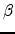 e (German for a one-way street) is a street on which vehicles should only move in one direction. One reason for having one-way streets is to facilitate
a smoother flow of traffic through crowded areas. This is useful in city centers, especially old cities like Cairo and Damascus. Careful planning guarantees that you can get to any location starting from any point. Nevertheless, drivers must carefully plan
their route in order to avoid prolonging their trip due to one-way streets. Experienced drivers know that there are multiple paths to travel between any two locations. Not only that, there might be multiple roads between the same two locations. Knowing the
shortest way between any two locations is a must! This is even more important when driving vehicles that are hard to maneuver (garbage trucks, towing trucks, etc.)
e (German for a one-way street) is a street on which vehicles should only move in one direction. One reason for having one-way streets is to facilitate
a smoother flow of traffic through crowded areas. This is useful in city centers, especially old cities like Cairo and Damascus. Careful planning guarantees that you can get to any location starting from any point. Nevertheless, drivers must carefully plan
their route in order to avoid prolonging their trip due to one-way streets. Experienced drivers know that there are multiple paths to travel between any two locations. Not only that, there might be multiple roads between the same two locations. Knowing the
shortest way between any two locations is a must! This is even more important when driving vehicles that are hard to maneuver (garbage trucks, towing trucks, etc.)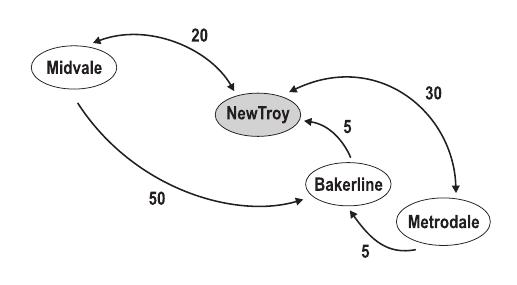
4 2 5 NewTroy Midvale Metrodale NewTroy <-20-> Midvale Midvale --50-> Bakerline NewTroy <-5-- Bakerline Metrodale <-30-> NewTroy Metrodale --5-> Bakerline 0 0 0
1. 8
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define inf 1000000000
const int L = 1005;
int n, c, m;
int a[105][105];
char location[1005][100];
char s1[100], s2[100];
char from, to;
int cnt;
map<string, int> mat;
void Floyd()
{
int i, j, k;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
for (k = 1; k <= n; k++)
if (a[j][i] + a[i][k]<a[j][k])
a[j][k] = a[j][i] + a[i][k];
}
int main()
{
int val, x, y, len, cas = 1, sum, start,end;
while (~scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &c, &m) && (n + c + m))
{
sum = 0;
mat.clear();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
a[i][j] = inf;
for (int i = 0; i <= c; i++)
scanf("%s", location[i]);
cnt = 1;
for (int i = 0; i<m; i++)
{
scanf("%s %c-%d-%c %s", s1, &from, &val, &to, s2);
if (!mat[s1])
mat[s1] = cnt++;
if (!mat[s2])
mat[s2] = cnt++;
x = mat[s1], y = mat[s2];
if (from == '<' && val<a[y][x])
a[y][x] = val;
if (to == '>' && val<a[x][y])
a[x][y] = val;
}
Floyd();
start = mat[location[0]];
for (int i = 1; i <= c; i++)
end = mat[location[i]];
sum += a[start][end] + a[end][start];
printf("%d. %d\n", cas++, sum);
}
return 0;
}
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u010736393/article/details/45102989