标签:
跟Java和C#类似,OC创建的对象在堆上。与Java和C#不同的是Java和C#有垃圾回收机制,所以不需要程序员手动释放堆上的内存。而OC没有垃圾回收机制,必须手动管理内存的创建和释放。下面介绍一下OC内存管理内存管理的方式。
OC管理内存的方式类似C++中的智能指针,创建一个对象时,在ObjC中每个对象内部都有一个与之对应的整数(retainCount),叫“引用计数器”,当一个对象在创建之后初始化它的引用计数器为1,当调用这个对象的alloc、retain、new、copy方法之后引用计数器自动在原来的基础上加1(ObjC中调用一个对象的方法就是给这个对象发送一个消息),当调用这个对象的release方法之后它的引用计数器减1,如果一个对象的引用计数器为0,则系统会自动调用这个对象的dealloc方法来销毁这个对象。
Student.h文件:
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 3 @interface Student : NSObject 4 5 #pragma mark - 属性 6 @property (nonatomic,copy)NSString *name; 7 @property (nonatomic,assign)float age; 8 9 @end
Student.m文件:
1 #import "Student.h" 2 3 @implementation Student 4 5 -(void)dealloc{ 6 NSLog(@"Invoke Student dealloc method"); 7 [super dealloc]; 8 } 9 @end
main.m文件:
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 #import "Student.h" 3 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) 4 { 5 6 @autoreleasepool { 7 8 // insert code here... 9 Student *stu = [[Student alloc]init]; 10 stu.name=@"lisi"; 11 stu.age=12; 12 NSLog(@"retainCount=%lu",[stu retainCount]); 13 //结果为1 14 [stu retain]; 15 NSLog(@"retainCount=%lu",[stu retainCount]); 16 //结果为2 17 [stu release]; 18 NSLog(@"retainCount=%lu",[stu retainCount]); 19 //结果为1 20 [stu release]; 21 stu=nil; 22 [stu release]; 23 } 24 return 0; 25 }
我们可以看出,在创建一个对象之后,初始化引用计数器为1,retain之后,计数器增加1,然后每release一次,计数器都会减1,直到这个对象被释放。
对象之间引用可以是复杂的,有时候会出现相互引用既循环引用的情况,所以对象的释放不能紧紧依靠自动化来完成。内存释放的原则是谁创建,谁释放。如下:
Book.h:
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 3 @interface Book : NSObject 4 @property (nonatomic,copy) NSString *bookName; 5 -(void)read; 6 -(id)initWithName:(NSString*) bname; 7 @end
Book.m
1 #import "Book.h" 2 3 @implementation Book 4 -(void)read{ 5 NSLog(@"now read this book %@...",self.bookName); 6 } 7 -(id)initWithName:(NSString*) bname{ 8 [super init]; 9 _bookName=bname; 10 return self; 11 } 12 -(void)dealloc{ 13 NSLog(@"Invoke book %@ dealloc method...",self.bookName); 14 [super dealloc]; 15 } 16 @end
Student.h
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 #import "Book.h" 3 @interface Student : NSObject{ 4 Book *_book; 5 } 6 7 #pragma mark - 属性 8 @property (nonatomic,copy)NSString *name; 9 @property (nonatomic,assign)float age; 10 -(id)initWithNameAndAge:(NSString*)sname andAge:(float) sage; 11 -(void)setBook:(Book*)book; 12 -(Book*)book; 13 @end
Student.m
1 #import "Student.h" 2 3 @implementation Student 4 5 -(id)initWithNameAndAge:(NSString *)sname andAge:(float)sage{ 6 self.name=sname; 7 self.age=sage; 8 return self; 9 } 10 -(void)setBook:(Book *)book{ 11 if (_book!=book) { 12 [_book release]; 13 _book = [book retain]; 14 } 15 } 16 17 -(Book*)book{ 18 return _book; 19 } 20 21 -(void)dealloc{ 22 NSLog(@"Invoke Student dealloc method"); 23 [_book release]; 24 [super dealloc]; 25 } 26 @end
main.m
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 #import "Student.h" 3 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) 4 { 5 6 @autoreleasepool { 7 8 // insert code here... 9 Student *stu = [[Student alloc]initWithNameAndAge:@"sili" andAge:12]; 10 11 Book *book1 = [[Book alloc]initWithName:@"AAA"]; 12 [book1 release]; 13 [stu.book read]; 14 15 Book *book2 = [[Book alloc]initWithName:@"BBB"]; 16 [stu setBook:book2]; 17 [book2 release]; 18 [stu.book read]; 19 [stu release]; 20 } 21 return 0; 22 }
运行结果:
1 2015-05-03 11:59:24.939 first[1814:303] Invoke book AAA dealloc method... 2 2015-05-03 11:59:24.941 first[1814:303] now read this book BBB... 3 2015-05-03 11:59:24.942 first[1814:303] Invoke Student dealloc method 4 2015-05-03 11:59:24.942 first[1814:303] Invoke book BBB dealloc method...
其实我们可以直接利用OC提供的属性来达到同样的效果:
@property (nonatomic,retain)Book *book;
属性包含的所有参数和用法如下:
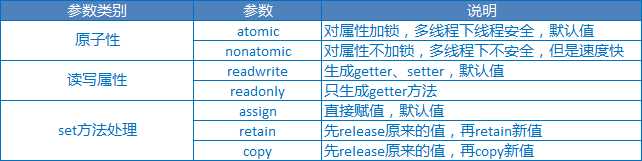
如果不进行设置或者只设置其中一类参数,程序会使用三类中的各个默认参数,默认参数:(atomic,readwrite,assign)。一般情况下如果是基本类型使用assign,非字符串对象使用retain,字符串对象使用copy。原子性和读写属性根据需要设置即可。
自动内存释放使用@autoreleasepool关键字声明一个代码块,如果一个对象在初始化时调用了autorelase方法,那么当代码块执行完之后,在块中调用过autorelease方法的对象都会自动调用一次release方法。
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 2 #import "Student.h" 3 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) 4 { 5 6 @autoreleasepool { 7 8 // insert code here... 9 Student *stu = [[Student alloc]initWithNameAndAge:@"lisi" andAge:12]; 10 Student *stu1 = [[[Student alloc]initWithNameAndAge:@"wanger" andAge:14]autorelease]; 11 [stu1 retain]; 12 [stu autorelease]; 13 } 14 return 0; 15 }
打印结果:
1 2015-05-03 12:27:39.949 first[1938:303] Invoke Student dealloc lisi method
我们可以看出,stu对象被完全释放,而stu1没有被释放,这是因为每个对象的release方法只被调用了一次,而stu1的引用计数为2,所以在代码块结束的时候stu1对象不会被释放(造成了内存泄露)。对于自动内存释放有以下几点需要注意:
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/desheng-Win/p/4474529.html