标签:
◆i :如果在修饰符中加上"i",则正则将会取消大小写敏感性,即"a"和"A" 是一样的。
◆m:默认的正则开始"^"和结束"$"只是对于正则字符串如果在修饰符中加上"m",那么开始和结束将会指字符串的每一行:每一行的开头就是"^",结尾就是"$"。
◆s:如果在修饰符中加入"s",那么默认的"."代表除了换行符以外的任何字符将会变成任意字符,也就是包括换行符!
◆x:如果加上该修饰符,表达式中的空白字符将会被忽略,除非它已经被转义。
◆e:本修饰符仅仅对于replacement有用,代表在replacement中作为PHP代码。
◆A:如果使用这个修饰符,那么表达式必须是匹配的字符串中的开头部分。比如说"/a/A"匹配"abcd"。
◆E:与"m"相反,如果使用这个修饰符,那么"$"将匹配绝对字符串的结尾,而不是换行符前面,默认就打开了这个模式。
◆U:和问号的作用差不多,用于设置"贪婪模式"。
如[\w]{3,5}或者[\w]*或者[\w]+这些[\w]后面的符号都表示限定符
* 匹配前面的子表达式零次或多次。例如,zo* 能匹配 "z" 以及 "zoo"。* 等价于{0,}。请注意在逗号和两个数之间不能有空格。
$regex = ‘/^http:\/\/([\w.]+)\/([\w]+)\/([\w]+)\.html$/i‘;$str = ‘http://www.youku.com/show_page/id_ABCDEFG.html‘;$matches = array();if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ var_dump($matches);}echo "\n"; |
preg_match中的$matches[0]将包含与整个模式匹配的字符串。
使用"#"定界符的代码如下.这个时候对"/"就不转义!
$regex = ‘#^http://([\w.]+)/([\w]+)/([\w]+)\.html$#i‘;$str = ‘http://www.youku.com/show_page/id_ABCDEFG.html‘;$matches = array();if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ var_dump($matches);}echo "\n"; |
¤ 修饰符:用于改变正则表达式的行为。
我们看到的(‘/^http:\/\/([\w.]+)\/([\w]+)\/([\w]+)\.html/i‘)中的最后一个"i"就是修饰符,表示忽略大小写,还有一个我们经常用到的是"x"表示忽略空格。
贡献代码:
$regex = ‘/HELLO/‘;$str = ‘hello word‘;$matches = array();if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ echo ‘No i:Valid Successful!‘,"\n";}if(preg_match($regex.‘i‘, $str, $matches)){ echo ‘YES i:Valid Successful!‘,"\n";} |
¤ 字符域:[\w]用方括号扩起来的部分就是字符域。
¤ 限定符:如[\w]{3,5}或者[\w]*或者[\w]+这些[\w]后面的符号都表示限定符。现介绍具体意义。
{3,5}表示3到5个字符。{3,}超过3个字符,{,5}最多5个,{3}三个字符。
* 表示0到多个
+ 表示1到多个。
¤ 脱字符号
^:
> 放在字符域(如:[^\w])中表示否定(不包括的意思)——“反向选择”
> 放在表达式之前,表示以当前这个字符开始。(/^n/i,表示以n开头)。
注意,我们经常管"\"叫"跳脱字符"。用于转义一些特殊符号,如".","/"
$regex = ‘/(?<=c)d(?=e)/‘; /* d 前面紧跟c, d 后面紧跟e*/$str = ‘abcdefgk‘;$matches = array();if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ var_dump($matches);}echo "\n"; |
否定意义:
$regex = ‘/(?<!c)d(?!e)/‘; /* d 前面不紧跟c, d 后面不紧跟e*/$str = ‘abcdefgk‘;$matches = array();if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ var_dump($matches);}echo "\n"; |
$regex = ‘/HE(?=L)LO/i‘;$str = ‘HELLO‘;$matches = array();if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ var_dump($matches);}echo "\n"; |
打印不出结果!
$regex = ‘/HE(?=L)LLO/i‘;$str = ‘HELLO‘;$matches = array();if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ var_dump($matches);}echo "\n"; |
能打印出结果!
说明:(?=L)意思是HE后面紧跟一个L字符。但是(?=L)本身不占字符,要与(L)区分,(L)本身占一个字符。
$regex = ‘/^(Chuanshanjia)[\w\s!]+\1$/‘; $str = ‘Chuanshanjia thank Chuanshanjia‘;$matches = array();if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ var_dump($matches);}echo "\n"; |
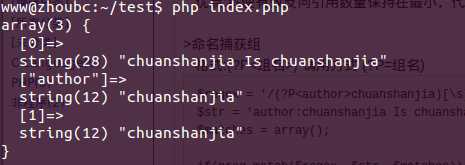
$regex = ‘/(?P<author>chuanshanjia)[\s]Is[\s](?P=author)/i‘;$str = ‘author:chuanshanjia Is chuanshanjia‘;$matches = array();if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ var_dump($matches);}echo "\n"; |
运行结果
惰性匹配(记住:会进行两部操作,请看下面的原理部分)
格式:限定符?
原理:"?":如果前面有限定符,会使用最小的数据。如“*”会取0个,而“+”会取1个,如过是{3,5}会取3个。
先看下面的两个代码:
代码1.
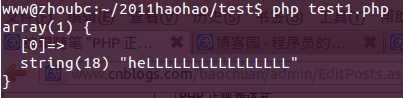
<?php$regex = ‘/heL*/i‘;$str = ‘heLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLL‘;if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ var_dump($matches);}echo "\n"; |
结果1.
代码2
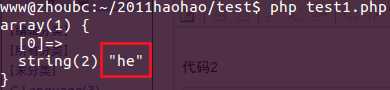
<?php$regex = ‘/heL*?/i‘;$str = ‘heLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLL‘;if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ var_dump($matches);}echo "\n"; |
结果2
代码3,使用“+”
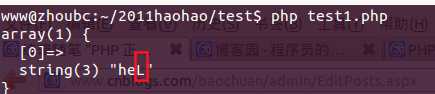
<?php$regex = ‘/heL+?/i‘;$str = ‘heLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLL‘;if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ var_dump($matches);}echo "\n"; |
结果3
代码4,使用{3,5}
<?php$regex = ‘/heL{3,10}?/i‘;$str = ‘heLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLL‘;if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ var_dump($matches);}echo "\n"; |
结果4
$regex = ‘/ ^host=(?<!\.)([\d.]+)(?!\.) (?#主机地址)\| ([\w!@#$%^&*()_+\-]+) (?#用户名)\| ([\w!@#$%^&*()_+\-]+) (?#密码)(?!\|)$/ix‘;$str = ‘host=192.168.10.221|root|123456‘;$matches = array();if(preg_match($regex, $str, $matches)){ var_dump($matches);}echo "\n"; |
| 特殊字符 | 解释 |
| * | 0到多次 |
| + | 1到多次还可以写成{1,} |
| ? | 0或1次 |
| . | 匹配除换行符外的所有单个的字符 |
| \w | [a-zA-Z0-9_] |
| \s | 空白字符(空格,换行符,回车符)[\t\n\r] |
| \d | [0-9] |
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/havoe/p/4376620.html