标签:
一、前言:
JDK为我们提供了很多Map接口的实现,使得我们可以方便地处理Key-Value的数据结构。
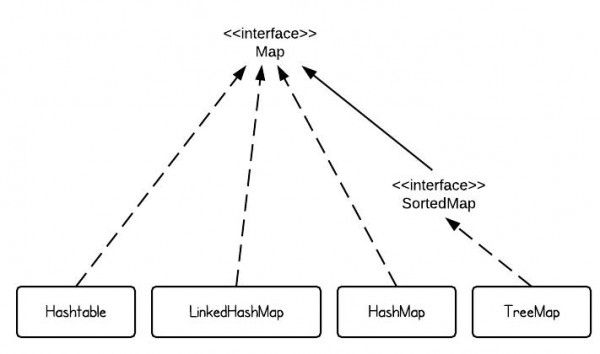
当我们希望快速存取<Key, Value>键值对时我们可以使用HashMap。
当我们希望在多线程并发存取<Key, Value>键值对时,我们会选择ConcurrentHashMap。
TreeMap则会帮助我们保证数据是按照Key的自然顺序或者compareTo方法指定的排序规则进行排序。
OK,那么当我们需要多线程并发存取<Key, Value>数据并且希望保证数据有序时,我们需要怎么做呢?
。。。。。。
也许,我们可以选择ConcurrentTreeMap。不好意思,JDK没有提供这么好的数据结构给我们。
当然,我们可以自己添加lock来实现ConcurrentTreeMap,但是随着并发量的提升,lock带来的性能开销也随之增大。
Don‘t cry......,JDK6里面引入的ConcurrentSkipListMap也许可以满足我们的需求。
JDK Documentation对ConcurrentSkipListMap的介绍

通过上面的介绍我们可以对ConcurrentSkipListMap中基本操作的时间复杂度有个基本的了解:
| Operation | Time Complexity |
| Insertion | O(log N) |
| Removal | O(log N) |
| Check if contains | O(log N) |
| Enumerate in order | O(N) |
二、ConcurrentSkipListMap实例:
1 import java.util.Iterator; 2 import java.util.NavigableSet; 3 import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentNavigableMap; 4 import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListMap; 5 6 public class ConcurrentSkipListMapExample { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 ConcurrentNavigableMap<String, String> concurrentSkipListMap = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<String, String>(); 9 concurrentSkipListMap.put("3", "Wednesday"); 10 concurrentSkipListMap.put("2", "Tuesday"); 11 concurrentSkipListMap.put("1", "Monday"); 12 concurrentSkipListMap.put("5", "Friday"); 13 concurrentSkipListMap.put("4", "Thursday"); 14 15 NavigableSet<String> navigableSet = concurrentSkipListMap.descendingKeySet(); 16 System.out.println("descendingKeySet: "); 17 Iterator<String> itr = navigableSet.iterator(); 18 while (itr.hasNext()) { 19 String s = itr.next(); 20 System.out.println(s); 21 } 22 System.out.println("ceilingEntry-2: " + concurrentSkipListMap.ceilingEntry("2")); 23 System.out.println("firstEntry: " + concurrentSkipListMap.firstEntry()); 24 System.out.println("lastEntry: " + concurrentSkipListMap.lastEntry()); 25 System.out.println("pollFirstEntry: " + concurrentSkipListMap.pollFirstEntry()); 26 System.out.println("now firstEntry: " + concurrentSkipListMap.firstEntry()); 27 System.out.println("pollLastEntry: " + concurrentSkipListMap.pollLastEntry()); 28 System.out.println("now lastEntry: " + concurrentSkipListMap.lastEntry()); 29 System.out.println("Entry-2: " + concurrentSkipListMap.get("2")); 30 } 31 32 }
三、ConcurrentSkipListMap性能测试:
下面,我们来比较一下ConcurrentSkipListMap与TreeMap在并发情况下查询的性能状况。
我们会启动n个线程随机读取Map中的记录,每个线程会读取106次。
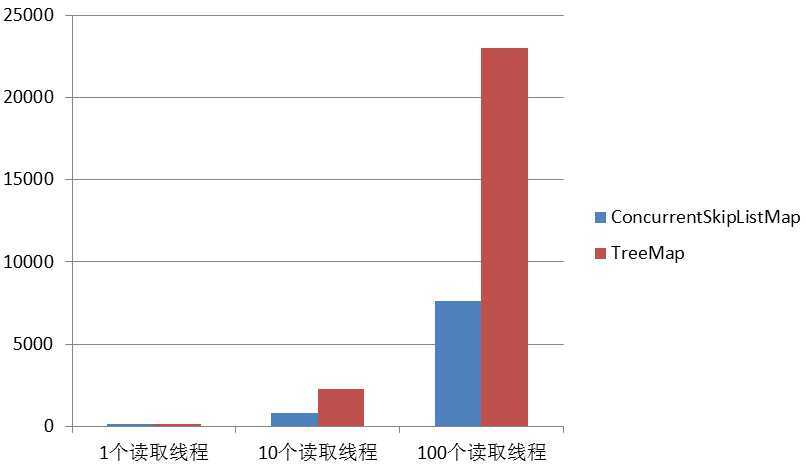
从测试结果,我们可以看出随着并发度的不断提高,ConcurrentSkipListMap相对于TreeMap的优势也越来越明显。
四、ConcurrentSkipListMap实现原理
未完,待续......(skiplist是什么样的数据结构,ConcurrentSkipListMap如何处理并发地操作)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/kaiblog/p/4231777.html