http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1325
题意:
判断一个图是不是说树
只有树的根入度为 0 ,其余结点入度均为 1;
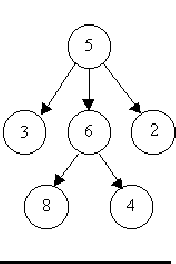
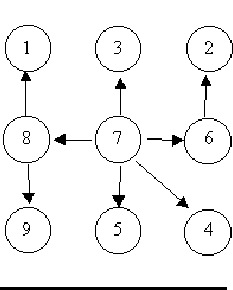
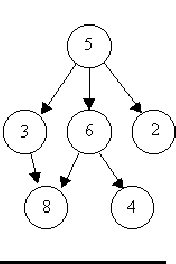
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4 5 6 0 0 8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5 7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0 3 8 6 8 6 4 5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0 -1 -1
Case 1 is a tree. Case 2 is a tree. Case 3 is not a tree.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
#define N 100010
bool used[N*10];
int queue[N];
int in[N];
int fa[N];
int findd(int x)
{
if (fa[x] == -1)
return x;
else
return fa[x] = findd(fa[x]);
}
void un(int n,int m)
{
int fx = findd(n);
int fy = findd(m);
if (fx != fy)
fa[fy] = fx;
}
int main()
{
int n, m, cases = 1;
memset(used,false,sizeof(used));
memset(in,0,sizeof(in));
memset(fa,-1,sizeof(fa));
bool ok = true; int num = 0;
while (scanf("%d %d", &n, &m) != EOF)
{
if (n == -1 && m == -1)
break;
else if (n == 0 && m == 0)
{
int num1 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
if (findd(queue[i]) != findd(queue[0]))
{
ok = false;
break;
}
if (in[queue[i]] == 0)
num1++;
if (in[queue[i]] > 1)
{
ok = false;
break;
}
}
if (num1 != 1)
ok = false;
if (num == 0)
ok = true;
if (ok)
printf("Case %d is a tree.\n",cases++);
else
printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n", cases++);
memset(used, false, sizeof(used));
memset(in, 0, sizeof(in));
memset(fa, -1, sizeof(fa));
ok = true, num = 0;
}
else
{
if (!used[n])
{
used[n] = true;
queue[num++] = n;
}
if (!used[m])
{
used[m] = true;
queue[num++] = m;
}
if (findd(n) == findd(m))
ok = false;
else
{
in[m]++;
un(n,m);
}
}
}
return 0;
}hdu-1325 & poj-1308 Is It A Tree?
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u014427196/article/details/43086419