标签:
发送http请求
URL url = new URL(address);
//获取连接对象,并没有建立连接
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
//设置连接和读取超时
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
conn.setReadTimeout(5000);
//设置请求方法,注意必须大写
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
//建立连接,发送get请求
//conn.connect();
//建立连接,然后获取响应吗,200说明请求成功
conn.getResponseCode();
服务器的图片是以流的形式返回给浏览器的
//拿到服务器返回的输入流
InputStream is = conn.getInputStream();
//把流里的数据读取出来,并构造成图片
Bitmap bm = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(is);
把图片设置为ImageView的显示内容
ImageView iv = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.iv);
iv.setImageBitmap(bm);
如果需要在子线程中刷新ui,使用消息队列机制
//消息队列
Handler handler = new Handler(){
//主线程中有一个消息轮询器looper,不断检测消息队列中是否有新消息,如果发现有新消息,自动调用此方法,注意此方法是在主线程中运行的
public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg) {
}
};
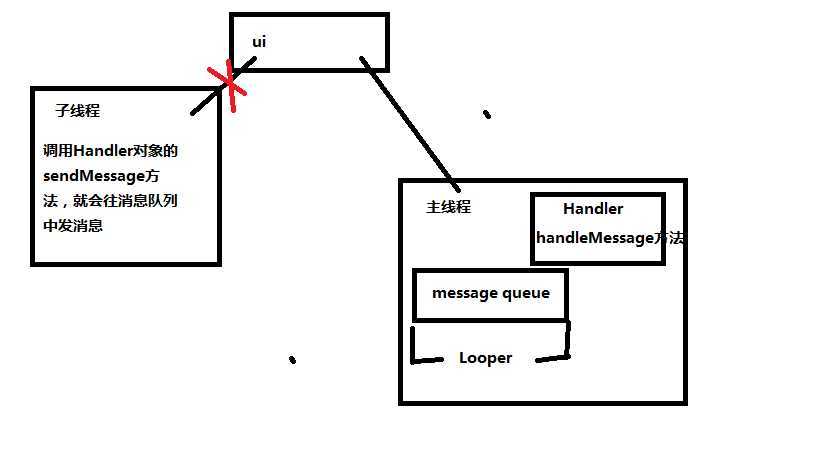
//创建消息对象
Message msg = new Message();
//消息的obj属性可以赋值任何对象,通过这个属性可以携带数据
msg.obj = bm;
//what属性相当于一个标签,用于区分出不同的消息,从而运行不能的代码
msg.what = 1;
//发送消息
handler.sendMessage(msg);
通过switch语句区分不同的消息
public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
//如果是1,说明属于请求成功的消息
case 1:
ImageView iv = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.iv);
Bitmap bm = (Bitmap) msg.obj;
iv.setImageBitmap(bm);
break;
case 2:
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "请求失败", 0).show();
break;
}
}
把服务器返回的流里的数据读取出来,然后通过文件输入流写至本地文件
//1.拿到服务器返回的输入流
InputStream is = conn.getInputStream();
//2.把流里的数据读取出来,并构造成图片
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = is.read(b)) != -1){
fos.write(b, 0, len);
}
创建bitmap对象的代码改成
Bitmap bm = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(file.getAbsolutePath());
使用自定义组件时,标签名字要写包名
<com.loopj.android.image.SmartImageView/>
SmartImageView的使用
SmartImageView siv = (SmartImageView) findViewById(R.id.siv);
siv.setImageUrl("http://192.168.1.102:8080/dd.jpg");
发送GET请求
URL url = new URL(path);
//获取连接对象
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
//设置连接属性
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
conn.setReadTimeout(5000);
//建立连接,获取响应吗
if(conn.getResponseCode() == 200){
}
获取服务器返回的流,从流中把html源码读取出来
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
while((len = is.read(b)) != -1){
//把读到的字节先写入字节数组输出流中存起来
bos.write(b, 0, len);
}
//把字节数组输出流中的内容转换成字符串
//默认使用utf-8
text = new String(bos.toByteArray());
乱码的出现是因为服务器和客户端码表不一致导致
//手动指定码表
text = new String(bos.toByteArray(), "gb2312");
get方式提交的数据是直接拼接在url的末尾
final String path = "http://192.168.1.104/Web/servlet/CheckLogin?name=" + name + "&pass=" + pass;
发送get请求,代码和之前一样
URL url = new URL(path);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setReadTimeout(5000);
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
if(conn.getResponseCode() == 200){
}
浏览器在发送请求携带数据时会对数据进行URL编码,我们写代码时也需要为中文进行URL编码
String path = "http://192.168.1.104/Web/servlet/CheckLogin?name=" + URLEncoder.encode(name) + "&pass=" + pass;
协议头中多了两个属性
Content-Length: 32,描述提交的数据的长度
//给请求头添加post多出来的两个属性
String data = "name=" + URLEncoder.encode(name) + "&pass=" + pass;
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Length", data.length() + "");
设置允许打开post请求的流
conn.setDoOutput(true);
获取连接对象的输出流,往流里写要提交给服务器的数据
OutputStream os = conn.getOutputStream();
os.write(data.getBytes());标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/McCa/p/4176767.html