标签:
原文:6天通吃树结构—— 第一天 二叉查找树
一直很想写一个关于树结构的专题,再一个就是很多初级点的码农会认为树结构无用论,其实归根到底还是不清楚树的实际用途。
一:场景:
1:现状
前几天我的一个大学同学负责的网站出现了严重的性能瓶颈,由于业务是写入和读取都是密集型,如果做缓存,时间间隔也只能在30s左
右,否则就会引起客户纠纷,所以同学也就没有做缓存,通过测试发现慢就慢在数据读取上面,总共需要10s,天啊...原来首页的加载关联
到了4张表,而且表数据中最多的在10w条以上,可以想象4张巨大表的关联,然后就是排序+范围查找等等相关的条件,让同学抓狂。
2:我个人的提供解决方案
① 读取问题
既然不能做缓存,那没办法,我们需要自己维护一套”内存数据库“,数据如何组织就靠我们的算法功底了,比如哈希适合等于性的查找,
树结构适合”范围查找“,lucene适合字符串的查找,我们在添加和更新的时候同时维护自己的内存数据库,最终杜绝表关联,老同学,还
是先应急,把常用的表灌倒内存,如果真想项目好的话,改架构吧...
② 添加问题
或许你的Add操作还没有达到瓶颈这一步,如果真的达到了那就看情况来进行”表切分“,”数据库切分“吧,让用户的Add或者Update
操作分流,虽然做起来很复杂,但是没办法,总比用户纠纷强吧,可对...
二:二叉查找树
正式切入主题,从上面的说明我们知道了二叉树非常适合于范围查找,关于树的基本定义,这里我就默认大家都知道,我就直接从
查找树说起了。
1:定义
查找树的定义非常简单,一句话就是左孩子比父节点小,右孩子比父节点大,还有一个特性就是”中序遍历“可以让结点有序。
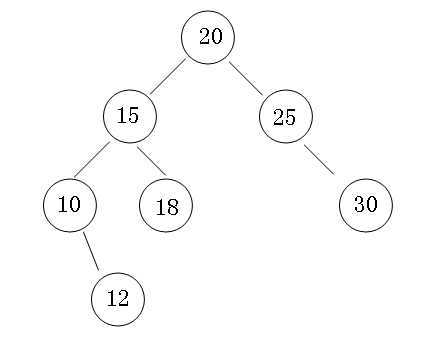
2:树节点
为了具有通用性,我们定义成泛型模板,在每个结点中增加一个”数据附加域”。
1 /// <summary> 2 /// 二叉树节点 3 /// </summary> 4 /// <typeparam name="K"></typeparam> 5 /// <typeparam name="V"></typeparam> 6 public class BinaryNode<K, V> 7 { 8 /// <summary> 9 /// 节点元素 10 /// </summary> 11 public K key; 12 13 /// <summary> 14 /// 节点中的附加值 15 /// </summary> 16 public HashSet<V> attach = new HashSet<V>(); 17 18 /// <summary> 19 /// 左节点 20 /// </summary> 21 public BinaryNode<K, V> left; 22 23 /// <summary> 24 /// 右节点 25 /// </summary> 26 public BinaryNode<K, V> right; 27 28 public BinaryNode() { } 29 30 public BinaryNode(K key, V value, BinaryNode<K, V> left, BinaryNode<K, V> right) 31 { 32 //KV键值对 33 this.key = key; 34 this.attach.Add(value); 35 36 this.left = left; 37 this.right = right; 38 } 39 }
3:添加
根据查找树的性质我们可以很简单的写出Add的代码,一个一个的比呗,最终形成的效果图如下
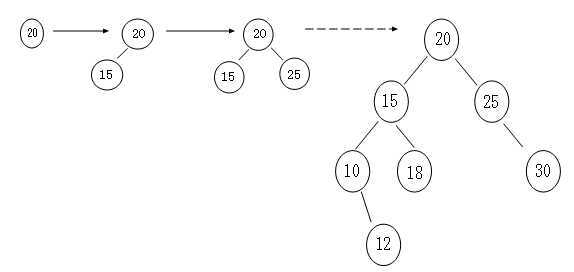
这里存在一个“重复节点”的问题,比如说我在最后的树中再插入一个元素为15的结点,那么此时该怎么办,一般情况下,我们最好
不要在树中再追加一个重复结点,而是在“重复节点"的附加域中进行”+1“操作。
1 #region 添加操作 2 /// <summary> 3 /// 添加操作 4 /// </summary> 5 /// <param name="key"></param> 6 /// <param name="value"></param> 7 public void Add(K key, V value) 8 { 9 node = Add(key, value, node); 10 } 11 #endregion 12 13 #region 添加操作 14 /// <summary> 15 /// 添加操作 16 /// </summary> 17 /// <param name="key"></param> 18 /// <param name="value"></param> 19 /// <param name="tree"></param> 20 /// <returns></returns> 21 public BinaryNode<K, V> Add(K key, V value, BinaryNode<K, V> tree) 22 { 23 if (tree == null) 24 tree = new BinaryNode<K, V>(key, value, null, null); 25 26 //左子树 27 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) < 0) 28 tree.left = Add(key, value, tree.left); 29 30 //右子树 31 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) > 0) 32 tree.right = Add(key, value, tree.right); 33 34 //将value追加到附加值中(也可对应重复元素) 35 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) == 0) 36 tree.attach.Add(value); 37 38 return tree; 39 } 40 #endregion
4:范围查找
这个才是我们使用二叉树的最终目的,既然是范围查找,我们就知道了一个”min“和”max“,其实实现起来也很简单,
第一步:我们要在树中找到min元素,当然min元素可能不存在,但是我们可以找到min的上界,耗费时间为O(logn)。
第二步:从min开始我们中序遍历寻找max的下界。耗费时间为m。m也就是匹配到的个数。
最后时间复杂度为M+logN,要知道普通的查找需要O(N)的时间,比如在21亿的数据规模下,匹配的元素可能有30个,那么最后
的结果也就是秒杀和几个小时甚至几天的巨大差异,后面我会做实验说明。
1 #region 树的指定范围查找 2 /// <summary> 3 /// 树的指定范围查找 4 /// </summary> 5 /// <param name="min"></param> 6 /// <param name="max"></param> 7 /// <returns></returns> 8 public HashSet<V> SearchRange(K min, K max) 9 { 10 HashSet<V> hashSet = new HashSet<V>(); 11 12 hashSet = SearchRange(min, max, hashSet, node); 13 14 return hashSet; 15 } 16 #endregion 17 18 #region 树的指定范围查找 19 /// <summary> 20 /// 树的指定范围查找 21 /// </summary> 22 /// <param name="range1"></param> 23 /// <param name="range2"></param> 24 /// <param name="tree"></param> 25 /// <returns></returns> 26 public HashSet<V> SearchRange(K min, K max, HashSet<V> hashSet, BinaryNode<K, V> tree) 27 { 28 if (tree == null) 29 return hashSet; 30 31 //遍历左子树(寻找下界) 32 if (min.CompareTo(tree.key) < 0) 33 SearchRange(min, max, hashSet, tree.left); 34 35 //当前节点是否在选定范围内 36 if (min.CompareTo(tree.key) <= 0 && max.CompareTo(tree.key) >= 0) 37 { 38 //等于这种情况 39 foreach (var item in tree.attach) 40 hashSet.Add(item); 41 } 42 43 //遍历右子树(两种情况:①:找min的下限 ②:必须在Max范围之内) 44 if (min.CompareTo(tree.key) > 0 || max.CompareTo(tree.key) > 0) 45 SearchRange(min, max, hashSet, tree.right); 46 47 return hashSet; 48 } 49 #endregion
5:删除
对于树来说,删除是最复杂的,主要考虑两种情况。
<1>单孩子的情况
这个比较简单,如果删除的节点有左孩子那就把左孩子顶上去,如果有右孩子就把右孩子顶上去,然后打完收工。
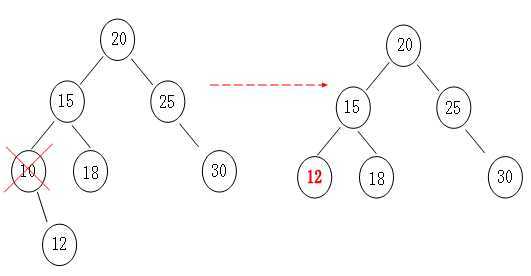
<2>左右都有孩子的情况。
首先可以这么想象,如果我们要删除一个数组的元素,那么我们在删除后会将其后面的一个元素顶到被删除的位置,如图
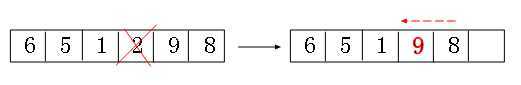
那么二叉树操作同样也是一样,我们根据”中序遍历“找到要删除结点的后一个结点,然后顶上去就行了,原理跟"数组”一样一样的。
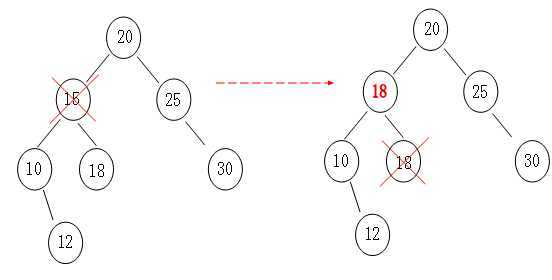
同样这里也有一个注意的地方,在Add操作时,我们将重复元素的值追加到了“附加域”,那么在删除的时候,就可以先判断是
不是要“-1”操作而不是真正的删除节点,其实这里也就是“懒删除”,很有意思。
1 #region 删除当前树中的节点 2 /// <summary> 3 /// 删除当前树中的节点 4 /// </summary> 5 /// <param name="key"></param> 6 /// <returns></returns> 7 public void Remove(K key, V value) 8 { 9 node = Remove(key, value, node); 10 } 11 #endregion 12 13 #region 删除当前树中的节点 14 /// <summary> 15 /// 删除当前树中的节点 16 /// </summary> 17 /// <param name="key"></param> 18 /// <param name="tree"></param> 19 /// <returns></returns> 20 public BinaryNode<K, V> Remove(K key, V value, BinaryNode<K, V> tree) 21 { 22 if (tree == null) 23 return null; 24 25 //左子树 26 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) < 0) 27 tree.left = Remove(key, value, tree.left); 28 29 //右子树 30 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) > 0) 31 tree.right = Remove(key, value, tree.right); 32 33 /*相等的情况*/ 34 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) == 0) 35 { 36 //判断里面的HashSet是否有多值 37 if (tree.attach.Count > 1) 38 { 39 //实现惰性删除 40 tree.attach.Remove(value); 41 } 42 else 43 { 44 //有两个孩子的情况 45 if (tree.left != null && tree.right != null) 46 { 47 //根据二叉树的中顺遍历,需要找到”有子树“的最小节点 48 tree.key = FindMin(tree.right).key; 49 50 //删除右子树的指定元素 51 tree.right = Remove(key, value, tree.right); 52 } 53 else 54 { 55 //单个孩子的情况 56 tree = tree.left == null ? tree.right : tree.left; 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 61 return tree; 62 } 63 #endregion
三:测试
假如现在我们有一张User表,我要查询"2012/7/30 4:30:00"到"2012/7/30 4:40:00"这个时间段登陆的用户,我在txt中生成一个
33w的userid和time的数据,看看在33w的情况下读取效率如何...
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Threading; 6 using System.IO; 7 using System.Diagnostics; 8 9 namespace DataStruct 10 { 11 class Program 12 { 13 static void Main(string[] args) 14 { 15 List<long> list = new List<long>(); 16 17 Dictionary<DateTime, int> dic = new Dictionary<DateTime, int>(); 18 19 BinaryTree<DateTime, int> tree = new BinaryTree<DateTime, int>(); 20 21 using (StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(Environment.CurrentDirectory + "//1.txt")) 22 { 23 var line = string.Empty; 24 25 while (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(line = sr.ReadLine())) 26 { 27 var userid = Convert.ToInt32(line.Split(new char[] { ‘,‘ }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries)[0]); 28 29 var time = Convert.ToDateTime(line.Split(new char[] { ‘,‘ }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries)[1]); 30 31 //防止dic出错,为了进行去重处理 32 if (!dic.ContainsKey(time)) 33 { 34 dic.Add(time, userid); 35 36 tree.Add(time, userid); 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 41 var min = Convert.ToDateTime("2012/7/30 4:30:00"); 42 43 var max = Convert.ToDateTime("2012/7/30 4:40:00"); 44 45 var watch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); 46 47 var result1 = dic.Keys.Where(i => i >= min && i <= max).Select(i => dic[i]).ToList(); 48 49 watch.Stop(); 50 51 Console.WriteLine("字典查找耗费时间:{0}ms,获取总数:{1}", watch.ElapsedMilliseconds, result1.Count); 52 53 watch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); 54 55 var result2 = tree.SearchRange(min, max); 56 57 watch.Stop(); 58 59 Console.WriteLine("二叉树耗费时间:{0}ms,获取总数:{1}", watch.ElapsedMilliseconds, result2.Count); 60 } 61 } 62 63 #region 二叉树节点 64 /// <summary> 65 /// 二叉树节点 66 /// </summary> 67 /// <typeparam name="K"></typeparam> 68 /// <typeparam name="V"></typeparam> 69 public class BinaryNode<K, V> 70 { 71 /// <summary> 72 /// 节点元素 73 /// </summary> 74 public K key; 75 76 /// <summary> 77 /// 节点中的附加值 78 /// </summary> 79 public HashSet<V> attach = new HashSet<V>(); 80 81 /// <summary> 82 /// 左节点 83 /// </summary> 84 public BinaryNode<K, V> left; 85 86 /// <summary> 87 /// 右节点 88 /// </summary> 89 public BinaryNode<K, V> right; 90 91 public BinaryNode() { } 92 93 public BinaryNode(K key, V value, BinaryNode<K, V> left, BinaryNode<K, V> right) 94 { 95 //KV键值对 96 this.key = key; 97 this.attach.Add(value); 98 99 this.left = left; 100 this.right = right; 101 } 102 } 103 #endregion 104 105 public class BinaryTree<K, V> where K : IComparable 106 { 107 public BinaryNode<K, V> node = null; 108 109 #region 添加操作 110 /// <summary> 111 /// 添加操作 112 /// </summary> 113 /// <param name="key"></param> 114 /// <param name="value"></param> 115 public void Add(K key, V value) 116 { 117 node = Add(key, value, node); 118 } 119 #endregion 120 121 #region 添加操作 122 /// <summary> 123 /// 添加操作 124 /// </summary> 125 /// <param name="key"></param> 126 /// <param name="value"></param> 127 /// <param name="tree"></param> 128 /// <returns></returns> 129 public BinaryNode<K, V> Add(K key, V value, BinaryNode<K, V> tree) 130 { 131 if (tree == null) 132 tree = new BinaryNode<K, V>(key, value, null, null); 133 134 //左子树 135 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) < 0) 136 tree.left = Add(key, value, tree.left); 137 138 //右子树 139 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) > 0) 140 tree.right = Add(key, value, tree.right); 141 142 //将value追加到附加值中(也可对应重复元素) 143 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) == 0) 144 tree.attach.Add(value); 145 146 return tree; 147 } 148 #endregion 149 150 #region 是否包含指定元素 151 /// <summary> 152 /// 是否包含指定元素 153 /// </summary> 154 /// <param name="key"></param> 155 /// <returns></returns> 156 public bool Contain(K key) 157 { 158 return Contain(key, node); 159 } 160 #endregion 161 162 #region 是否包含指定元素 163 /// <summary> 164 /// 是否包含指定元素 165 /// </summary> 166 /// <param name="key"></param> 167 /// <param name="tree"></param> 168 /// <returns></returns> 169 public bool Contain(K key, BinaryNode<K, V> tree) 170 { 171 if (tree == null) 172 return false; 173 //左子树 174 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) < 0) 175 return Contain(key, tree.left); 176 177 //右子树 178 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) > 0) 179 return Contain(key, tree.right); 180 181 return true; 182 } 183 #endregion 184 185 #region 树的指定范围查找 186 /// <summary> 187 /// 树的指定范围查找 188 /// </summary> 189 /// <param name="min"></param> 190 /// <param name="max"></param> 191 /// <returns></returns> 192 public HashSet<V> SearchRange(K min, K max) 193 { 194 HashSet<V> hashSet = new HashSet<V>(); 195 196 hashSet = SearchRange(min, max, hashSet, node); 197 198 return hashSet; 199 } 200 #endregion 201 202 #region 树的指定范围查找 203 /// <summary> 204 /// 树的指定范围查找 205 /// </summary> 206 /// <param name="range1"></param> 207 /// <param name="range2"></param> 208 /// <param name="tree"></param> 209 /// <returns></returns> 210 public HashSet<V> SearchRange(K min, K max, HashSet<V> hashSet, BinaryNode<K, V> tree) 211 { 212 if (tree == null) 213 return hashSet; 214 215 //遍历左子树(寻找下界) 216 if (min.CompareTo(tree.key) < 0) 217 SearchRange(min, max, hashSet, tree.left); 218 219 //当前节点是否在选定范围内 220 if (min.CompareTo(tree.key) <= 0 && max.CompareTo(tree.key) >= 0) 221 { 222 //等于这种情况 223 foreach (var item in tree.attach) 224 hashSet.Add(item); 225 } 226 227 //遍历右子树(两种情况:①:找min的下限 ②:必须在Max范围之内) 228 if (min.CompareTo(tree.key) > 0 || max.CompareTo(tree.key) > 0) 229 SearchRange(min, max, hashSet, tree.right); 230 231 return hashSet; 232 } 233 #endregion 234 235 #region 找到当前树的最小节点 236 /// <summary> 237 /// 找到当前树的最小节点 238 /// </summary> 239 /// <returns></returns> 240 public BinaryNode<K, V> FindMin() 241 { 242 return FindMin(node); 243 } 244 #endregion 245 246 #region 找到当前树的最小节点 247 /// <summary> 248 /// 找到当前树的最小节点 249 /// </summary> 250 /// <param name="tree"></param> 251 /// <returns></returns> 252 public BinaryNode<K, V> FindMin(BinaryNode<K, V> tree) 253 { 254 if (tree == null) 255 return null; 256 257 if (tree.left == null) 258 return tree; 259 260 return FindMin(tree.left); 261 } 262 #endregion 263 264 #region 找到当前树的最大节点 265 /// <summary> 266 /// 找到当前树的最大节点 267 /// </summary> 268 /// <returns></returns> 269 public BinaryNode<K, V> FindMax() 270 { 271 return FindMin(node); 272 } 273 #endregion 274 275 #region 找到当前树的最大节点 276 /// <summary> 277 /// 找到当前树的最大节点 278 /// </summary> 279 /// <param name="tree"></param> 280 /// <returns></returns> 281 public BinaryNode<K, V> FindMax(BinaryNode<K, V> tree) 282 { 283 if (tree == null) 284 return null; 285 286 if (tree.right == null) 287 return tree; 288 289 return FindMax(tree.right); 290 } 291 #endregion 292 293 #region 删除当前树中的节点 294 /// <summary> 295 /// 删除当前树中的节点 296 /// </summary> 297 /// <param name="key"></param> 298 /// <returns></returns> 299 public void Remove(K key, V value) 300 { 301 node = Remove(key, value, node); 302 } 303 #endregion 304 305 #region 删除当前树中的节点 306 /// <summary> 307 /// 删除当前树中的节点 308 /// </summary> 309 /// <param name="key"></param> 310 /// <param name="tree"></param> 311 /// <returns></returns> 312 public BinaryNode<K, V> Remove(K key, V value, BinaryNode<K, V> tree) 313 { 314 if (tree == null) 315 return null; 316 317 //左子树 318 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) < 0) 319 tree.left = Remove(key, value, tree.left); 320 321 //右子树 322 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) > 0) 323 tree.right = Remove(key, value, tree.right); 324 325 /*相等的情况*/ 326 if (key.CompareTo(tree.key) == 0) 327 { 328 //判断里面的HashSet是否有多值 329 if (tree.attach.Count > 1) 330 { 331 //实现惰性删除 332 tree.attach.Remove(value); 333 } 334 else 335 { 336 //有两个孩子的情况 337 if (tree.left != null && tree.right != null) 338 { 339 //根据二叉树的中顺遍历,需要找到”有子树“的最小节点 340 tree.key = FindMin(tree.right).key; 341 342 //删除右子树的指定元素 343 tree.right = Remove(tree.key, value, tree.right); 344 } 345 else 346 { 347 //单个孩子的情况 348 tree = tree.left == null ? tree.right : tree.left; 349 } 350 } 351 } 352 353 return tree; 354 } 355 #endregion 356 } 357 }

比普通的dictionary效率还仅仅是快11倍,从数量级来说还不是非常明显,为什么说不是非常明显,这是因为普通的查找树的时间复杂度
不是严格的log(N),在最坏的情况下会出现“链表”的形式,复杂度退化到O(N),比如下图。
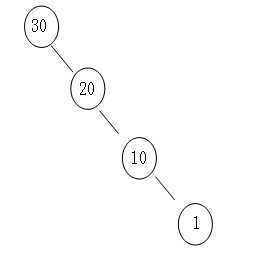
不过总会有解决办法的,下一篇我们继续聊如何旋转,保持最坏复杂度在O(logN)。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lonelyxmas/p/4228066.html