本题使用树状数组果然更加快。
树状数组难点:
1 如何遍历树
2 如何利用数组数据
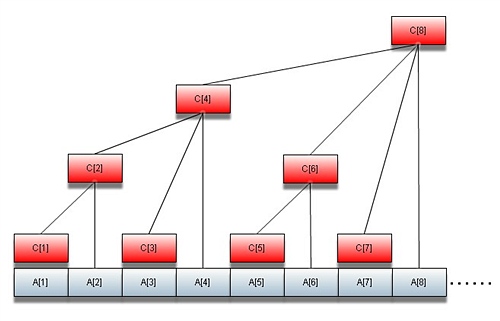
建立一个树状数组就如上图红色部分代表所有的树状数组节点了。
基本操作:
查找下一个节点的计算,如不明白下面函数的作用,请查看负数内存存放的问题。
简而言之就是:内存放是求反+1; 利用这个函数可以神奇地寻找到其单亲节点和兄弟节点,比如上图6->8,6->4或者7->8, 7 -> 6这样跳转节点。
这是树状数组实现的关键了,理解了如何遍历这样的树,就会使用这个数据结构了。
inline int lowbit(int x)
{
return x & (-x);//or return x&(x^(x-1));
}void update(int i, int val, int len)
{
while (i <= len)
{
c[i] += val;
i += lowbit(i);
}
}int getsum(int x)
{
int ans = 0;
while (x > 0)
{
ans += c[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return ans;
}参考资料:
http://www.cppblog.com/Ylemzy/articles/98322.html
主要是看图,然后自己思考,看代码吧。解决这道题的代码:
class MinimumInversionNumber_3_TreeArray
{
static const int SIZE = 5005;
int *a, *c;//一般数组和树状数组
inline int lowbit(int x)
{
return x & (-x);//or return x&(x^(x-1));
}
void update(int i, int val, int len)
{
while (i <= len)
{
c[i] += val;
i += lowbit(i);
}
}
int getsum(int x)
{
int ans = 0;
while (x > 0)
{
ans += c[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return ans;
}
public:
MinimumInversionNumber_3_TreeArray() : a((int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*SIZE)),
c((int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*SIZE))
{
int n, t;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &t);
a[i] = t + 1;
}
//memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));最好不要使用memset设置初值
fill(c, c+n+1, 0);
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
update(a[i], 1, n);
res += i - getsum(a[i]);//目前为止,出现了多少个小于等于a[i]的数位getsum(a[i]),所以大于a[i]的数位i-getsum(a[i]),即为逆序数
}
int ans = res;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
res += n - 2*a[i-1] + 1;
if(res < ans) ans = res;
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}
~MinimumInversionNumber_3_TreeArray()
{
free(a);
free(c);
}
};
hdu1394 树状数组 解法,布布扣,bubuko.com
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/kenden23/article/details/28891421