标签:
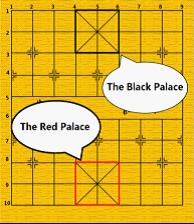
 General: the generals can move and capture one point either vertically or horizontally and cannot leave the “palace” unless the situation called
“flying general” (see the figure above). “Flying general” means that one general can “fly” across the board to capture the enemy general if they stand on the same line without intervening pieces.
General: the generals can move and capture one point either vertically or horizontally and cannot leave the “palace” unless the situation called
“flying general” (see the figure above). “Flying general” means that one general can “fly” across the board to capture the enemy general if they stand on the same line without intervening pieces. Chariot: the chariots can move and capture vertically and horizontally by any distance, but may not jump over intervening pieces
Chariot: the chariots can move and capture vertically and horizontally by any distance, but may not jump over intervening pieces Cannon: the cannons move like the chariots, horizontally and vertically, but capture by jumping exactly one piece (whether it is friendly or enemy) over to its
target.
Cannon: the cannons move like the chariots, horizontally and vertically, but capture by jumping exactly one piece (whether it is friendly or enemy) over to its
target. Horse: the horses have 8 kinds of jumps to move and capture shown in the left figure. However, if there is any pieces lying on a point away from the horse horizontally or vertically
it cannot move or capture in that direction (see the figure below), which is called “hobbling the horse’s leg”.
Horse: the horses have 8 kinds of jumps to move and capture shown in the left figure. However, if there is any pieces lying on a point away from the horse horizontally or vertically
it cannot move or capture in that direction (see the figure below), which is called “hobbling the horse’s leg”.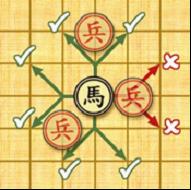
2 1 4 G 10 5 R 6 4 3 1 5 H 4 5 G 10 5 C 7 5 0 0 0
YES NO 其实这样子的题做一做还是蛮有意思的,实现一个完整程序中的一小部分,对编程能力还是有锻炼的。我的思路是把红方棋子的攻击范围标出来,当然不能让将帅直接面对,注意下细节就好了。不过作为一道细节题我竟然一次直接过了,难道我的强项真的是考细节的水题吗??好吧,我水题是做得好。#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<string> using namespace std; int map[13][13]; //初始化为0,1表示有棋子 int sign[13][13]; //初始化为0,1表示在红方棋子攻击范围内 struct node { char c; int x, y; }; int main() { int n, bx, by; while (cin >> n >> bx >> by&&n) { memset(map, 0, sizeof(map)); //初始化 memset(sign, 0, sizeof(sign)); node qizi[10]; int rjx, rjy; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin >> qizi[i].c >> qizi[i].x >> qizi[i].y; if (qizi[i].c == 'G') { rjx = qizi[i].x; rjy = qizi[i].y; } map[qizi[i].x][qizi[i].y] = 1; } if (rjy == by) //对特殊情况,黑将和红帅如果直接相对,直接是NO { int ok = 0; for (int i = bx + 1; i < rjx; i++) if (map[i][rjy]) ok = 1; if (!ok) { cout << "NO" << endl; continue; } } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) //处理出红方棋子的攻击范围,棋子本身不在其内(可以被吃) { if (qizi[i].c == 'G') //处理出将的攻击范围 { for (int i = rjx - 1; i >= bx; i--) { sign[i][rjy] = 1; if (map[i][rjy]) break; } } else if (qizi[i].c == 'R') //处理出车的攻击范围 { int xx = qizi[i].x; int yy = qizi[i].y; for (int i = xx + 1; i <= 10; i++) { sign[i][yy] = 1; if (map[i][yy]) break; } for (int i = xx - 1; i >= 1; i--) { sign[i][yy] = 1; if (map[i][yy]) break; } for (int i = yy + 1; i <= 9; i++) { sign[xx][i] = 1; if (map[xx][i]) break; } for (int i = yy - 1; i >= 1; i--) { sign[xx][i] = 1; if (map[xx][i]) break; } } if (qizi[i].c == 'C') //处理出炮的攻击范围 { int xx = qizi[i].x; int yy = qizi[i].y; int ok; ok = 0; for (int i = xx + 1; i <= 10; i++) { if (ok == 1) sign[i][yy] = 1; if (map[i][yy]) ok++; } ok = 0; for (int i = xx - 1; i >= 1; i--) { if (ok == 1) sign[i][yy] = 1; if (map[i][yy]) ok++; } ok = 0; for (int i = yy + 1; i <= 9; i++) { if (ok == 1) sign[xx][i] = 1; if (map[xx][i]) ok++; } ok = 0; for (int i = yy - 1; i >= 1; i--) { if (ok == 1) sign[xx][i] = 1; if (map[xx][i]) ok++; } } if (qizi[i].c == 'H') //处理出马的攻击范围 { int xx = qizi[i].x; int yy = qizi[i].y; if (!map[xx - 1][yy]) { if (xx - 2 >= 1 && yy - 1 >= 1) sign[xx - 2][yy - 1] = 1; if (xx - 2 >= 1 && yy + 1 <= 9) sign[xx - 2][yy + 1] = 1; } if (!map[xx + 1][yy]) { if (xx + 2 <= 10 && yy - 1 >= 1) sign[xx + 2][yy - 1] = 1; if (xx + 2 <= 10 && yy + 1 <= 9) sign[xx + 2][yy + 1] = 1; } if (!map[xx][yy - 1]) { if (yy - 2 >= 1 && xx - 1 >= 1) sign[xx - 1][yy - 2] = 1; if (yy - 2 >= 1 && xx + 1 <= 10) sign[xx + 1][yy - 2] = 1; } if (!map[xx][yy + 1]) { if (yy + 2 <= 9 && xx - 1 >= 1) sign[xx - 1][yy + 2] = 1; if (yy + 2 <= 9 && xx + 1 <= 10) sign[xx + 1][yy + 2] = 1; } } } /*for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) //测试 { for (int j = 1; j <= 9; j++) cout << sign[i][j] << " "; cout << endl; }*/ int cnt = 0; //判断黑将四个方向是否可以走 if (bx - 1 >= 1) { if (sign[bx - 1][by]) cnt++; } else cnt++; if (bx + 1 <= 3) { if (sign[bx + 1][by]) cnt++; } else cnt++; if (by - 1 >= 4) { if (sign[bx][by - 1]) cnt++; } else cnt++; if (by + 1 <= 6) { if (sign[bx][by + 1]) cnt++; } else cnt++; //cout << cnt << endl; if (cnt == 4) cout << "YES" << endl; else cout << "NO" << endl; } }
标签:
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_18738333/article/details/44869823