标签:
桥连模式:将抽象部分与实现部分分离,使它们都可以独立的变化。它是一种结构性模式,又称柄体(Handle and body)模式或者接口(Interface)模式。
类结构图:
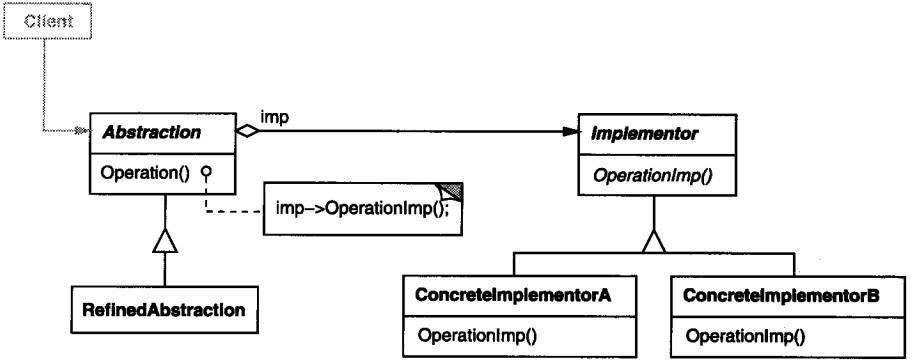
桥接模式效果:
Bridge模式有以下一些优点:
1) 分离接口及其实现部分 一个实现未必不变地绑定在一个接口上。抽象类的实现可以在运行时刻进行配置,一个对象甚至可以在运行时刻改变它的实现。将Abstraction与Implementor分离有助于降低对实现部分编译时刻的依赖性,当改变一个实现类时,并不需要重新编译 Abstraction类和它的客户程序。为了保证一个类库的不同版本之间的二进制兼容性,一定要有这个性质。另外,接口与实现分离有助于分层,从而产生更好的结构化系统,系统的高层部分仅需知道Abstraction和Implementor即可。
2) 提高可扩充性 你可以独立地对Abstraction和Implementor层次结构进行扩充。
3 ) 实现细节对客户透明 你可以对客户隐藏实现细节,例如共享 Implementor对象以及相应的引用计数机制(如果有的话) 。
<?php
class HandsetSoft{
function Run(){
}
}
class HandsetGame extends HandsetSoft{
function Run(){
print "Game\n";
}
}
class HandsetAddressList extends HandsetSoft{
function Run(){
print "Address List\n";
}
}
class HandsetBrand{
protected $m_soft;
function __construct(){
$this -> m_soft = null;
}
function SetHandset($temp){
$this -> m_soft = $temp;
}
function Run(){
}
}
class HandsetBrandM extends HandsetBrand{
function Run(){
if(!is_null($this -> m_soft)){
print "BrandM\n";
$this -> m_soft -> Run();
}
}
}
class HandsetBrandN extends HandsetBrand{
function Run(){
if(!is_null($this -> m_soft)){
print "BrandN\n";
$this -> m_soft -> Run();
}
}
}
$brand = new HandsetBrandM();
$game = new HandsetGame();
$brand -> SetHandset($game);
$brand -> Run();
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhutianpeng/p/4232154.html