标签:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <malloc.h>
3 #define LEN sizeof(struct student)
4
5 /*----------------数据定义----------------------*/
6
7 //定义一个学生信息的结构体,包括学号,姓名和结构体类型的指针
8 struct student
9 {
10 long num; //学号
11 char name[128]; //姓名
12 struct student *next; //结构体指针
13 };
14
15 typedef struct student * stuNode;
16
17 int n=0; //全局变量,记录链表的长度
18
19 /*---------------函数声明---------------------*/
20
21 stuNode Create(); //创建一个新的链表
22
23 void Print(stuNode head); //通过传入的链表头指针打印整个链表
24
25 stuNode Delete(stuNode head,int num); //通过传入的链表头指针和学生学号删除节点
26
27 stuNode Insert(stuNode head,stuNode newStu); //依照学生学号的顺序向链表中插入新元素
28
29
30 /*---------------函数定义----------------------*/
31
32 struct student *Create()
33 {
34 struct student *head,*p1,*p2;
35
36 //开辟一个LEN大小的空间,并让p1,p2指针指向它
37 p2=p1=(struct student *)malloc(LEN);
38 //将头指针置为NULL
39 head=NULL;
40
41 //创建链表节点并给节点的元素赋值
42 printf("请输入学生的学号和姓名:");
43 scanf("%ld %s",&p1->num,p1->name);
44 while(p1->num!=0)
45 {
46 n=n+1;
47 if(NULL==head)
48 {
49 head=p1;
50 }
51 else
52 {
53 p2->next=p1;
54 }
55 p2=p1;
56 p1=(struct student *)malloc(LEN);
57 printf("请输入学生的学号和姓名:");
58 scanf("%ld %s",&p1->num,p1->name);
59 }
60 //将尾节点的指针置为NULL
61 p2->next=NULL;
62 return head;
63 }
64
65
66 void Print(struct student *head)
67 {
68 struct student * p;
69 p=head;
70
71 //判断链表是否为空
72 if(NULL==head)
73 {
74 printf("链表为空!\n");
75 return head;
76 }
77 else
78 {
79 //循环打印链表中的元素
80 printf("%d 个记录分别为:\n",n);
81 while(p!=NULL)
82 {
83 printf("%ld %s\n",p->num,p->name);
84 //指针指向下一个节点
85 p=p->next;
86 }
87 }
88 }
89
90
91 struct student *Delete(struct student * head,int num)
92 {
93 struct student *p1;
94 struct student *p2;
95 p1=head;
96 //判断链表是否为空
97 if(NULL==head)
98 {
99 printf("链表为空!\n");
100 return head;
101 }
102 //遍历节点,判断当前节点是不是需要删除的节点及是否为尾节点
103 //如果找到相应节点,或者已经遍历到尾节点就跳出循环
104 while(p1->num!=num&&p1->next!=NULL)
105 {
106 p2=p1;
107 p1=p1->next;
108 }
109 //判断是否找到相应节点
110 if(p1->num==num)
111 {
112 //要删除的节点是不是链表的第一个节点
113 //如果是,就将头指针指向该节点的后一个节点
114 //如果不是,就将该节点的前一个节点的指针指向该节点的后一个节点
115 if(head==p1)
116 {
117 head=p1->next;
118 }
119 else
120 {
121 p2->next=p1->next;
122 }
123 n=n-1;
124 printf("%ld 节点已删除.\n",num);
125 }
126 else
127 {
128 printf("链表中没有要删除的元素.\n");
129 }
130 return head;
131 }
132
133
134 struct student *Insert(struct student * head,struct student * newStu)
135 {
136 struct student *p0;
137 struct student *p1;
138 struct student *p2;
139 p0=newStu;
140 p1=head;
141 //判断链表是否为空,如果是空链表,就将新节点作为第一个节点
142 if(NULL==head)
143 {
144 head=p0;
145 p0->next=NULL;
146 }
147 else
148 {
149 //遍历每一个节点中的学号,与新学号比较大小
150 //如果找到一个学号比新学号大,就将新学号的节点插入它之前
151 //如果尾节点的学号仍比新学号小,就将新节点插入到链表尾部
152 while((p0->num > p1->num)&&(p1->next!=NULL))
153 {
154 p2=p1;
155 p1=p1->next;
156 }
157 //找到一个比新学号大的节点
158 if(p0->num <= p1->num)
159 {
160 //判断该节点是否为头节点,如果是,则将新节点设置为头节点
161 if(p1==head)
162 {
163 head=p0;
164 }
165 else
166 {
167 p2->next=p0;
168 }
169 p0->next=p1;
170 }
171 else
172 {
173 p1->next=p0;
174 p0->next=NULL;
175 }
176 }
177 //链表长度加1
178 n=n+1;
179 printf("%ld 插入成功!\n",newStu->num);
180 return head;
181 }
182
183 void main()
184 {
185 struct student *head;
186 struct student *stu;
187 int num;
188 head=Create();
189 Print(head);
190 printf("请输入要删除的学号:");
191 scanf("%ld",&num);
192 while(num!=0)
193 {
194 head=Delete(head,num);
195 Print(head);
196 printf("请输入要删除的学号:");
197 scanf("%ld",&num);
198 }
199 printf("请输入要插入的节点:");
200 stu=(struct student *)malloc(LEN);
201 scanf("%ld %s",&stu->num,stu->name);
202 while(stu->num!=0)
203 {
204 head=Insert(head,stu);
205 printf("请输入要插入的节点:");
206 stu=(struct student *)malloc(LEN);
207 scanf("%ld %s",&stu->num,stu->name);
208 }
209 Print(head);
210 }
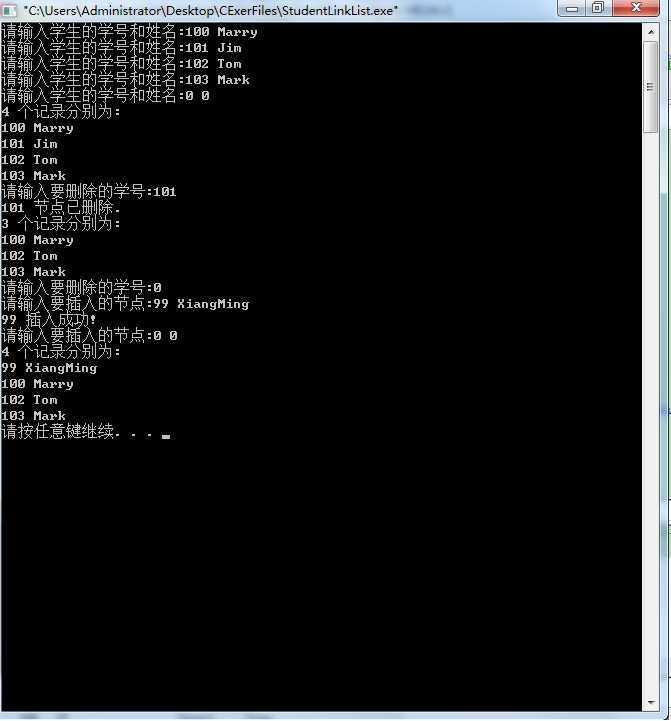
mingw5编译通过,链表结构是数据结构中的基础,掌握链表的逻辑,存储结构和基本操作,并能自己用代码实现,将有助于对后续复杂数据结构和算法的学习!
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yqsqqq/p/4213567.html