标签:
When performing authentication, SSL uses a technique called public-key cryptography.
Public-key cryptography is based on the concept of a key pair, which consists of a public key and a private key. Data that has been encrypted with a public key can be decrypted only with the corresponding private key. Conversely, data that has been encrypted with a private key can be decrypted only with the corresponding public key.
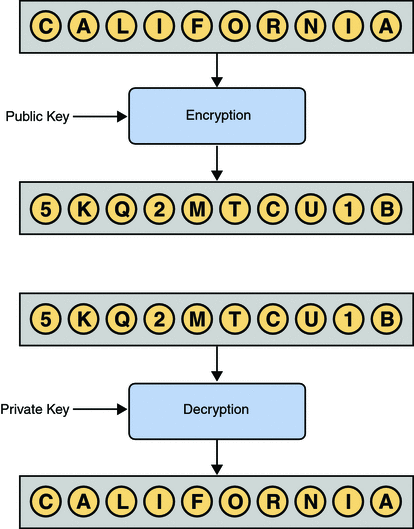
The owner of the key pair makes the public key available to anyone, but keeps the private key secret.
A certificate verifies that an entity is the owner of a particular public key.
Certificates that follow the X.509 standard contain a data section and a signature section. The data section includes such information as:
The Distinguished Name of the entity that owns the public key
The Distinguished Name of the entity that issued the certificate
The period of time during which the certificate is valid
The public key itself
You can obtain a certificate from a Certificate Authority (CA) such as VeriSign. Alternately, you can create a self-signed certificate, in which the owner and the issuer are the same.
An organization that issues certificates can establish a hierarchy of CAs. The root CA has a self-signed certificate. Each subordinate CA has a certificate that is signed by the next highest CA in the hierarchy. A certificate chain is the certificate of a particular CA, plus the certificates of any higher CAs up through the root CA.
Public Keys, Private Keys, and Certificates
标签:
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/opengl_es/article/details/43928793