标签:style blog http color strong width
A、确定性数学计算,水,读题要快

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 int N,d; 6 int main(){ 7 while(~scanf("%d%d",&N,&d)){ 8 int cnt=0; 9 for(int i=0;i<N;i++){ 10 int t; 11 scanf("%d",&t); 12 cnt+=t; 13 } 14 if (cnt+(N-1)*10>d){ 15 printf("-1\n");continue; 16 } 17 int ans=(N-1)*10/5+(d-(cnt+(N-1)*10))/5; 18 cout<<ans<<endl; 19 20 } 21 return 0; 22 }
B、贪心,章节少的课先学,排序+贪心+long long 处理细节

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #include<stdlib.h> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 int n,s; 8 int a[100005]; 9 10 int main(){ 11 while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&s)){ 12 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); 13 sort(a,a+n); 14 long long ans=0; 15 s++; 16 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 17 if (s>1) s--; 18 ans+=(long long)s*a[i];//在s前面加了long long 就过了,伤不起,应该是要强制转化成long long,不然后面两个int计算只保留了int部分 19 } 20 cout<<ans<<endl; 21 } 22 return 0; 23 }
注意:ans+=(long long)s*a[i];//在s前面加了long long 就过了,伤不起,应该是要强制转化成long long,不然后面两个int计算只保留了int部分
C、确定性数学证明(奇偶证明)+策略模拟 (很容易粗)
我的写法还是不是很好,下标算来算去,这道题一定要考虑到p-k==0的情况,不然会出错,
给自己出数据的时候,没有考虑到这个情况,比赛的时候可能就会跪了

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 int n,k,p,d;//p个偶数组合 6 int a[100006],b[100006]; 7 int main() 8 { 9 while(~scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&k,&p)){ 10 int cnt1=0,cnt2=0; 11 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 12 int num; 13 scanf("%d",&num); 14 if (num % 2 == 0) a[cnt1++]=num;else b[cnt2++]=num; 15 } 16 int p1=p,p2=k-p; 17 if (cnt1+cnt2/2<p1){ 18 cout<<"NO"<<endl; 19 continue; 20 } 21 if (cnt1>=p1){ 22 if (cnt2<p2 || cnt2 % 2 != p2 % 2){ 23 cout<<"NO"<<endl; 24 continue; 25 } 26 cout<<"YES"<<endl; 27 if (p2>0){ 28 for(int i=0;i<p1;i++){ 29 cout<<1<<" "<<a[i]<<endl; 30 } 31 cnt1=cnt1-p1; 32 cout<<cnt1+(cnt2-p2)+1<<" "; 33 for(int i=p1;i<p1+cnt1;i++){ 34 cout<<a[i]<<" "; 35 } 36 for(int i=0;i<(cnt2-p2)+1;i++){ 37 if (i==cnt2-p2){ 38 cout<<b[i]<<endl; 39 }else cout<<b[i]<<" "; 40 } 41 for(int i=cnt2-p2+1;i<cnt2;i++){ 42 cout<<1<<" "<<b[i]<<endl; 43 } 44 }else{ 45 cout<<cnt1-p1+1+cnt2; 46 for(int i=0;i<cnt1-p1+1;i++) cout<<" "<<a[i]; 47 for(int i=0;i<cnt2;i++) cout<<" "<<b[i]; 48 cout<<endl; 49 for(int i=cnt1-p1+1;i<cnt1;i++){ 50 cout<<1<<" "<<a[i]<<endl; 51 } 52 } 53 54 continue; 55 }else { 56 if (cnt2-(p1-cnt1)*2<p2 || (cnt2-(p1-cnt1)*2) % 2 != p2 %2 ){ 57 cout<<"NO"<<endl; 58 continue; 59 } 60 cout<<"YES"<<endl; 61 for(int i=0;i<cnt1;i++){ 62 cout<<1<<" "<<a[i]<<endl; 63 } 64 65 d=0; 66 if (p2>0){//这里是个大坑 67 for(int i=cnt1;i<p1;i++){ 68 cout<<2<<" "<<b[d++]<<" "<<b[d++]<<endl; 69 } 70 }else {//p2==0 71 for(int i=cnt1;i<p1-1;i++){ 72 cout<<2<<" "<<b[d++]<<" "<<b[d++]<<endl; 73 } 74 cout<<cnt2-d<<" "; 75 for(int i=d;i<cnt2;i++){ 76 if (i==cnt2-1) cout<<b[i]<<endl;else cout<<b[i]<<" "; 77 d++; 78 } 79 } 80 if (cnt2==d) continue; 81 if (cnt2 - d > p2){ 82 83 cout<<cnt2-d-p2+1<<" "; 84 for(int i=d;i<cnt2-p2+1;i++){ 85 if (i==cnt2-p2){ 86 cout<<b[i]<<endl; 87 }else { 88 cout<<b[i]<<" "; 89 } 90 } 91 for(int i=cnt2-p2+1;i<cnt2;i++) cout<<1<<" "<<b[i]<<endl; 92 }else {//cnt2-d==p2 93 for(int i=d;i<cnt2;i++) cout<<1<<" "<<b[i]<<endl; 94 } 95 } 96 } 97 return 0; 98 99 }
D、三分搜索+贪心+枚举(也可以排序+二分搜索(优化1/2的常数))
题目描述:给定A数组,n个数,给定B数组,m个数,
定义操作:一次任选数组,任选一个元素,可以增大或减少;
求一个最小操作数,使得改变后,A中最小的元素a大于等于B中最大的元素b。
方法就是上面所说的:
1、三分F(X):假设最终a=b=x,注意a和b肯定相等,因为我们是向中间取数的。不等没有相等步数少。
这样能确定x的范围,min(A)到max(B),因为我们肯定是增大A中元素,减小B中元素。
但是我不能证明是凹性的函数啊!!!
2、选定x,贪心的策略就定下来了:
if (a[i]<x) ans+=x-a[i];//尽可能用最小的步数达成目的
3、三分写法再总结:
(1)用t控制次数,不写while
(2)最终在[l,r]的范围内找到极值
(3)注意画图,尽可能地包含极值点
下面是别人的证明:
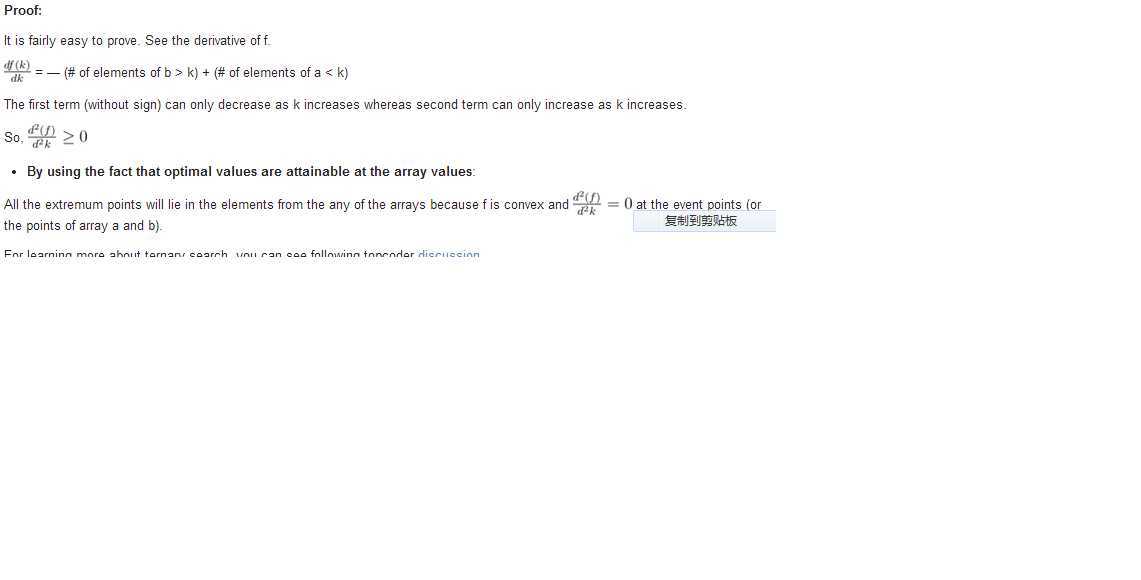

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #include<stdlib.h> 5 #define LL long long 6 using namespace std; 7 int n,m; 8 LL a[100005],b[100005]; 9 LL F(LL x) 10 { 11 //将A数组中的变成至少为x;(增加) 12 LL ans=0; 13 for(int i=0; i<n; i++) //可二分优化 14 { 15 if (a[i]<x) ans+=x-a[i]; 16 } 17 //将A数组中的变成最多为x;(减少) 18 for(int i=0; i<m; i++) 19 { 20 if (b[i]>x) ans+=b[i]-x; 21 } 22 return ans; 23 } 24 int main() 25 { 26 // freopen("out.txt","w",stdout); 27 while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)) 28 { 29 LL Min=1e12,Max=-1; 30 for(int i=0; i<n; i++) 31 { 32 scanf("%I64d",&a[i]); 33 Min=min(Min,a[i]); 34 } 35 for(int i=0; i<m; i++) 36 { 37 scanf("%I64d",&b[i]); 38 Max=max(Max,b[i]); 39 } 40 sort(a,a+n); 41 sort(b,b+m); 42 LL l=Min-1,r=Max+1; 43 for(int i=0; i<100; i++) 44 { 45 int m1=l+(r-l)/3,m2=r-(r-l)/3; 46 if (F(m1)<F(m2)) r=m2; 47 else l=m1; 48 } 49 LL ans=F(l); 50 for(LL i=l;i<=r;i++) ans=min(ans,F(i)); 51 cout<<ans<<endl; 52 } 53 return 0; 54 }
E、dp(关键是记忆化的思想)+乘法逆(数学考得好啊)
ps:题解:http://codeforces.com/blog/praveen123
推导过程太精妙了
暂时超时的代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #define LL long long 5 #define Mod 1000000007 6 LL d[100005]; 7 LL Jie[100005]; 8 using namespace std; 9 void gcd(LL a,LL b,LL& d,LL& x,LL& y){ 10 if (!b){d=a;x=1;y=0;} 11 else {gcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);y-=x*(a/b);} 12 } 13 LL inv(LL a,LL n){ 14 LL d,x,y; 15 gcd(a,n,d,x,y); 16 return d==1?(x+n)%n:-1; 17 } 18 void init(){//生成C[x,f]的数表,n是最大范围 19 Jie[0]=1; 20 for(int i=1;i<=100005;i++) 21 Jie[i]=(Jie[i-1]*i)%Mod; 22 } 23 LL calC(int n,int r){ 24 LL ans=Jie[n]; 25 LL k=Jie[r] * Jie[n-r];k=k%Mod; 26 return (ans * inv(k,Mod)) % Mod; 27 } 28 LL dp(int n,int f){ 29 // cout<<"n="<<n<<","<<"f="<<f<<endl; 30 if (n<f) return 0; 31 if (n==f) return 1; 32 if (d[n]!=-1) return d[n]; 33 LL ans=calC(n-1,f-1);//得到C(n-1,f-1) //隔板法 34 LL sum=0; 35 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){ 36 if (n % i == 0) sum+=dp(n/i,f); 37 sum=sum % Mod; 38 } 39 ans=(ans-sum + Mod) % Mod; 40 return d[n]=ans; 41 } 42 int main(){ 43 init(); 44 int n,f,t; 45 scanf("%d",&t); 46 while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&f)){ 47 if (n<f){ 48 cout<<0<<endl; 49 continue; 50 } 51 memset(d,-1,sizeof(d)); 52 LL ans=dp(n,f); 53 cout<<ans<<endl; 54 } 55 return 0; 56 }
*Codeforces Round #251 (Div. 2)AK),布布扣,bubuko.com
*Codeforces Round #251 (Div. 2)AK)
标签:style blog http color strong width
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/little-w/p/3769864.html