标签:
1- 问题描述
Given a roman numeral, convert it to an integer.
Input is guaranteed to be within the range from 1 to 3999.
2- 罗马数字[1]
罗马数字共有7个,即I(1)、V(5)、X(10)、L(50)、C(100)、D(500)和M(1000)。按照下述的规则可以表示任意正整数。需要注意的是罗马数字中没有“0”,与进位制无关。一般认为罗马数字只用来记数,而不作演算。
 )表示,而是用XCIX(
)表示,而是用XCIX(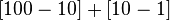 )表示。(等同于阿拉伯数字每位数字分别表示。)
)表示。(等同于阿拉伯数字每位数字分别表示。) )倍。
)倍。数码限制:
3- 思路分析
两种思路:从左向右、从右向左^_^
左 —> 右:从前向后遍历罗马数字,如果某个数比前一个数小,则加上该数。反之,减去前一个数的两倍然后加上该数。详见[2]
左 <— 右:如果当前数比前一位小,则减去该数,否则加上。
4- Python实现(从右往左遍历)
1 class Solution: 2 # @param {string} s 3 # @return {integer} 4 def romanToInt(self, s): 5 r2a = {‘I‘:1, ‘V‘:5, ‘X‘:10, ‘L‘:50, ‘C‘:100, ‘D‘:500, ‘M‘:1000} 6 sList = list(s.strip()) 7 nList = map(lambda x: r2a[x], sList) 8 nList.reverse() 9 10 # 方法1 11 res = 0 12 last = 0 # 上一位数值(右一位) 13 for i in nList: 14 if last <= i: # 不小于上一位,加 15 res += i 16 else: # 小于上一位,减 17 res -= i 18 last = i 19 return res 20 21 ‘‘‘ 22 # 方法2 23 s = [nList[0]] 24 for i in range(1, len(nList)): 25 if nList[i] >= nList[i-1]: 26 s.append(nList[i]) 27 else: 28 s.append(-nList[i]) 29 return sum(s) 30 31 32 # 方法3 33 digits = { "I":1, "V":5, "X":10, "L":50, "C":100, "D":500, "M":1000 } 34 len_s = len(s) 35 num = 0 36 for i in range(0, len_s - 1): 37 cur = digits[s[i]] 38 next = digits[s[i + 1]] 39 if cur >= next: 40 num += cur 41 else: 42 num -= cur 43 num += digits[s[len_s - 1]] 44 return num 45 ’‘’
[1] 罗马数字
[2] [leetcode] Roman to Integer
Roman to Integer [LeetCode 13]
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/freyr/p/4504118.html