标签:c++
智能指针通常使用类模板来实现。模拟类指针的各种行为。但是,其最重要的作用是对类指针成员的管理,防止悬垂指针的出现。
template<class T> class SmartPointer{ public: SmartPointer(T *t):pt(t){} T& operator *(){ return *pt; } T* operator ->() { return pt; } private: T *pt; };
为了实现引用计数,我们定义一个_counter类来记录引用次数,把_counter类的所有成员设定为private,因为其他的类型并不需要访问_counter,只有SmartPointer对其进行操作就行了,SmartPointer将设为其友元类。
class _counter{ template<class T> friend class SmartPointer; _counter(int u):use(u){} ~_counter(){} int use; };
在SmartPointer类中,保留_counter的指针。
template<class T> class SmartPointer{ public: SmartPointer(T *t):pc(new _counter(1)){ cout<<"SmartPointer::SmartPointer() invoded use is: "<<pc->use<<endl; this->pt = t; } SmartPointer(SmartPointer<T> &rhs){ this->pc = rhs.pc; this->pt = rhs.pt; this->pc->use++; cout<<"SmartPointer copy invoked use is: "<<pc->use<<endl; } ~SmartPointer(){ pc->use--; cout<<"SmartPointer::~SmartPointer() invoded use is: "<<pc->use<<endl; if(pc->use == 0) { delete pt; delete pc; } } SmartPointer<T>& operator=(SmartPointer<T> rhs){ if(rhs == *this){ return *this; }if(--pc->use==0){deletept;deletepc;this->pt = rhs.pt; this->pc = rhs.pc; this->pc->use++; cout<<"SmartPointer::operator=() invoked use is: "<<pc->use<<endl; return *this; } private: T *pt; _counter* pc; };}
例如:我们有一个HasPtr类,其类成员中有一个为指针*p。
class HasPtr{ public: HasPtr(int val):value(val),p(new int(3)){ cout<<"HasPtr::HasPtr() invoked"<<endl; } ~HasPtr(){ delete p; cout<<"HasPtr::~HasPtr() invoded"<<endl;} private: int *p; int value; };
如果如下调用:
HasPtr *php = new HasPtr(3); SmartPointer<HasPtr> psp(php); SmartPointer<HasPtr> npsp(psp);
我们现在有两个智能指针对象,指向同一个HasPtr对象,其模型如下:
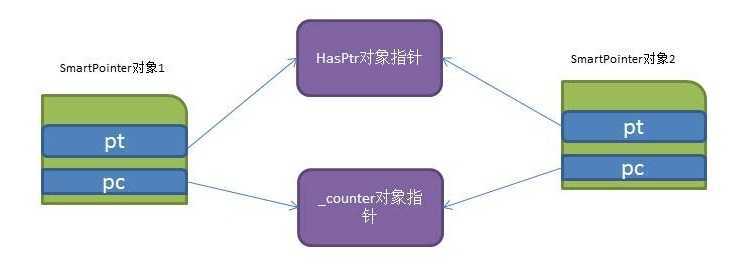
_counter的use成员(引用计数)为2.
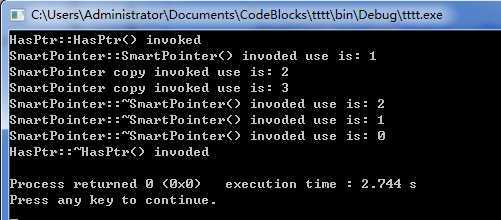
int main(void) { HasPtr *php = new HasPtr(3); SmartPointer<HasPtr> psp(php); SmartPointer<HasPtr> npsp(psp); SmartPointer<HasPtr> nnpsp = npsp; return 0; }
使用gcc编译器,运行结果如下:
再找一份实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
using namespace std;
#define SAFE_DELETE(p) if (p) { delete p; p = NULL; }
class KRefCount
{
public:
KRefCount():m_nCount(0){}
public:
unsigned AddRef(){ return InterlockedIncrement(&m_nCount); }
unsigned Release(){ return InterlockedDecrement(&m_nCount); }
void Reset(){ m_nCount = 0; }
private:
unsigned long m_nCount;
};
template <typename T>
class SmartPtr
{
public:
SmartPtr(void)
: m_pData(NULL)
{
m_pReference = new KRefCount();
m_pReference->AddRef();
}
SmartPtr(T* pValue)
: m_pData(pValue)
{
m_pReference = new KRefCount();
m_pReference->AddRef();
}
SmartPtr(const SmartPtr<T>& sp)
: m_pData(sp.m_pData)
, m_pReference(sp.m_pReference)
{
m_pReference->AddRef();
}
~SmartPtr(void)
{
if (m_pReference && m_pReference->Release() == 0)
{
SAFE_DELETE(m_pData);
SAFE_DELETE(m_pReference);
}
}
inline T& operator*()
{
return *m_pData;
}
inline T* operator->()
{
return m_pData;
}
SmartPtr<T>& operator=(const SmartPtr<T>& sp)
{
if (this != &sp)
{
if (m_pReference && m_pReference->Release() == 0)
{
SAFE_DELETE(m_pData);
SAFE_DELETE(m_pReference);
}
m_pData = sp.m_pData;
m_pReference = sp.m_pReference;
m_pReference->AddRef();
}
return *this;
}
SmartPtr<T>& operator=(T* pValue)
{
if (m_pReference && m_pReference->Release() == 0)
{
SAFE_DELETE(m_pData);
SAFE_DELETE(m_pReference);
}
m_pData = pValue;
m_pReference = new KRefCount;
m_pReference->AddRef();
return *this;
}
T* Get()
{
T* ptr = NULL;
ptr = m_pData;
return ptr;
}
void Attach(T* pObject)
{
if (m_pReference->Release() == 0)
{
SAFE_DELETE(m_pData);
SAFE_DELETE(m_pReference);
}
m_pData = pObject;
m_pReference = new KRefCount;
m_pReference->AddRef();
}
T* Detach()
{
T* ptr = NULL;
if (m_pData)
{
ptr = m_pData;
m_pData = NULL;
m_pReference->Reset();
}
return ptr;
}
private:
KRefCount* m_pReference;
T* m_pData;
};
class CTest
{
public:
CTest(int b) : a(b) {}
private:
int a;
};
int main()
{
SmartPtr<CTest> pSmartPtr1(new CTest(10));
SmartPtr<CTest> pSmartPtr2(new CTest(20));
pSmartPtr1 = pSmartPtr2;
} 标签:c++
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/yusiguyuan/article/details/42131183