标签:des c style blog a http
One of the most important use-case in any cloud is provisioning a VM . In
this article we shall do a walk through about an instance(VM) being provisioned
in a Openstack based cloud. This article deals with the request flow and the
component interaction of various projects under Openstack. The end result will
be booting up a VM.
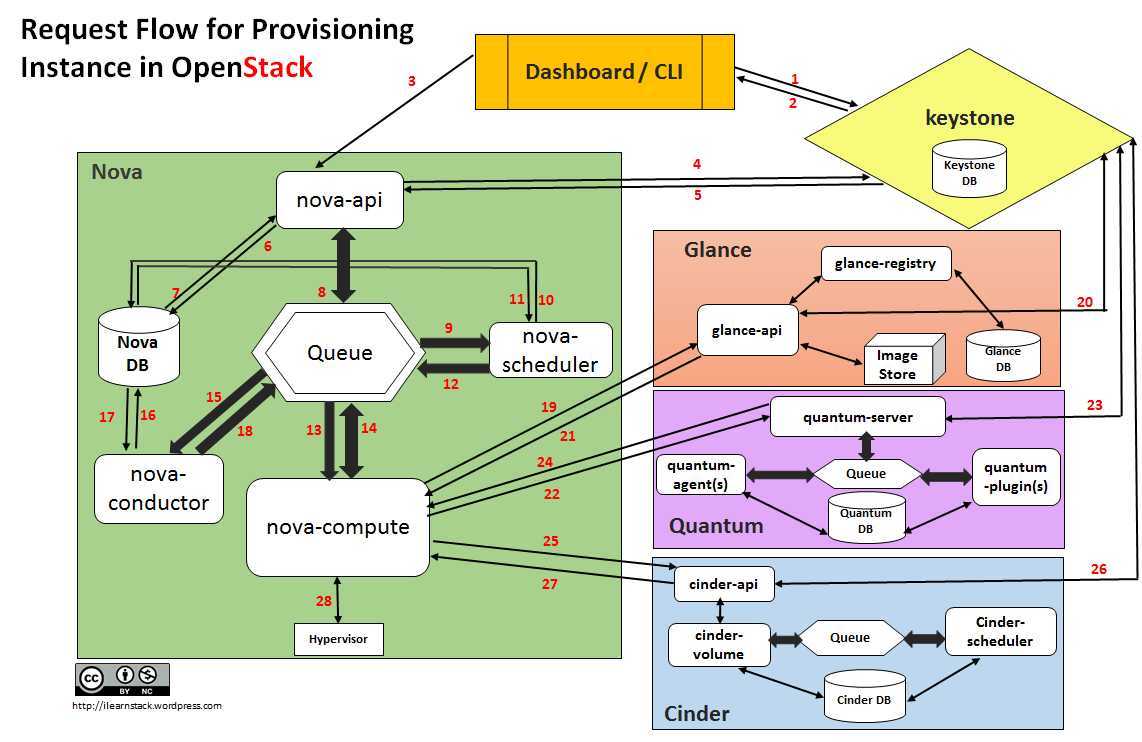
Provisioning a new instance involves the interaction between multiple
components inside OpenStack :
- CLI Command Line Interpreter for submitting commands to
OpenStack Compute.
- Dashboard (“Horizon”) provides the interface for all the
OpenStack services.
- Compute (“Nova”) retrieves virtual disks images(“Glance”)
, attach flavor and associated metadata and transforms end user API requests
into running instances.
- Network (“Quantum”) provides virtual networking for
Compute which allows users to create their own networks and then link them to
the instances.
- Block Storage (“Cinder”) provides persistent storage
volumes for Compute instances.
- Image (“Glance”) can store the actual virtual disk files
in the Image Store.
- Identity (“Keystone”) provides authentication and
authorization for all OpenStack services.
- Message Queue(“RabbitMQ”) handles the internal
communication within Openstack components such as Nova , Quantum and
Cinder.
The request flow for provisioning an Instance goes like this:
- Dashboard or CLI gets the user
credential and does the REST call to Keystone for
authentication.
- Keystone authenticate the credentials and generate &
send back auth-token which will be used for sending request to other
Components through REST-call.
- Dashboard or CLI convert the new
instance request specified in ‘launch instance’ or ‘nova-boot’ form to
REST API request and send it to nova-api.
- nova-api receive the request and sends the request for
validation auth-token and access permission to keystone.
- Keystone validates the token and sends updated auth
headers with roles and permissions.
- nova-api interacts with
nova-database.
- Creates initial db entry for new instance.
- nova-api sends the rpc.call request to
nova-scheduler excepting to get updated instance entry
with host ID specified.
- nova-scheduler picks the request from the
queue.
- nova-scheduler interacts with
nova-database to find an appropriate host via filtering and
weighing.
- Returns the updated instance entry with appropriate host ID after
filtering and weighing.
- nova-scheduler sends the rpc.cast request to
nova-compute for ‘launching instance’ on appropriate host
.
- nova-compute picks the request from the
queue.
- nova-compute send the rpc.call request to
nova-conductor to fetch the instance information such as host
ID and flavor( Ram , CPU ,Disk).
- nova-conductor picks the request from the
queue.
- nova-conductor interacts with
nova-database.
- Return the instance information.
- nova-compute picks the instance information from the
queue.
- nova-compute does the REST call by passing auth-token to
glance-api to get the Image URI by Image ID from glance
and upload image from image storage.
- glance-api validates the auth-token with
keystone.
- nova-compute get the image metadata.
- nova-compute does the REST-call by
passing auth-token to Network API to allocate and configure
the network such that instance gets the IP address.
- quantum-server validates the auth-token with
keystone.
- nova-compute get the network info.
- nova-compute does the REST call by passing auth-token to
Volume API to attach volumes to instance.
- cinder-api validates the auth-token
with keystone.
- nova-compute gets the block storage info.
- nova-compute generates data for
hypervisor driver and executes request on Hypervisor( via
libvirt or api).
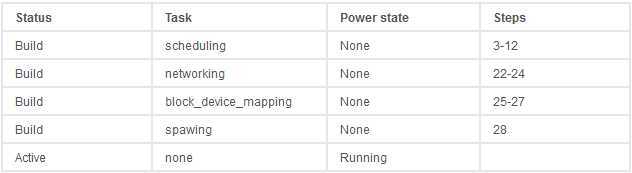
The table represents the Instance state at various steps during the
provisioning :
Request Flow for Provisioning Instance in Openstack,布布扣,bubuko.com
Request Flow for Provisioning Instance in Openstack
标签:des c style blog a http
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/forfuture1978/p/3765225.html