标签:
4.1 概述
管道只在亲缘进程间使用,FIFO在任意进程间使用
4.2 管道
#include <unistd.h> int pipe(int fd[2])
fd[0]用来读管道,fd[1]用来写管道
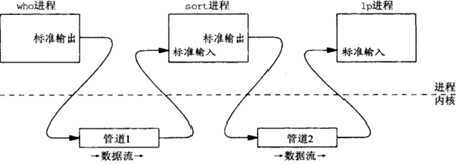
1)命令who | sort | lp中的管道:
2)管道实现文件服务器与客户端:
#include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <error.h> #define MAXLINE 1024 void client(int readfd,int writefd); void server(int readfd,int writefd); int main() { int fd1[2]; int fd2[2]; pipe(fd1); pipe(fd2); int pid; if( (pid = fork()) < 0) { fprintf(stderr,"fork error\n"); exit(-1); } if(pid > 0) { close(fd1[1]); close(fd2[0]); server(fd1[0],fd2[1]); exit(0); } close(fd1[0]); close(fd2[1]); client(fd2[0],fd1[1]); waitpid(pid,NULL,0); exit(0); } void client(int readfd,int writefd) { size_t len; char buf[MAXLINE]; fgets(buf,MAXLINE,stdin); len = strlen(buf); if(buf[len-1] == ‘\n‘) --len; write(writefd,buf,len); while( (len = read(readfd,buf,MAXLINE)) > 0) write(STDOUT_FILENO,buf,len); } void server(int readfd,int writefd) { char buf[MAXLINE]; ssize_t n; if( (n = read(readfd,buf,MAXLINE)) ==0) { fprintf(stderr,"error\n"); exit(-1); } buf[n] = ‘\0‘; int fd; if( (fd = open(buf,O_RDONLY)) < 0) { snprintf(buf+n,sizeof(buf)-n,"can‘t open: %s\n",strerror(errno)); n = strlen(buf); write(writefd,buf,n); } else while( (n = read(fd,buf,MAXLINE)) > 0) write(writefd,buf,n); close(fd); }
4.3 popen和pclose函数
#include <stdio.h> FILE *popen(char *cmd,char *type) int pclose(FILE *fp)
popen函数创建另外一个进程执行cmd,并在调用进程与创建进程之间建立一个单向管道,管道的一端与返回的FILE对象绑定
type为"w",FILE对象与管道的写端绑定,cmd的标准输入为管道的读端
type为"r",FILE对象与管道的读端绑定,cmd的标准输出为管道的写端

#include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define MAXLINE 1024 int main() { char buf[MAXLINE]; fgets(buf,MAXLINE,stdin); int n = strlen(buf); if(buf[n-1] == ‘\n‘) --n; char cmd[MAXLINE]; snprintf(cmd,MAXLINE,"cat %s",buf); FILE *fp = popen(cmd,"r"); while(fgets(buf,MAXLINE,fp) != NULL) fputs(buf,stdout); exit(0); }
4.4 FIFO
FIFO又称命名管道
#include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/types.h> int mkfifo(char *pathname,mode_t mode)
FIFO实现文件服务器和客户端

#include <sys/stat.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { if(mkfifo("./fifo1",S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR) < 0) { fprintf(stderr,"mkfifo error\n"); exit(-1); } if(mkfifo("./fifo2",S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR) < 0) { fprintf(stderr,"mkfifo error\n"); exit(-1); } int pid; if( (pid = fork()) < 0) { fprintf(stderr,"fork error\n"); exit(-1); } if(pid == 0) { int fd1 = open("./fifo1",O_RDONLY); int fd2 = open("./fifo2",O_WRONLY); server(fd1,fd2); exit(0); } int fd1 = open("./fifo1",O_WRONLY); int fd2 = open("./fifo2",O_RDONLY); client(fd2,fd1); waitpid(pid,NULL,0); exit(0); }
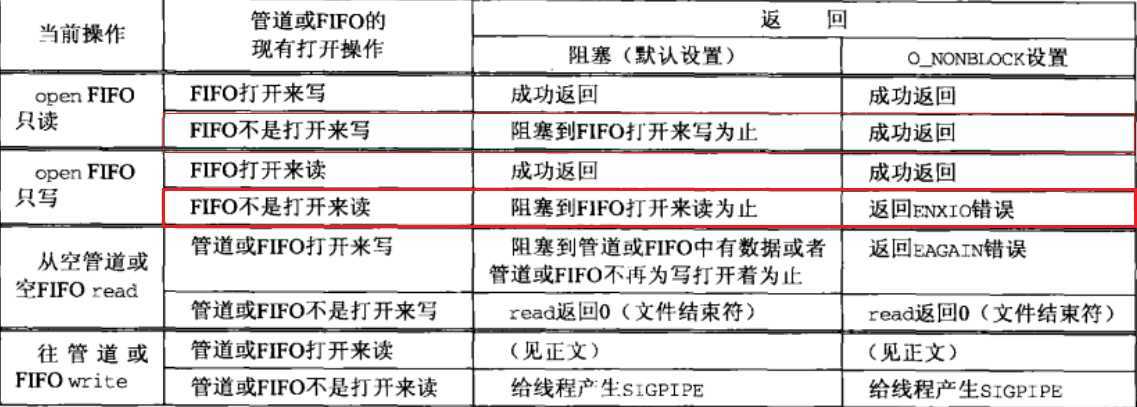
4.5 管道、FIFO的阻塞与非阻塞
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/buptlyn/p/4178912.html