标签:
首先我们先要写一个DLL文件:
我先创建一个win32的DLL工程,在工程中添加了Math.h和Math.cpp文件,具体内容如下:
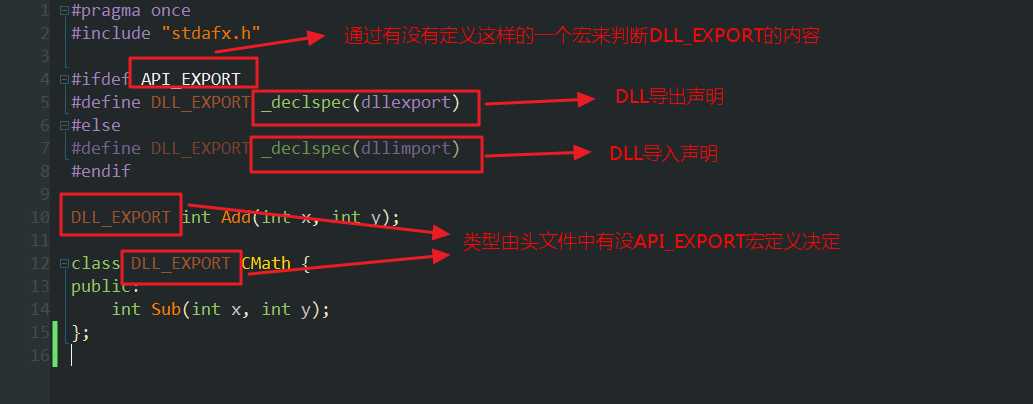
Math.h:
#pragma once #include "stdafx.h" #ifdef API_EXPORT #define DLL_EXPORT _declspec(dllexport) #else #define DLL_EXPORT _declspec(dllimport) #endif DLL_EXPORT int Add(int x, int y); class DLL_EXPORT CMath { public: int Sub(int x, int y); };
Math.cpp:
#include "StdAfx.h" #define API_EXPORT #include "Math.h" int Add(int x, int y) { return x+y; } int CMath::Sub(int x, int y) { return x-y; }
简单的解释:

现在我们创建一个win32工程,接着引用我们写好的DLL文件:
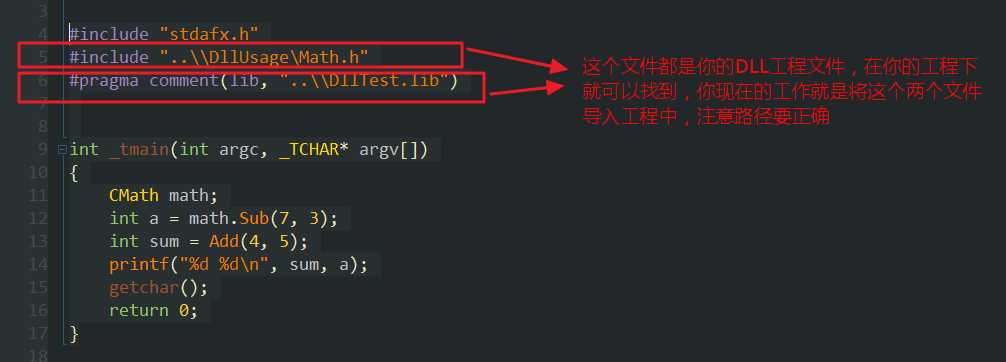
使用示例:
#include "stdafx.h" #include "..\\DllUsage\Math.h" #pragma comment(lib, "..\\DllTest.lib") int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { CMath math; int a = math.Sub(7, 3); int sum = Add(4, 5); printf("%d %d\n", sum, a); getchar(); return 0; }
必须注意的是下面几点:
1.引入文件
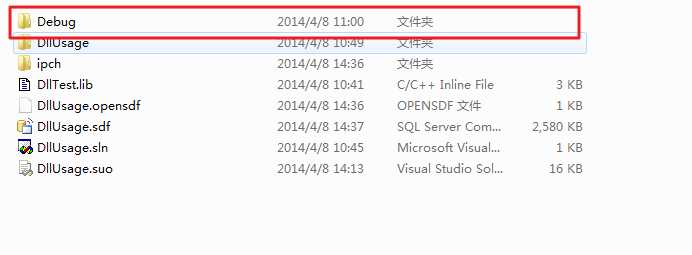
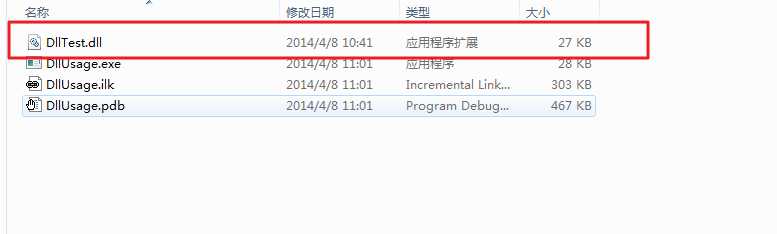
2.放置好你的DLL位置
进入Debug文件夹中放置好你的DLL文件
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/rayguo/p/3651979.html