标签:
Description

Input
Output
Sample Input
3 8 4 7 4 8
Sample Output
6 2 1
题意:队伍里面有f和m, 对于长度为L的队伍,可组成这样的队伍:fm, mf, mm, ff。如果存在 fmf 或 fff 这样的子队伍,就称队伍为O-queues,否则为E-queues。问长度为L的队伍里E-queues的数目模M是多少。
思路:因为假设F(N)为已经是E队列的个数, 那么有3种情况
1,在F(N-1)后加一个M
2,在F(N-3)后加MMF
3,在F(N-4)后加MMFF
所以得到递推公式:f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-3)+f(n-4);
数值较大,递推肯定会TLE,所以构造一个矩阵,用矩阵快速幂做。
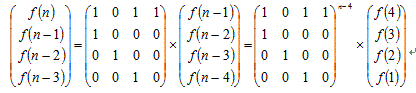
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
int mod;
int a[10];
struct node
{
int mp[5][5];
}init,res;
struct node Mult(struct node x,struct node y)
{
struct node tmp;
int i,j,k;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
for(j=0;j<4;j++){
tmp.mp[i][j]=0;
for(k=0;k<4;k++){
tmp.mp[i][j]=(tmp.mp[i][j]+x.mp[i][k]*y.mp[k][j])%mod;
}
}
return tmp;
};
struct node expo(struct node x,int k)
{
struct node tmp;
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
for(j=0;j<4;j++){
if(i==j)
tmp.mp[i][j]=1;
else
tmp.mp[i][j]=0;
}
while(k){
if(k&1) tmp=Mult(tmp,x);
x=Mult(x,x);
k>>=1;
}
return tmp;
};
int main()
{
int i,j,k;
while(~scanf("%d %d",&k,&mod)){
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
a[0]=0;a[1]=2;a[2]=4;a[3]=6;a[4]=9;
if(k<5){
printf("%d\n",a[k]%mod);
continue;
}
init.mp[0][0]=1;
init.mp[0][1]=0;
init.mp[0][2]=1;
init.mp[0][3]=1;
for(i=1;i<4;i++)
for(j=0;j<4;j++){
if(i==j+1)
init.mp[i][j]=1;
else
init.mp[i][j]=0;
}
res=expo(init,k-4);
int ans=0;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
ans=(ans+res.mp[0][i]*a[4-i])%mod;
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
标签:
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u013486414/article/details/44102337