数据结构之初探二叉树
树的一些基本概念:
树:N个节点组成的有限集合(N>=0)。
子树:上一个根节点的孩子,并且也是下一层子树的根节点。
二叉树:最多只有两个孩子节点的树。
空树:没有子节点的树。
非空树:
树中至少有一个节点——根。
树中各子树是互不相交的集合。
树的表示方法:
嵌套集合表示法,广义表法,凹入表示法。
树的基本术语:
结点:表示树中的元素,包括数据项及若干指向其子树的分支。
结点的度:结点拥有的子树个数。
叶子结点:度为0的结点。
树的度:一颗树中最大的结点度数(子树数)。
孩子:结点的子树的根称为该结点的孩子(结点)。
双亲:孩子结点的上一层结点叫该结点的父节点。
兄弟:同一双亲的孩子互称兄弟(结点)。
结点的层次 :从根节点算起根为第一层。
树的深度 :树中结点的最大层次数。
堂兄弟:其双亲在同一层的结点互称为堂兄弟
结点的祖先:从根节点到该结点所经分支上的所有结点。
结点的子孙:以某根节点为根的子树中的任一结点叫之。
有序树:树中各结点的子树从左到右有次序(不能互换)。
森林:
多棵互不相交的树构成的集合。
树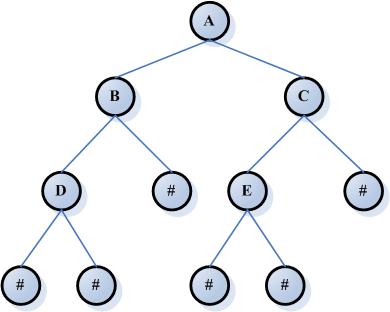
例如这就是一棵二叉树。
二叉树的基本特征:
1.每个结点最多只有两棵子树。
2.子树有左右之分,其次序不能任意颠倒,是一个有序树。
二叉树的几个基本性质:
一。
在二叉树的第i层上至多有2^(i-1)次方个结点。
二。
深度为k的二叉树上至多含2^k-1个结点。
三。
对任何一棵二叉树,若它含有N个叶子节点,N1个度为2的结点,则N=N1+1;
四。
具有N个结点的完全二叉树的深度为:
log2N(取整)+1.
五。
对于含有N个结点的完全二叉树从上到下且从左至右进行1至N的编号,则对完全二叉树中的任意一个编号为i的结点。
若i=1,该结点是二叉树的根,无双亲;否则编号为i/2向上取整的结点为其双亲。
若2i>n, 则该结点无左孩子,否则编号为2i的结点无右孩子结点,否则,编号为2i+1的结点为其右孩子结点,
若2i+1>n,则该结点无右孩子结点,否则编号为2i+1的结点为其右孩子结点。
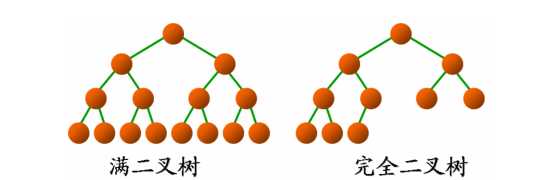
满二叉树:
指的是深度为K且含有2^(k)-1个结点的二叉树。
特点:每一层的结点树都是最大结点数
性质:第i层上至多有2^(i-1)个结点。
性质:深度为K的二叉树至多有2^k-1个结点。
完全二叉树:
若一棵二叉树中所含的N个结点与满二叉树中编号为1至N的结点一一对应(编号和位置一一对应)。
特点:
1.叶子节点只可能在层次最大的两层上出现。
2.对任一结点,若其右分支下子孙的最大层次为1.则其左分支下子孙的最大层次必为1或1+1.
下面将附上用二叉链表的方式建立二叉树,并且用#占位,显示先中后三种遍历方式:
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: mytree.c
> Author: zmr
> Mail: 1797763610@qq.com
> Created Time: Sun 03 May 2015 02:46:57 PM CST
************************************************************************/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define PE '#'
typedef struct tree{ //定义树结点结构
char ele;
char nous[3]; //由与内存对齐问题先用数组占位
#ifndef SYSTEM32
char nouse[4];
#endif
struct tree *lchd,*rchd;
}_tree;
typedef struct quenode{ //队列结点
_tree *root;
struct quenode *next;
}_que;
typedef struct nodectl{ //队列控制结构
_que *head,*tail;
int lenth;
}_quectl;
typedef struct treectl { //树的控制结构
_tree *root;
int nodes;
#ifndef SYSTEM32
char nous[4];
#endif
}_treectl;
enum { CMD=0,STR };
void inq(_quectl *qctl,_tree *tree) //队列的入队操作
{
_que * qnode = NULL;
if(NULL == qctl || NULL == tree){
return ;
}
qnode = (_que*)malloc(sizeof(_que));
if(NULL == qnode){
return ;
}
qnode->root = tree;
qnode->next = NULL;
if(0 == qctl->lenth){
qctl->head=qctl->tail=qnode;
}else{
qctl->tail->next = qnode;
qctl->tail = qnode;
}
qctl->lenth += 1;
}
_tree *deq (_quectl *qctl) //删除一个队列结点
{
_que * qnode = NULL ;
_tree * tree = NULL ;
if(NULL == qctl || 0 >= qctl->lenth){
return NULL;
}
qnode = qctl->head;
qctl->head = qnode->next;
qctl->lenth -= 1;
tree = qnode->root;
free(qnode);
return tree;
}
void que_destory(_quectl *qctl) //破坏队列
{
_que * qnode = NULL;
if(NULL == qctl){
return ;
}
qnode = qctl->head;
while(NULL != qnode){
qctl->tail = qnode->next;
if(PE == qnode->root->ele){
free(qnode->root);
}
free(qnode);
qnode = qctl->tail;
}
}
void tree_create(_treectl *ctl,char *str) //建立二叉树
{
_tree *root = NULL,*mtree = NULL;
_tree *left = NULL,*right = NULL;
int index=0 ,lenstr = 0 ;
_quectl qctl = {NULL,NULL,0} ;
if(NULL == ctl || NULL == str){
return ;
}
ctl->root = NULL ;
ctl->nodes = 0 ;
lenstr = strlen(str);
if(0 >= lenstr){
return ;
}
mtree =(_tree *)malloc(sizeof(_tree));
if(NULL == mtree){
return ;
}
mtree->ele = str[0];
mtree->lchd= mtree->rchd =NULL;
ctl->root = mtree;
inq(&qctl,mtree);
index += 1;
while(index < lenstr){
mtree = deq(&qctl);
if(NULL == mtree){
break ;
}
left = (_tree *)malloc(sizeof(_tree));
right= (_tree *)malloc(sizeof(_tree));
memset(left,0x00,sizeof(_tree));
memset(right,0x00,sizeof(_tree));
left->ele = str[index];
right->ele= str[index+1];
inq(&qctl,left);
inq(&qctl,right);
if(PE == mtree->ele){ //遇到#给它的左右子树分别赋值NULL
left->ele = PE;
right->ele= PE;
free(mtree);
}else{
if(PE == left->ele){
mtree->lchd = NULL;
}else{
mtree->lchd = left;
}
if(PE == right->ele){
mtree->rchd = NULL;
}else{
mtree->rchd = right;
}
}
index += 2;
}
que_destory(&qctl);
}
void tree_destory(_tree *tree) //删除一棵树
{
if(tree){
tree_destory(tree->lchd);
tree_destory(tree->rchd);
free(tree);
}
}
void pre(_tree *tree) //前序遍历一棵树
{
if(tree)
{
printf("%c ",tree->ele);
pre(tree->lchd);
pre(tree->rchd);
}
}
void middle(_tree *tree) //中序遍历一颗树
{
if(tree){
middle(tree->lchd);
printf("%c ",tree->ele);
middle(tree->rchd);
}
}
void post(_tree *tree) //后序遍历一颗树
{
if(tree)
{
post(tree->lchd);
post(tree->rchd);
printf("%c ",tree->ele);
}
}
int dowork(int ac,char **av)
{
_treectl mytree = {NULL,0};
int height = 0;
_tree *node = NULL;
if(ac <= STR){
printf("NO input\n");
return -1;
}
tree_create(&mytree,av[STR]);
pre(mytree.root);
printf("\n");
middle(mytree.root);
printf("\n");
post(mytree.root);
printf("\n");
tree_destory(mytree.root);
return 0;
}
int main(int ac,char **av)
{
return dowork(ac,av);
}原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/zmrlinux/article/details/45675181