标签:des style blog http io ar color os 使用
1.序列化
所谓的序列化,就是将结构化对象转化为字节流,以便在网络上传输或是写道磁盘进行永久存储。反序列化,就是将字节流转化为结构化对象。在Java中也存在序列化,刚学Java的时候,接触的第一个项目就是QQ聊天系统,也就是网络编程,其中,用到的就是字符流传输数据,通过对象序列化,然后转化为字符流或字节流,通过socket传递数据。同理,序列化在分布式数据处理的两大领域经常出现:进程间通信和永久存储。
在Hadoop中,系统中多个节点上进程间的通信是通过“远程过程调用”(remote procedure call, RPC)实现的。RPC将消息序列化成二进制流后发送到远程节点,远程节点接着将二进制流饭序列化为原始消息。通常情况下,RPC序列化格式许紧凑、快速、可扩展、和胡操作!紧凑的格式能够使我们充分利用数据中心中最稀缺的资源——网络带宽。
在Hadoop中,它使用自己的序列化框架Writable,它格式紧凑、速度快,缺点是很难用Java以外的语言来扩展。
2.Writable接口
序列化抓住两个关键:序列化和反序列化。所有的都是围绕这这两个展开的。无非就是把结构化数据转化为字节流或是把字节流转化为结构化对象。
Writable接口定义了两个接口,一个是将其状态写如到DataOutput二进制流,另一个是从DataInput中读取结构化对象。
import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; import java.io.IOException; public interface Writable { void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException; void readFields(DataInput in)throws IOException; }
通过一个例子,看看Writable是如何把结构化对象写入到字节流中,以及如何从字节流中读取结构化对象。还有就是DataOutput,DataInput是如何工作的。
Example:
1 package cn.roboson.writable; 2 3 import java.io.DataInput; 4 import java.io.DataOutput; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable; 8 /* 9 * 1.Writable中两个函数的作用 10 * 2.DataInput、DataOutput有什么用? 11 */ 12 13 public class MyWritable implements Writable{ 14 15 private int counter; 16 private long timestamp; 17 @Override 18 public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { 19 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 20 21 //从DataInput 数据流中读取值 22 this.counter=in.readInt(); 23 this.timestamp=in.readLong(); 24 } 25 26 @Override 27 public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { 28 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 29 //写入到DataOutput二进制流中 30 out.writeInt(counter); 31 out.writeLong(timestamp); 32 } 33 34 public static MyWritable read(DataInput in) throws IOException { 35 MyWritable w = new MyWritable(); 36 w.readFields(in); 37 return w; 38 } 39 40 public int getCounter() { 41 return counter; 42 } 43 44 public void setCounter(int counter) { 45 this.counter = counter; 46 } 47 48 public long getTimestamp() { 49 return timestamp; 50 } 51 52 public void setTimestamp(long timestamp) { 53 this.timestamp = timestamp; 54 } 55 56 }
3.实例
通过一个特殊的类IntWritable来举例
1 package cn.roboson.writable; 2 3 import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; 4 import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; 5 import java.io.DataInputStream; 6 import java.io.DataOutputStream; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 9 import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; 10 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable; 11 12 public class Writable01 { 13 14 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 15 16 //IntWritable是一个特殊的Writable类,对其进行序列化 17 IntWritable writable = new IntWritable(); 18 writable.set(163); 19 20 //对InWritable的对象进行序列化为字节流,把字节流中的数据存入到一个字节数组中 21 byte[] bytes = serizlize(writable); 22 23 //判断字节数组中的长度是否为4,一个整数占据4个字节 24 System.out.println("字节数组的长度:"+bytes.length); 25 26 //创建一个对象,将刚刚的字节数组中的数据,反序列化写入到结构化数据中 27 IntWritable dewritable = new IntWritable(); 28 deserizlize(dewritable, bytes); 29 System.out.println(dewritable.get()); 30 } 31 32 public static byte[] serizlize(Writable writable) throws IOException{ 33 34 //创建一个输出字节流对象 35 ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); 36 DataOutputStream dataout = new DataOutputStream(out); 37 38 //将结构化数据的对象writable写入到输出字节流。 39 writable.write(dataout); 40 return out.toByteArray(); 41 } 42 43 public static byte[] deserizlize(Writable writable,byte[] bytes) throws IOException{ 44 45 //创建一个输入字节流对象,将字节数组中的数据,写入到输入流中 46 ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes); 47 DataInputStream datain = new DataInputStream(in); 48 49 //将输入流中的字节流数据反序列化 50 writable.readFields(datain); 51 return bytes; 52 53 } 54 }
运行结果:
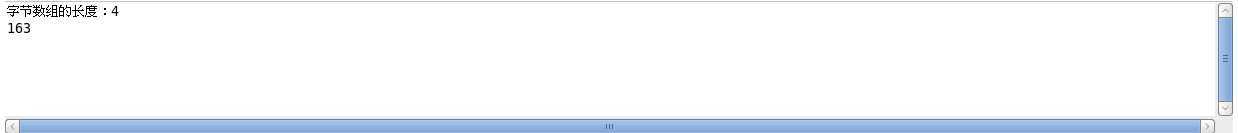
标签:des style blog http io ar color os 使用
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/robert-blue/p/4157768.html