标签:
一句话:原型模式就是实现类的深度复制,而不是简单使用clone()。
1.直接用=只是复制了引用的地址,根本不算复制。
2.调用clone(),只保证引用的地址不同,该实例里面的对象(如果没实现clone)引用地址还是被直接复制(即里面回到了1的情况)。
public class 原型模式 { public static void main(String[] args) { //不使用clone来复制类 foo f1 = new foo(); System.out.println("f1: " + f1.i); foo f2 = f1; f2.i = 7; System.out.println("f1: " + f1.i);//可以看见原来的f1改变了 //使用clone来复制类 coo c1 = new coo(); coo c2 = (coo) c1.clone(); c2.i = 8; c2.s = "def"; c2.f.i = 10; System.out.println("c1: " + c1.i + " " + c1.s + " " + c1.f.i); System.out.println("c2: " + c2.i + " " + c2.s + " " + c2.f.i); } } class foo { public int i = 3; } class coo implements Cloneable{ public int i = 3; public String s = "abc"; public foo f = new foo(); @Override public Object clone() { Object obj = null; try { obj = super.clone(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return obj; } }
结果: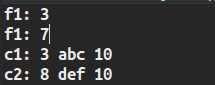
3.实现深度复制的方法
(1)不止被复制的对象要调用clone,该对象内部的属性也要实现clone()
public class 原型模式 { public static void main(String[] args) { //不使用clone来复制类 foo f1 = new foo(); System.out.println("f1: " + f1.i); foo f2 = f1; f2.i = 7; System.out.println("f1: " + f1.i);//可以看见原来的f1改变了 //使用clone来复制类 coo c1 = new coo(); coo c2 = (coo) c1.clone(); c2.i = 8; c2.s = "def"; c2.f.i = 5; System.out.println("c1: " + c1.i + " " + c1.s + " " + c1.f.i); System.out.println("c2: " + c2.i + " " + c2.s + " " + c2.f.i); } } class foo implements Cloneable{ public int i = 3; @Override public Object clone() { Object obj = null; try { obj = super.clone(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return obj; } } class coo implements Cloneable{ public int i = 3; public String s = "abc"; public foo f = new foo(); @Override public Object clone() { coo temp = new coo(); try { temp.i = i; temp.s = s; temp.f = (foo) f.clone(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return temp; } }
(2)利用序列化
public class 原型模式 { public static void main(String[] args) { //不使用clone来复制类 foo f1 = new foo(); System.out.println("f1: " + f1.i); foo f2 = f1; f2.i = 7; System.out.println("f1: " + f1.i);//可以看见原来的f1改变了 //使用clone来复制类 coo c1 = new coo(); coo c2 = c1.deepCopy(); c2.i = 8; c2.s = "def"; c2.f.i = 5; System.out.println("c1: " + c1.i + " " + c1.s + " " + c1.f.i); System.out.println("c2: " + c2.i + " " + c2.s + " " + c2.f.i); } } class foo implements Serializable{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public int i = 3; } class coo implements Serializable{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 3742135905473578347L; public int i = 3; public String s = "abc"; public foo f = new foo(); public coo deepCopy() { try { ByteArrayOutputStream buf = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream o = new ObjectOutputStream(buf); o.writeObject(this); ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(buf.toByteArray())); return (coo)in.readObject(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }
结果同上。
总结:原型模式 <==> (深度)复制。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/programmer-kaima/p/4356749.html