wait,0.0021248497466662443}],
[]}
21>
上面说过它只是在unix操作系统可用,如果是在Windows 环境中:
cpu_sup:util([detailed]).
=ERROR REPORT==== 21-Nov-2012::17:25:11 ===
OS_MON (cpu_sup) called by <0.30.0>, unavailable {all,0,0,[]}
[os_mon 官方文档] http://www.erlang.org/doc/apps/os_mon/index.html
平时用的最多的可能就是etop,两种用法:
[1] 在/usr/local/lib/erlang/lib/observer-1.0/priv/bin目录下面(视安装情况而异)执行:
./etop -node t@zen.com -setcookie abc -lines 10 -sort memory -interval 10 -accumulate true -tracing on
可能遇到的下面的问题:
[root@localhost bin]# ./etop -name m@zen.com -node t@zen.com -setcookie abc -lines 5 -sort memory -interval 10 -accumulate true -tracing on
Erlang R15B (erts-5.9) [source] [64-bit] [async-threads:0] [hipe] [kernel-poll:false]
Error Couldn‘t connect to node ‘t@zen.com‘
=ERROR REPORT==== 22-Nov-2012::20:00:45 ===
** System NOT running to use fully qualified hostnames **
** Hostname zen.com is illegal **
Usage of the erlang top program
Options are set as command line parameters as in -node a@host -..
or as parameter to etop:start([{node, a@host}, {...}])
很简单,连不上要监控的节点,解决这种问题我们早就驾轻就熟了;打开一下etop文件,修改一下里面的sname setcookie即可;
[2] 还有一种方法就是连入了要监控的节点之后运行etop,由于etop本身执行会阻塞输入,我们创建一个进程做这个事情
spawn(fun() -> etop:start([{output, text}, {interval, 20}, {lines, 20}, {sort, memory}]) end).
官方文档难得图文并茂的介绍了一下etop:http://www.erlang.org/doc/apps/observer/etop_ug.html
使用RabbitMQ的时候我们可以配置Rabbit内存消耗的水位线,完成内存使用监控的模块是vm_memory_monitor [链接];这个模块提供的方法还是通用的:检测操作系统类型--> 根据操作系统,使用os:cmd执行特定命令获取系统信息 -->解析返回结果;写一个简单的例子获取系统版本,以及简单做一下ping:
-module(m).
-compile(export_all).
uname() ->
cmd("uname -a").
ping5(Host) when is_list(Host)->
R= cmd("ping -c 5 "++ Host),
string:tokens(R,"\n").
cmd(Command) ->
Exec = hd(string:tokens(Command, " ")),
case os:find_executable(Exec) of
false -> throw({command_not_found, Exec});
_ -> os:cmd(Command)
end.
查看一下结果:
Eshell V5.9 (abort with ^G)
1> m:uname().
"Linux localhost 2.6.32-279.9.1.el6.x86_64 #1 SMP Tue Sep 25 21:43:11 UTC 2012 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux\n"
2> m:ping5("www.baidu.com").
["PING www.a.shifen.com (61.135.169.105) 56(84) bytes of data.",
"64 bytes from 61.135.169.105: icmp_seq=1 ttl=51 time=3.34 ms",
"64 bytes from 61.135.169.105: icmp_seq=2 ttl=51 time=3.01 ms",
"64 bytes from 61.135.169.105: icmp_seq=3 ttl=51 time=2.85 ms",
"64 bytes from 61.135.169.105: icmp_seq=4 ttl=51 time=2.76 ms",
"64 bytes from 61.135.169.105: icmp_seq=5 ttl=51 time=2.87 ms",
"--- www.a.shifen.com ping statistics ---",
"5 packets transmitted, 5 received, 0% packet loss, time 4009ms",
"rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 2.760/2.970/3.348/0.205 ms"]
3>
这个针对Erlang的监控工具目标明确"A top-like Erlang node monitoring tool",先看下使用:
首先启动一个需要监控的节点:
erl -name t@zen.com -setcookie abc
然后,启动entop连接进去:
./entop t@zen.com -name top@zen.com -setcookie abc
效果如图:
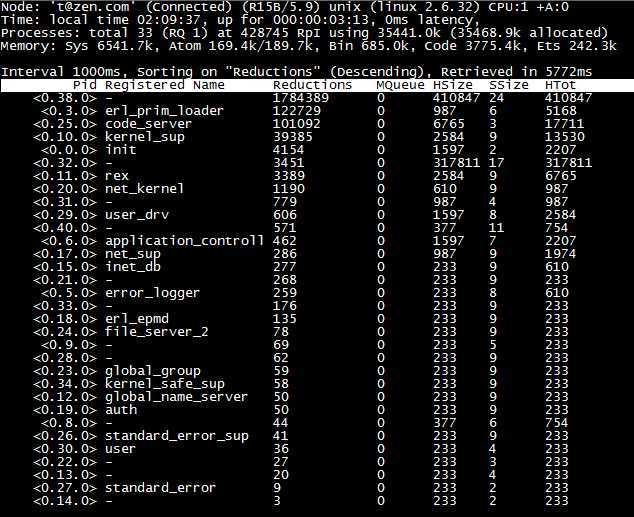
它的解决方案是这样的:配置cookie,name参数,启动监控节点之后紧接着entop就会向要监控的节点"注入"一个用于收集数据的模块entop_collector;
remote_load_code(Module, Node) ->
{_, Binary, Filename} = code:get_object_code(Module),
rpc:call(Node, code, load_binary, [Module, Filename, Binary]).
在entop启动前后你可以在被监控的节点执行一下entop_collector:get_data().看看效果,由于输出内容较多这里只贴片段;
(t@zen.com)4> entop_collector:get_data().
{ok,[{uptime,{330312,169}},
{local_time,{{2012,11,22},{19,7,24}}},
{process_count,32},
{run_queue,0},
{reduction_count,{992425,2841}},
{process_memory_used,2106328},
{process_memory_total,2107083},
{memory,[{system,6730661},
{atom,194289},
{atom_used,173447},
{binary,733296},
{code,3866052},
{ets,248144}]}],
[[{pid,"<0.0.0>"}, {registered_name,init}, {reductions,4154}, {message_queue_len,0},
{heap_size,1597}, {stack_size,2}, {total_heap_size,2207}], [{pid,"<0.3.0>"},
{registered_name,erl_prim_loader},
... ...
有了这样一个采集信息的模块,rpc就可以获得被监控节点的数据了;这里还有一个问题,就是top之类的工具需要不断重绘字符终端界面以及响应用户控制命令,这个怎么搞定呢?entop借助了另外一个开源项目cecho完成了这件事情,这个项目的设计目标就是"An ncurses library for Erlang",恰到好处.看看我们比较关心的两处:
刷新字符界面:
update_screen(Time, HeaderData, RowDataList, State) ->
print_nodeinfo(State),
draw_title_bar(State),
print_showinfo(State, Time),
{Headers, State1} = process_header_data(HeaderData, State),
lists:foldl(fun(Header, Y) ->
cecho:hline($ , ?MAX_HLINE),
cecho:mvaddstr(Y, 0, Header), Y + 1
end, 1, Headers),
{RowList, State2} = process_row_data(RowDataList, State1),
SortedRowList = sort(RowList, State),
{Y, _} = cecho:getmaxyx(),
StartY = (Y-(Y-7)),
lists:foreach(fun(N) -> cecho:move(N, 0), cecho:hline($ , ?MAX_HLINE) end, lists:seq(StartY, Y)),
update_rows(SortedRowList, State2#state.columns, StartY, Y),
cecho:refresh(),
State2.
响应用户命令:
control(ViewPid) ->
P = cecho:getch(),
case P of
N when N >= 49 andalso N =< 57 -> ViewPid ! {sort, N - 48}, control(ViewPid);
$> -> ViewPid ! {sort, next}, control(ViewPid);
$< -> ViewPid ! {sort, prev}, control(ViewPid);
$r -> ViewPid ! reverse_sort, control(ViewPid);
$q -> do_exit(ViewPid);
3 -> do_exit(ViewPid); %Ctrl-C
_ -> ViewPid ! force_update, control(ViewPid)
end.
这两个项目的地址:
[1] ENTOP https://github.com/mazenharake/entop
[2] CECHO https://github.com/mazenharake/cecho
标签:blog http io ar os 使用 sp for on
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/fvsfvs123/p/4146335.html