标签:
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define MAX 1000+10 char mat[MAX][MAX], vis[MAX][MAX]; void dfs(int x, int y) //mat[][]存图像,1代表黑; vis[][]标记是否访问过这个格子 { if (!mat[x][y] || vis[x][y]) { return; } vis[x][y] = 1; //标记此点访问过 dfs(x-1, y-1); dfs(x-1, y); dfs(x-1, y+1); //递归访问周围8个点 dfs(x, y-1); dfs(x, y+1); dfs(x+1, y-1); dfs(x+1, y); dfs(x+1, y+1); } int main(void) { memset(mat, 0, sizeof(mat)); memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); int i, j, n, cnt = 0; scanf("%d", &n); for (i=1; i<=n; i++) { for (j=1; j<=n; j++) { scanf("%d", &mat[i][j]); } } for (i=1; i<=n; i++) { for (j=1; j<=n; j++) { if (mat[i][j] && !vis[i][j]) //找没访问过的黑格 { cnt++; dfs(i, j); } } } printf("%d\n", cnt); return 0; }
参考链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/RootJie/archive/2012/02/21/2361327.html
这个是白书上的一个例题,刚刚来开始研究图论。这个地方使用了两个二维数组,一个用来记录图的形状,另外一个用来判断当前点是否是被访问过的。即mat和vis。
输入一个n*n的黑白图像(1表示黑色,0表示白色),任务是统计其中八连块的个数。如果两个黑格子有公共边或者有公共顶点,就说它们属于同一个八连块。
如下图所示,八连块的个数为3。
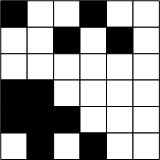
即输入为:
6
1 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 0 0
输出
3
属于入门级别的dfs
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/tianxia2s/p/4479561.html