标签:
------- android培训、java培训、iOS培训 期待与您交流! ----------
(由于博客园屏蔽了超链接所以地址发在这里:http://www.itheima.com)
今天咱俩来絮叨絮叨程序猿挂在嘴边面向对象的三大特性。Object-C既然也是面向对象的,那她肯定是具备这三大特性喽!话说这三大特性到底是什么呢?
面向对象的三大特性:封装、继承、多态。
接下来,咱们就开始叨叨一下,首先从封装开始。
封装,什么是封装?为什么要封装或者说封装的好处有哪些呢?
封装:封装就是将对象具有的一些属性和方法通过封装打包到一起,共同体现一个事物的特征。为什么要封装?因为对象也是隐私的,没有人希望外界能知道自己的隐私,所以为了确保对象(爱人)在外界的良好形象就要保护好对象的隐私(对于人来说),那么对于程序来说,让别人知道的隐私越少,暴露出来的bug也能越少。当然隐私有时候也不是绝对的,比如有些事情对于家人就不算隐私,对同事,同学就完全算是隐私。总不能天天把自家的大门开着,谁想进就进。怎么滴咱也要按把锁,阔气点再找个门卫啥的,让谁进让谁不进,钥匙给不给谁,当然你是看情况而定喽。
Object-C中的成员变量使用了@public、@protected、@private作为访问修饰符,默认的是@protected(类访问和子类访问)。Object-C中只有成员变量有访问修饰符,类变量、类方法、成员方法是没有访问修饰符的,所有的方法都是@public,所有的类变量都是@private。
由于@public的成员可以被随意赋值,就像我家的大门像谁都开着,你想拿啥就拿啥,甚至在里面吃喝拉撒,当然这只是个比喻。为了避免这一情况的发生。我们应该使用set方法和get方法来管理成员的访问。
接下来我们就说说set、get方法。
set方法
作用:用来设置成员变量,可以在方法里面过滤掉一些不合理的值
命名规范:
方法都是以set开头,而且后面跟上成员变量名,成员变量名的首字母必须大写
形参名称不要跟成员变量同名
作用:返回对象内部的成员变量
命名规范:get方法的名称一般就跟成员变量同名
成员变量都以下划线 _ 开头,可以跟get方法的名称区分开,可以跟其他局部变量区分开,一看到下划线开头的变量,肯定是成员变量。
下面,我写一个学生类作为例子??,这个学生类很简单,只有一个属性:年龄,一个行为:学习。下面来看看代码:
1 /**
2 定义一个Student类
3 属性:年龄
4 行为:学习
5 */
6 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
7 //声明Student类
8 @interface Student : NSObject
9 {
10 int _age;//成员变量年龄
11 }
12
13 //成员变量age 对外提供的set方法。
14 - (void)setAge:(int)age;
15 //成员变量age,对外提供的get方法。
16 - (int)age;
17 - (void)study;
18 @end
19
20 //实现
21 @implementation Student
22
23 - (void)study
24 {
25 NSLog(@"%d岁的学生好好学习撒!",age);
26 }
27 - (void)setAge:(int)age
28 {//对年龄小于0岁的进行过滤。
29 if(age >= 0)
30 {
31 _age = age;
32 }else
33 {
34 _age = 1;
35 }
36
37 }
38 //age 的get方法
39 - (int)age
40 {
41 return _age;
42 }
43 @end
44
45 int main()
46 {
47 Student *stu = [Student new];
48 //使用set方法将age设置为25
49 [stu setAge:25];
50 [stu study];
51
52 NSLog(@"学生的年龄是%d",[stu age]);
53 return 0;
54
55 }
运行结果如下:
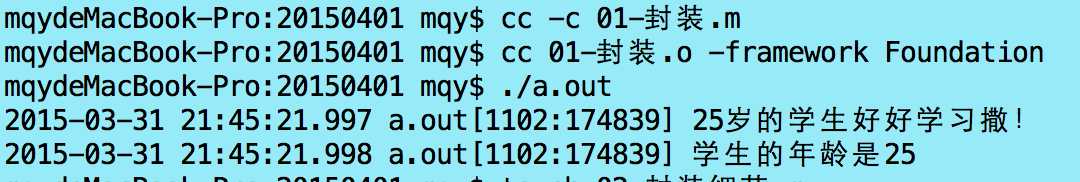 从上面的代码咱们就能简单的认识到封装的好处:1.可以过滤不不合理的值。2.屏蔽内部的赋值过程,不对外体现。3.让外界不必关心内部的细节。就像你要开车,你直接开就行,你不必关系发动机轮胎是怎么协同工作的。
从上面的代码咱们就能简单的认识到封装的好处:1.可以过滤不不合理的值。2.屏蔽内部的赋值过程,不对外体现。3.让外界不必关心内部的细节。就像你要开车,你直接开就行,你不必关系发动机轮胎是怎么协同工作的。
下面继续以学生类来拓展:如下:
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
2 /*
3 成员变量的命名规范:1.一定以_下划线开头
4
5 好处:
6 1.让成员变量和get方法的名称区分开来,
7 2.和局部变量区分开来
8 **/
9 typedef enum
10 {
11 Sexman,
12 Sexwoman
13 } SEX;
14 @interface Student:NSObject
15 {
16 SEX _sex ;
17 int _no ;
18
19 //sex 的get set 方法
20 - (void)setSex:(SEX)sex;
21 - (SEX)sex;
22
23 //no的set get方法
24 - (void)setNo:(int)no ;
25 - (int)no;
26 @end
27
28 @implementation Student
29 - (void)setSex:(SEX)sex
30 {
31 _sex = sex;
32 }
33
34 - (SEX)sex
35 {
36 return _sex;
37 }
38
39 - (void)setNo:(int)no
40 {
41 _no = no;
42 }
43 - (int)no
44 {
45 return _no;
46 }
47 @end
48
49 int main()
50 {
51 Student *stu = [Student new];
52 [stu setSex:Sexwoman];
53 [stu setNo:15];
54 NSLog(@"学生的性别是:%d,学号是%d",[stu sex],[stu no]);
55 }
下面做一个小练习来巩固今天的知识点:
1 /*
2 设计一个成绩类
3 属性:c语言成绩
4 oc成绩
5 ios成绩
6
7 行为:
8 1.比较C语言成绩:跟另外一个成绩对象比较C语言成绩,返回成绩差的。
9 2.比较OC
10 3.比较IOS成绩
11 4.计算总分
12 5计算平均分
13
14 */
15 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
16
17 //声明成绩类
18 @interface Score:NSObject
19 {
20 int _cScore;//c语言成绩
21 int _ocScore;//oc成绩
22 int _iosScore;//ios成绩
23 int _totalScore;//总分
24 int _avgScore;//平均分
25 }
26 //声明_cScore 的set get方法
27 - (void)setCScoer:(int)cScore;
28 - (int)cScore;
29 //声明_ocScore 的set get方法
30 - (void)setOcScore:(int)ocScore;
31 - (int)ocScore;
32 //声明_iosScore 的set get方法
33 - (void)setIosScore:(int)iosScore;
34 - (int)iosScore;
35 //总分的get方法
36 - (int)totalScore;
37 //平均分的get方法
38 - (int)avgScore;
39 //比较c语言
40 - (int)compareScoreWithC:(int)cScore andWithOther:(int)otherScoer;
41
42 @end
43
44 //实现Score类
45 @implementation Score
46 //c实现 get set方法
47 - (void)setCScoer:(int)cScore
48 {
49 _cScore = cScore;
50 }
51 - (int)cScore
52 {
53 return _cScore;
54 }
55
56 //oc get set方法
57
58 - (void)setOcScore:(int)ocScore
59 {
60 _ocScore = ocScore;
61 }
62
63 - (int)ocScore
64 {
65 return _ocScore;
66 }
67
68 //ios get set方法
69
70 - (void)setIosScore:(int)iosScore
71 {
72 _iosScore = iosScore;
73 }
74 - (int)iosScore
75 {
76 return _iosScore;
77 }
78
79 - (int)compareScoreWithC:(int)cScore andWithOther:(int)otherScoer
80 {
81 return cScore - otherScoer;
82 }
83 //总分的get方法
84 - (int)totalScore
85 {
86 return _cScore + _ocScore + _iosScore;
87 }
88 //平均分的get方法
89 - (int)avgScore
90 {
91 return (_cScore + _ocScore + _iosScore)/3 ;
92 }
93 @end
94
95 int main()
96 {
97 Score *s1 = [Score new];
98 [s1 setCScoer:80];
99 [s1 setOcScore:85];
100 [s1 setIosScore:90];
101 NSLog(@"C语言成绩和OC成绩的差是:%d,C语言和IOS成绩的差是:%d,三门成绩总和是:%d,平均分是:%d",[s1 compareScoreWithC: [s1 cScore] andWithOther: [s1 ocScore]],[s1 compareScoreWithC: [s1 cScore] andWithOther: [s1 iosScore]],[s1 totalScore],[s1 avgScore]);
102
103 }
运行结果如下图:

好啦!封装咱们就先暂时叨bi到这里了。下一回合,咱去bibi一下继承如何?( ̄▽ ̄)。就这么结束好像不礼貌啊!借用少安叔的一句话:感谢党!??。
------- android培训、java培训、iOS培训 期待与您交流! ----------
黑马程序员--03.Object-C--揭开三大特性的神秘面纱之封装
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/741162830qq/p/4383191.html