标签:
package creeper;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class size {
private static int intercePosition = 0; // 记录单个运算数据的长度
private static int[] intercePositionIndex = null; // 记录“(”的下标
private static int[] intercePositionEnd = null; // 记录“)”的下标
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
do {
System.out.println("请输入你要计算的字符串(注意:只能输入数字和加,减,乘除符号;输入完毕后,请直接回车):");
String numberString = input.next().trim();
// 判断输入的运算字符串是否符合规定
if (ispassString(numberString) == false) {
System.out.println("您输入的计算字符串有误,请正确输入!");
} else {
// 计算结果返回
System.out.println(interceResult(numberString));
}
} while (true);
}
// 判断是否有带括号的运算字符串存在
private static String interceResult(String str) {
String result = str;
char[] numberString = str.toCharArray(); // 1+2+(1*2+1-1*2+5)+2+(1+5+9+10-11)+1*5/2+3
// 1+8-9+(1*8/2-5+(1+2+8))+4/5*8/3*2
int IndexStart = 0; // 记录“(”的实际数量
int EndStart = 0; // 记录“)”的实际数量
for (int i = 0; i < numberString.length; i++) {
if (‘(‘ == numberString[i]) {
// 记录最后一个正括号的位置
IndexStart = i;
}
if (‘)‘ == numberString[i]) {
// 记录反括号的最初始下标的位置
EndStart = i;
// 截取最里面一个括号里的运算字符串
result = result.substring(IndexStart + 1, EndStart);
// 截取括号的运算字符串进行运算,生成新的运算字符串
result = str.substring(0, IndexStart)
+ interceptOperation(result, ‘*‘, ‘/‘)
+ str.substring(EndStart + 1, str.length());
// 回调执行,其它小括号的运算字符串
return interceResult(result);
}
if (i == numberString.length - 1)
if (EndStart == 0)
break;
}
// 不存在括号了,再进行混合运算
result = interceptOperation(str, ‘*‘, ‘/‘);
return result;
}
// 不带括号的四则运算
private static String interceptOperation(String operationNumber, char a,
char b) {
String mess = operationNumber;
char[] stringOperation = mess.toCharArray();
// 循环遍历运算字符串,并做相应的运算
for (int i = 0; i < stringOperation.length; i++) {
// 判断运算符所在的索引
if (stringOperation[i] == a || stringOperation[i] == b) {
if (i != 0) {
// 运算符前的第一个数
double num1 = interceptNumIndex(mess.substring(0, i));
// 记录第一个数据的长度
int frontPosition = intercePosition;
// 运算符前的第二个数
double num2 = interceptNumEnd(mess.substring(i + 1,
stringOperation.length));
// 记录第二个数据的长度
int backPosition = intercePosition;
// 算完乘除,将结果替换到原来运算的位置,得到新的运算字符串
String IndexMess = mess.substring(0, i - frontPosition + 1);
String IndexResult = "";
// 判断是否运算到最后的结果了
if (IndexMess.indexOf(‘+‘) == -1
&& IndexMess.indexOf(‘*‘) == -1
&& IndexMess.indexOf(‘/‘) == -1
&& IndexMess.lastIndexOf(‘-‘) == -1)
IndexMess = "";
if (IndexMess != "")
IndexResult = IndexMess.lastIndexOf(‘-‘) == IndexMess
.length() - 1 ? IndexMess.substring(0, i
- frontPosition) : IndexMess;
// 组装新的运算字符串
mess = IndexResult// mess.substring(0,i-frontPosition+1)
+ reslutString("" + stringOperation[i], num1, num2)
+ mess.substring(i + backPosition + 1);
// 0.111/1212/2/2/2/2/2/2/2
if (mess.lastIndexOf(‘-‘) == 0 && mess.indexOf(‘+‘) == -1
&& mess.indexOf(‘*‘) == -1
&& mess.indexOf(‘/‘) == -1) {
break;
}
// 回调,继续运算
return interceptOperation(mess, a, b);// 1+7-5+89/3+4-6*8/2+4-6
} else
continue;
}
if (i == stringOperation.length - 1) {
// 递归出口,判断是否还有运算字符串在
if (mess.indexOf(‘+‘) != -1 || mess.indexOf(‘-‘) != -1)
return interceptOperation(mess, ‘+‘, ‘-‘);
break;
}
}
return mess;
}
// 截取第二个数
private static double interceptNumEnd(String str) {
double a = 0;
int InrerceIndex = 0;
char[] stringOperation = str.toCharArray();
boolean ispas = false; // 记录是否为负数
for (int i = 0; i < stringOperation.length; i++) {
switch (stringOperation[i]) {
case ‘*‘:
case ‘/‘:
case ‘+‘:
case ‘-‘:
InrerceIndex = i;
if (i != 0) // 判断该数是否为负数
ispas = true;
break;
default:
break;
}
if (ispas)
break;
}
// 判断此数据是否在运算字符串的最后一位
if (InrerceIndex == 0) {
a = Double.parseDouble(str);
intercePosition = str.length();
if (ispas)
intercePosition++;
} else {
a = Double.parseDouble(str.substring(0, InrerceIndex));
// 记录数据的真实长度
intercePosition = str.substring(0, InrerceIndex).length();
}
return a;
}
// 截取第一个数
private static double interceptNumIndex(String str) {
double a = 0; // 记录数据
int InrerceIndex = 0; // 记录运算符的位置
boolean temp = false; // 记录数据前运算符的状态
char[] stringOperation = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = stringOperation.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
switch (stringOperation[i]) {
case ‘*‘:
case ‘/‘:
case ‘+‘:
case ‘-‘:
InrerceIndex = i;
temp = true;
break;
default:
break;
}
if (temp)
break;
}
// 判断此数据是否在运算字符串的第一位
if (InrerceIndex == 0) {
a = Double.parseDouble(str);
intercePosition = str.length();
// if(temp)
// intercePosition++;
} else {
a = Double.parseDouble(str.substring(InrerceIndex, str.length()));
// 记录数据的真实长度
intercePosition = str.substring(InrerceIndex, str.length())
.length();
}
return a;
}
// 计算结果
private static double reslutString(String operation, double num1,
double num2) {
double sumResult = 0;
if (operation.equals("*"))
sumResult = num1 * num2;
if (operation.equals("-"))
sumResult = num1 - num2;
if (operation.equals("/"))
sumResult = num1 / num2;
if (operation.equals("+"))
sumResult = num1 + num2;
return sumResult;
}
// 判断是否正确输入运算方式
private static boolean ispassString(String messString) {
boolean ispass = false;
boolean operationIspass = true; // 记录被除数的状态
int ai = 0; // 记录是否有运算符号的存在
char[] IsString = messString.toCharArray();
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < IsString.length; i++) {
// 记录有几对小括号的存在
if (‘(‘ == IsString[i])
num1++;
if (‘)‘ == IsString[i])
num2++;
// 判断除数是否为零
if (‘/‘ == IsString[i] && IsString[i + 1] == ‘0‘)
operationIspass = false;
// 判断是否输入了运算符合
if (IsString[i] == ‘+‘ || IsString[i] == ‘-‘ || IsString[i] == ‘*‘
|| IsString[i] == ‘/‘)
ai++;
if (i == IsString.length - 1)
if (ai == 0)
num2++;
}
if (operationIspass)
if (num1 == num2)
ispass = true;
return ispass;
}
}
运行结果如下
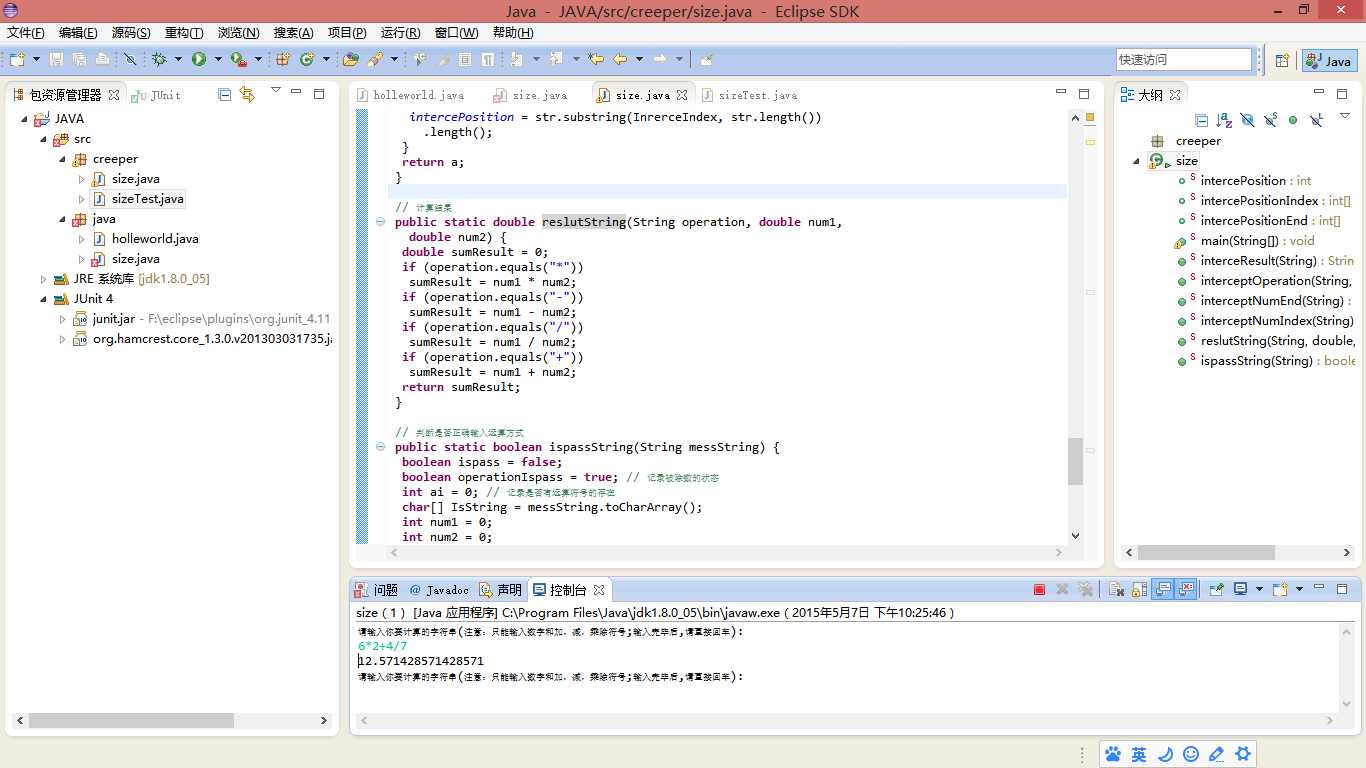
然后使用junit进行测试
测试代码如下
package creeper;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.Test;
public class sizeTest {
@Test
public void testReslutString() {
Double expectedAnswer = Double.valueOf(12);
Double actualAnswer = Double.valueOf(2*6);
assertEquals(expectedAnswer, actualAnswer);
}
}
结果如下
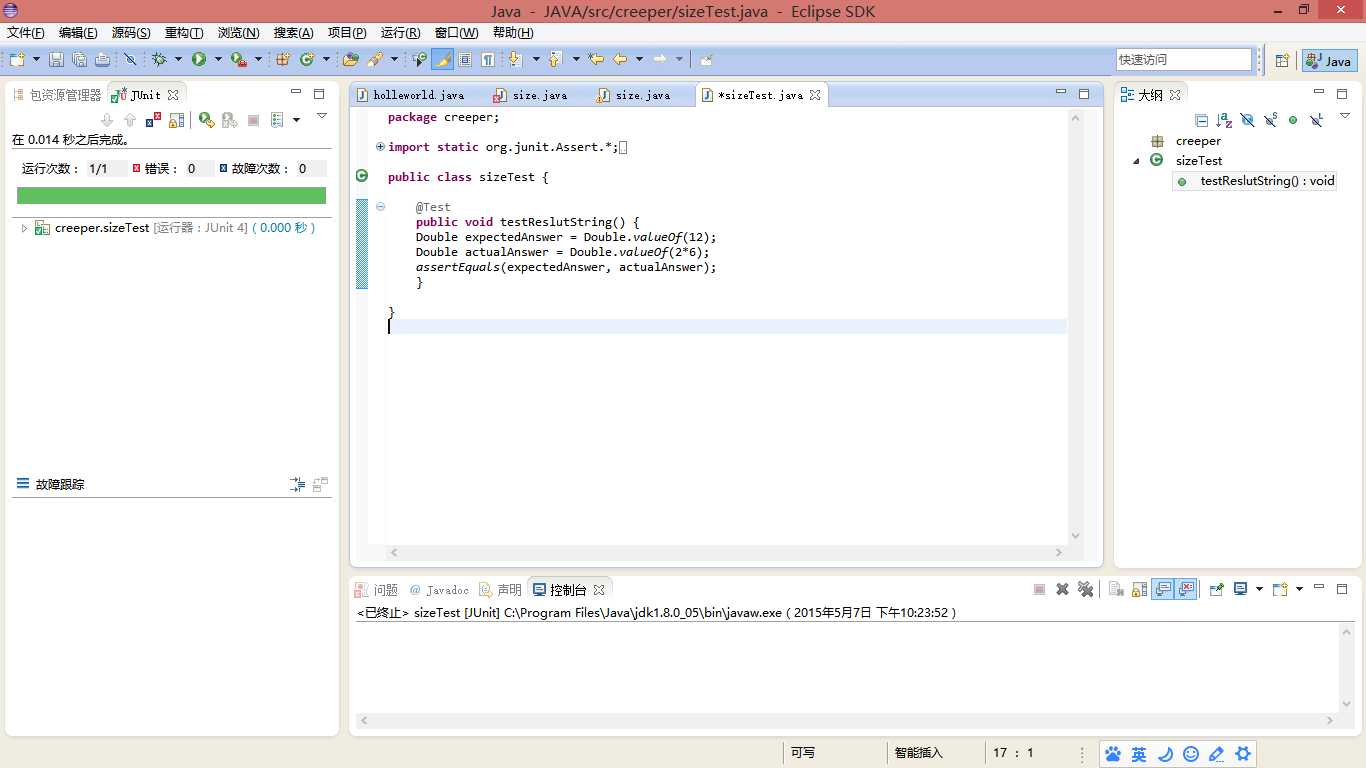
测试条为绿色,说明测试结果与预期结果相同,程序没有问题
总结:
经过对JUnit 的了解,简单对之前写的计算器代码做个测试,收获颇丰:JUnit作为最佳实践测试任何可能的错误。单元测试不是用来证明是对的,而是为了证明没有错。JUnit还有更强大的功能等着我们去探索。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/weixiaobaobao/p/4503829.html