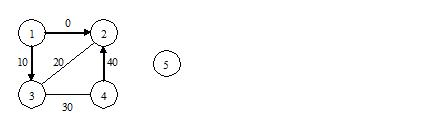
2 1 1 2 0 10 5 5 1 2 1 0 1 3 1 10 2 3 0 20 3 4 0 30 4 2 1 40
10 100
题意:有 n 个城市, m 条边,每条边连接两个城市。x y d w 表示,x y 之间有一条边,边上有财富值 w ,d 为 1 表示有向边, d 为 0 表示 无向边。小偷集团要窃取这些财富值,在每个 城市都有一个小偷,经过相邻的边时就会得到该条边对应的财富值。每条边只可以走一次。问最后可以得到的最大值。
思路:贪心,按边权从大到小排序。对于有向边,只能选起点,那无向边呢,两个点都是可以的,而且怎么选择对后面是有影响的。于是想到先把这两个点标记为待确定点,根绝后面的选择再确定这两个点。注意到一个点可能是多条无向边的端点,也就是说可能有许多点互相关联,待确定,只要其中有一个点被确定了,那么其他所有的点就都被确定好了。这样这些点构成了一个联通块,可以用并查集实现。这样贪心的时候,每个联通块缩为一个点,每个点的状态有已被选,和未选,再根据相应的策略去贪心就好了。
<span style="font-size:18px;">#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double e = 2.718281828459;
const double eps = 1e-8;
const int MAXN = 1010;
int father[MAXN];
struct Edge
{
int u, v;
int d, w;
} edge[MAXN*MAXN/2];
int vis[MAXN];
int n, m;
int Find(int x)
{ // 路径压缩
return (x==father[x])?x:(father[x]=Find(father[x]));
}
int cmp(Edge a, Edge b)
{
return a.w > b.w;
}
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
//freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
while(cin>>n>>m)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &edge[i].u, &edge[i].v, &edge[i].d, &edge[i].w);
}
sort(edge+1, edge+1+m, cmp);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
father[i] = i;
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int x = Find(edge[i].u);
int y = Find(edge[i].v);
if(vis[x] && vis[y])
continue;
if(edge[i].d==1 && vis[x])
continue;
ans += edge[i].w;
if(edge[i].d == 1)
vis[x] = 1;
else
{
if(x == y)
vis[x] = 1;
if(!vis[x] && !vis[y])
father[x] = y;
else if(vis[x])
vis[y] = 1;
else if(vis[y])
vis[x] = 1;
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}</span>HDU 2480 - Steal the Treasure(贪心+并查集)
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u014028317/article/details/45703115