标签:数据结构
数据结构之栈与队列
数据结构的有一个重要结构栈,栈这种数据结构就是满足先进后出的这种规则的数据结构就是栈,引用《大话数据结构》中的一个形象例子就是,子弹的弹夹,最先压入弹夹的子弹最后一个出弹夹,正好往一个栈里添加一个元素叫压栈、入栈,从栈里出来一个元素叫弹栈,出栈。指示器就叫栈帧。
栈图

现在就贴上代码:
栈的几个基本操作:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node{ //声明栈中的元素类型,数据域与指针域
int data;
struct node *next;
}_node;
typedef struct nodectl{ //栈的一个总体结构包含了栈顶,栈底
_node *top ;
_node *base;
int count ;
}_ndctl;
void starck_init(_ndctl *ctl) //初始化栈的空间
{
memset(ctl,0x00,sizeof(_ndctl));
}
void push(_ndctl *ctl,_node *node) //压栈,压入一个元素
{
if(NULL == ctl && NULL == node)
return ;
if(NULL == ctl->top){
ctl->top = node ;
ctl->base= node ;
}else{
node->next = ctl->top ;
ctl->top = node;
}
ctl->count++ ;
}
_node *pop(_ndctl *ctl) //弹栈,取出一个元素
{
_node *p;
if(NULL == ctl){
return NULL ;
}
p = ctl->top;
if(ctl->count>0){
ctl->top = ctl->top->next;
ctl->count--;
}
return p;
}
void stack_destory(_ndctl *ctl) //删除这个栈
{
_node *ptemp ;
if(NULL == ctl)
{
return ;
}
while(0 <ctl->count){
ptemp = ctl->top->next ;
free(ctl->top);
ctl->top = ptemp;
ctl->count--;
}
}
int main(int ac,char **av) //从命令行输入需要入栈的元素个数
{
_ndctl ctl = {NULL,NULL,0};
_node *node = NULL;
int size = 0,cnt = 1;
if(ac <= 1){
printf("OH no!\n");
return -1;
}
size = atoi(av[1]) ;
while(size > 0 ){
node =(_node *)malloc(sizeof(_node));
if(NULL == node)
{
printf("malloc : oh no!\n");
break ;
}
node->data = cnt++;
push(&ctl,node);
size--;
}
while(ctl.count > 0){ //弹出所有的元素
node = pop(&ctl);
printf("->%02d ",node->data);
free(node);
}
printf("\n");
stack_destory(&ctl);
return 0;
} 队列 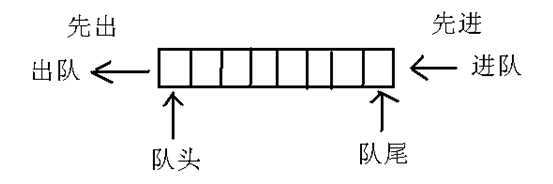
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<errno.h>
typedef struct node{ //建立每一个元素
int data;
struct node *next;
}_node;
typedef struct {
_node *head ;
_node *tail ;
int count ;
}_ctl;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//入队操作
{
if(NULL == ctl || NULL == node){
return ;
}
if(!ctl->count){
ctl->head = node;
}else{
ctl->tail->next = node ;
}
ctl->tail = node ;
node->next = NULL;
ctl->count += 1 ;
}
_node *que_deq(_ctl *ctl) //出队一个元素
{
_node *rst = NULL ;
if(NULL == ctl){
return NULL;
}
rst = ctl->head ;
if(rst){
ctl->head = rst->next ;
ctl->count -= 1;
rst->next =NULL ;
}
return rst ;
}
void que_del(_ctl *ctl) //删除一个队列
{
_node *pos = NULL;
if(NULL == ctl){
return ;
}
pos = ctl->head;
while(pos!=NULL){
ctl->head = pos->next;
free(pos);
pos = ctl->head;
}
}
void que_create(_ctl *ctl,int len) //建立一个队列,入队操作
{
_node *pnt = NULL;
int fact = 0;
if(NULL == ctl || len < 1){
return ;
}
while(fact < len)
{
pnt = (_node *)malloc(sizeof(_node));
pnt->data = fact +1;
que_inq(ctl,pnt);
fact++;
}
}
int main()
{
_ctl ctl = {NULL,NULL,0};
_node *rst = NULL;
que_create(&ctl,10);
while(ctl.count){
rst = que_deq(&ctl);
printf("%d ",rst->data);
free(rst);
}
printf("\n");
que_del(&ctl);
return 0;
}标签:数据结构
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/zmrlinux/article/details/45174523