标签:
硬件环境:还是使用四节点OpenStack部署环境,参见 http://www.cnblogs.com/sammyliu/p/4190843.html
OpenStack配置:
使用 http://www.cnblogs.com/sammyliu/p/4201143.html 中相同的方法,画出Neutron节点上网络组件图:
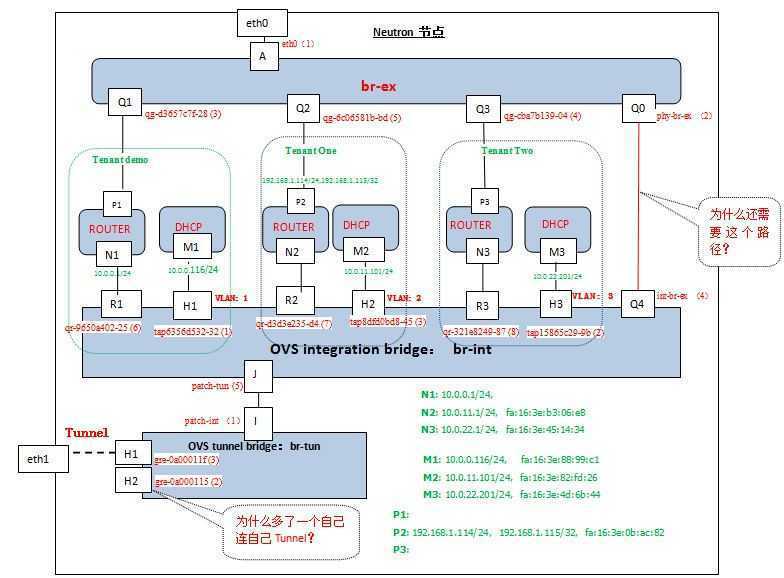
可见:
(1). 同样有OVS Tunnel bridge br-tun和OVS Integration bridge br-int,多了br-ex来提供外部网络连接,br-ex和物理网卡eth0绑定。
(2). Neutron使用Linux network namespace来实现tenant之间的网络隔离。本例中有三个network namespace,每个network namspace包括router,dhcp,interface,routing tables,iptable rules等。
root@network:/home/s1# ip netns qdhcp-d24963da-5221-481e-adf5-fe033d6e0b4e qrouter-e506f8fe-3260-4880-bd06-32246225aeae qdhcp-d04a0a06-7206-4d05-9432-3443843bc199 qrouter-33e2b1bf-04cb-4811-9c58-7e03856022c1 qrouter-9ba04071-f32b-435e-8f44-e32936568102 qdhcp-0a4cd030-d951-401a-8202-937b788bea43
(3). OpenStack中每个subnet都有一个不同的VLAN ID。H1/H2/H3端口上分布有不同的VLAN ID,对应不同的tenant的subnet。
(4). 不知道为什么br-tun上多了一个Tunnel H2。从下面的分析中可见它是被用到的,具体作用待进一步研究。
插播Mac地址的基础知识:
root@network:/home/s1# ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-tun NXST_FLOW reply (xid=0x4): cookie=0x0, duration=6975.734s, table=0, n_packets=1511, n_bytes=160614, idle_age=621, priority=1,in_port=3 actions=resubmit(,3) //从H1进来的traffic,到table 3 cookie=0x0, duration=6977.009s, table=0, n_packets=1427, n_bytes=173531, idle_age=622, priority=1,in_port=1 actions=resubmit(,2) //从patch-int 进来的traffic,到table 2 cookie=0x0, duration=6975.946s, table=0, n_packets=11, n_bytes=766, idle_age=913, priority=1,in_port=2 actions=resubmit(,3) //从H2 GRE端口进来的traffic,到table 3 cookie=0x0, duration=6976.942s, table=0, n_packets=7, n_bytes=558, idle_age=6967, priority=0 actions=drop cookie=0x0, duration=6976.88s, table=2, n_packets=1370, n_bytes=168941, idle_age=622, priority=0,dl_dst=00:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00 actions=resubmit(,20) //目的地址是单播地址,到table 20 cookie=0x0, duration=6976.808s, table=2, n_packets=56, n_bytes=4500, idle_age=913, priority=0,dl_dst=01:00:00:00:00:00/01:00:00:00:00:00 actions=resubmit(,22) //目的地址是组播地址,到table 22 cookie=0x0, duration=6974.658s, table=3, n_packets=1121, n_bytes=122012, idle_age=3734, priority=1,tun_id=0x1 actions=mod_vlan_vid:1,resubmit(,10) //Tunnel 1的traffic,修改VLAN ID 为 1, 再到 table 10 cookie=0x0, duration=989.219s, table=3, n_packets=269, n_bytes=26421, idle_age=621, priority=1,tun_id=0x3 actions=mod_vlan_vid:3,resubmit(,10) //Tunnel id 为 3的traffic,修改VLAN ID 为 3,到table 10 cookie=0x0, duration=1393.201s, table=3, n_packets=132, n_bytes=12947, idle_age=1239, priority=1,tun_id=0x2 actions=mod_vlan_vid:2,resubmit(,10) //Tunnel id 为 2 的traffic,修改VLAN ID 为2, 到table 10 cookie=0x0, duration=6976.736s, table=3, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=6976, priority=0 actions=drop cookie=0x0, duration=6976.656s, table=4, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=6976, priority=0 actions=drop cookie=0x0, duration=6976.585s, table=10, n_packets=1522, n_bytes=161380, idle_age=621, priority=1 actions=learn(table=20,hard_timeout=300,priority=1,NXM_OF_VLAN_TCI[0..11],NXM_OF_ETH_DST[]=NXM_OF_ETH_SRC[],load:0->NXM_OF_VLAN_TCI[],load:NXM_NX_TUN_ID[]->NXM_NX_TUN_ID[],output:NXM_OF_IN_PORT[]),output:1 //学习一条新的规则到20,traffic从patch-tun出到br-int cookie=0x0, duration=6976.507s, table=20, n_packets=0, n_bytes=0, idle_age=6976, priority=0 actions=resubmit(,22) //重新到table 22 cookie=0x0, duration=989.283s, table=22, n_packets=4, n_bytes=292, idle_age=913, dl_vlan=3 actions=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:0x3,output:3,output:2 //如果目的VLAN ID 是 3, 去掉VLAN ID, 设置Tunnel ID 为 3,从H1和H2 GRE 端口发出 cookie=0x0, duration=1393.309s, table=22, n_packets=5, n_bytes=382, idle_age=1333, dl_vlan=2 actions=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:0x2,output:3,output:2 //如果目的VLAN ID是2,去掉VLAN ID, 设置 TunnelID 为 2, 从 H1和H2 GRE 端口发出 cookie=0x0, duration=6974.728s, table=22, n_packets=4, n_bytes=272, idle_age=6892, dl_vlan=1 actions=strip_vlan,set_tunnel:0x1,output:3,output:2 //如果目的VLAN ID 是 1,去掉VLAN ID, 设置Tunnel ID 为 1,从 H1 和H2 GRE端口发出 cookie=0x0, duration=6976.436s, table=22, n_packets=43, n_bytes=3554, idle_age=920, priority=0 actions=drop
从这里可以看出,似乎端口 H2 用于Neutron内部的一些traffic的routing。它的作用还得继续研究。总之,br-tun会:
root@network:/home/s1# ip netns exec qrouter-33e2b1bf-04cb-4811-9c58-7e03856022c1 ip addr 22: qr-d3d3e235-d4: <BROADCAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default link/ether fa:16:3e:b3:06:e8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 10.0.11.1/24 brd 10.0.11.255 scope global qr-d3d3e235-d4 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::f816:3eff:feb3:6e8/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 26: qg-6c06581b-bd: <BROADCAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default link/ether fa:16:3e:0b:ac:82 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.1.114/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global qg-6c06581b-bd valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet 192.168.1.115/32 brd 192.168.1.115 scope global qg-6c06581b-bd valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::f816:3eff:fe0b:ac82/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
可见:
再看看它的route:
root@network:/home/s1# ip netns exec qrouter-33e2b1bf-04cb-4811-9c58-7e03856022c1 ip route
default via 192.168.1.1 dev qg-d3657c7f-28 //默认路由,所以目的不在本网络中的traffic都要通过 qg-d3657c7f-28 interface 发到外网网关192.168.1.1
10.0.11.0/24 dev qr-d3d3e235-d4 proto kernel scope link src 10.0.11.1 //目的为本子网内的traffic 经过 qr-d3d3e235-d4 发到子网网关 10.0.11.1
192.168.1.0/24 dev qg-6c06581b-bd proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.100 //目的为 192.168.1.0/24 的traffic通过 qg-6c06581b-bd 发到网关192.168.1.100
Router namespace中的 netfilter NAT 表负责 Neutron Floating IP 的实现。下面是tenant-two (有两个虚机)的router的NAT表:
每一个有DHCP的网络都在Neutron节点上有一个DHCP服务,每个DHCP Server都是一个运行在一个network namespace中的dnsmasq进程。 dnsmasq是一个用在Linux上的轻型DNS和DHCP服务,具体见 http://www.thekelleys.org.uk/dnsmasq/docs/dnsmasq-man.html.
root@network:/home/s1# ps -ef | grep dns nobody 1602 1 0 02:08 ? 00:00:00 dnsmasq --no-hosts --no-resolv --strict-order --bind-interfaces --interface=tap6356d532-32 --except-interface=lo --pid-file=/var/lib/neutron/dhcp/0a4cd030-d951-401a-8202-937b788bea43/pid --dhcp-hostsfile=/var/lib/neutron/dhcp/0a4cd030-d951-401a-8202-937b788bea43/host --addn-hosts=/var/lib/neutron/dhcp/0a4cd030-d951-401a-8202-937b788bea43/addn_hosts --dhcp-optsfile=/var/lib/neutron/dhcp/0a4cd030-d951-401a-8202-937b788bea43/opts --leasefile-ro --dhcp-range=set:tag0,10.0.22.0,static,86400s --dhcp-lease-max=256 --conf-file= --domain=openstacklocal
说明:
1. --interface=tap6356d532-32: 该process绑定/监听一个TAP设备,即上图中的 H3
2. --dhcp-hostsfile=/var/lib/neutron/dhcp/0a4cd030-d951-401a-8202-937b788bea43/host:
# /var/lib/neutron/dhcp/0a4cd030-d951-401a-8202-937b788bea43/host
fa:16:3e:fe:c7:87,host-10-0-22-200.openstacklocal,10.0.22.200 //虚机的Mac地址,虚机的主机名字,虚机的fixed IP
在虚机的创建过程中,Neutron会把这些信息(应该是从neutron db中拿到一个可用的IP地址)写到该文件中,这样,当虚机使用Mac地址向DHCP Server查询IP地址的时候,dnsmasq会读取该文件把IP地址返回给它。
root@network:/home/s1# ip netns exec qdhcp-d24963da-5221-481e-adf5-fe033d6e0b4e ip addr 19: tap15865c29-9b: <BROADCAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default link/ether fa:16:3e:4d:6b:44 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 10.0.22.201/24 brd 10.0.22.255 scope global tap15865c29-9b valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::f816:3eff:fe4d:6b44/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
DHCP使用fix ip range的第一个可用IP地址做为其IP地址。它的interface的MAC地址 fa:16:3e:4d:6b:44 会出现在br-tun的rules里面。
具体步骤在下一篇博文中详细描述。
学习OpenStack之(7):Neutron 深入学习之 OVS + GRE 之 Neutron节点篇
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/sammyliu/p/4201721.html