标签:
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1972 Accepted Submission(s): 308
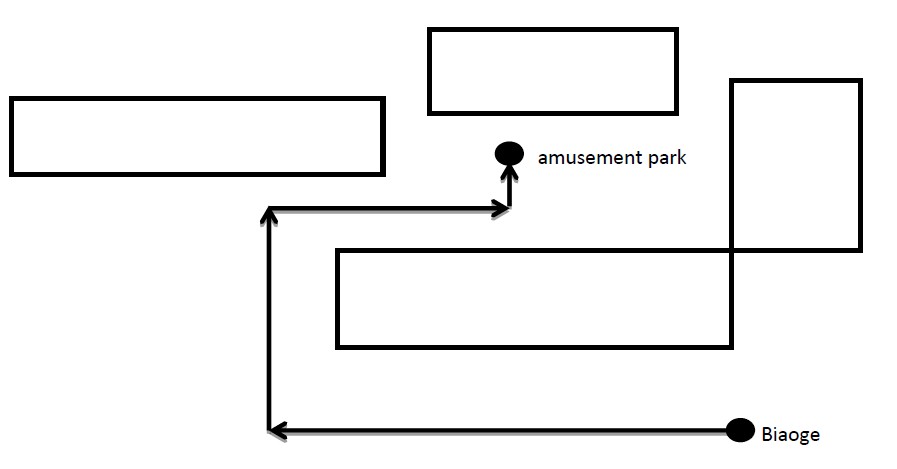

 可以走
可以走
 不可以走
不可以走1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <vector> 6 #include <queue> 7 #include <cmath> 8 #include <set> 9 #include <bitset> 10 #include <map> 11 using namespace std; 12 13 #define N 400 14 #define inf 999999999 15 16 int max(int x,int y){return x>y?x:y;} 17 int min(int x,int y){return x<y?x:y;} 18 int abs(int x,int y){return x<0?-x:x;} 19 20 int xx[]={-1,0,1,0}; 21 int yy[]={0,1,0,-1}; 22 int lx, ly; 23 int n; 24 25 struct node{ 26 int x1, y1, x2, y2; 27 }a[55]; 28 int llx[N], lly[N]; 29 map<int,int>mapx, mapy; 30 int stx, sty, endx, endy; 31 int sx, sy, ex, ey; 32 int g[N][N]; 33 int dp[N][N][4]; 34 bool visited[N][N][4]; 35 36 void creat(){ //建图 37 memset(g,0,sizeof(g)); 38 int i, j, k; 39 for(i=0;i<n;i++){ 40 for(j=mapx[a[i].x1];j<=mapx[a[i].x2];j++){ 41 g[j][mapy[a[i].y1]]=2;//printf("11111\n"); 42 g[j][mapy[a[i].y2]]=2; 43 } 44 for(j=mapy[a[i].y1]+1;j<mapy[a[i].y2];j++){ 45 g[mapx[a[i].x1]][j]=2; 46 g[mapx[a[i].x2]][j]=2; 47 } 48 for(j=mapx[a[i].x1]+1;j<mapx[a[i].x2];j++){ 49 for(k=mapy[a[i].y1]+1;k<mapy[a[i].y2];k++){ 50 g[j][k]=2; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 for(i=0;i<=lx;i++){ 55 for(j=0;j<=ly;j++){ 56 if(j<ly&&!g[i][j]&&g[i][j+1]) g[i][j+1]=1; 57 if(j>0&&!g[i][j]&&g[i][j-1]) g[i][j-1]=1; 58 if(i<lx&&!g[i][j]&&g[i+1][j]) g[i+1][j]=1; 59 if(i>0&&!g[i][j]&&g[i-1][j]) g[i-1][j]=1; 60 } 61 } 62 for(i=1;i<lx;i++){ 63 for(j=1;j<ly;j++){ 64 if(g[i][j]==2){ 65 if(!g[i+1][j+1]&&g[i-1][j]==1&&g[i][j-1]==1) g[i][j]=1; 66 if(!g[i-1][j-1]&&g[i-1][j]==1&&g[i][j-1]==1) g[i][j]=1; 67 if(!g[i+1][j-1]&&g[i-1][j]==1&&g[i][j+1]==1) g[i][j]=1; 68 if(!g[i-1][j+1]&&g[i-1][j]==1&&g[i][j+1]==1) g[i][j]=1; 69 if(!g[i-1][j+1]&&g[i+1][j]==1&&g[i][j-1]==1) g[i][j]=1; 70 if(!g[i+1][j-1]&&g[i+1][j]==1&&g[i][j-1]==1) g[i][j]=1; 71 if(!g[i-1][j-1]&&g[i+1][j]==1&&g[i][j+1]==1) g[i][j]=1; 72 if(!g[i+1][j+1]&&g[i+1][j]==1&&g[i][j+1]==1) g[i][j]=1; 73 } 74 if(g[i][j]==1&&g[i-1][j-1]==2&&g[i+1][j+1]==2&&!g[i+1][j-1]&&!g[i-1][j+1]) g[i][j]=2; 75 if(g[i][j]==1&&!g[i-1][j-1]&&!g[i+1][j+1]&&g[i+1][j-1]==2&&g[i-1][j+1]==2) g[i][j]=2; 76 } 77 } 78 } 79 80 struct G{ 81 int x, y, z, f; 82 }; 83 84 void bfs(){ 85 int i, j, k; 86 queue<G>Q; 87 G p, q; 88 for(i=0;i<=lx;i++){ 89 for(j=0;j<=ly;j++){ 90 for(k=0;k<4;k++){ 91 dp[i][j][k]=inf; 92 } 93 } 94 } 95 memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited)); 96 p.x=sx;p.y=sy;p.f=0; 97 for(i=0;i<4;i++){ 98 p.z=i; 99 dp[p.x][p.y][p.z]=0; 100 visited[p.x][p.y][p.z]=true; 101 Q.push(p); 102 } 103 while(!Q.empty()){ 104 p=Q.front();Q.pop(); 105 visited[p.x][p.y][p.z]=false; 106 for(i=0;i<4;i++){ 107 q.x=p.x+xx[i]; 108 q.y=p.y+yy[i]; 109 q.z=i; 110 if(p.f>0&&q.z!=p.f-1) continue; //之前的点是拐角的话,必须按照走特定的方向 111 if(q.x<0||q.x>lx||q.y<0||q.y>ly) continue; 112 if(p.f>0) q.f=0; 113 if(g[q.x][q.y]==2){ //拐角判断 114 if(!g[q.x-1][q.y-1]&&!g[q.x+1][q.y+1]){ 115 if(q.z==0) q.f=1+1; 116 else if(q.z==3) q.f=2+1; 117 else if(q.z==1) q.f=0+1; 118 else if(q.z==2) q.f=3+1; 119 } 120 else if(!g[q.x+1][q.y-1]&&!g[q.x-1][q.y+1]){ 121 if(q.z==0) q.f=3+1; 122 else if(q.z==3) q.f=0+1; 123 else if(q.z==1) q.f=2+1; 124 else if(q.z==2) q.f=1+1; 125 } 126 else continue; 127 } 128 else q.f=0; 129 if(q.z==p.z){ 130 if(dp[q.x][q.y][q.z]>dp[p.x][p.y][p.z]){ 131 dp[q.x][q.y][q.z]=dp[p.x][p.y][p.z]; 132 if(!visited[q.x][q.y][q.z]){ 133 Q.push(q); 134 visited[q.x][q.y][q.z]=true; 135 } 136 } 137 } 138 else{ 139 if(dp[q.x][q.y][q.z]>dp[p.x][p.y][p.z]+1){ 140 dp[q.x][q.y][q.z]=dp[p.x][p.y][p.z]+1; 141 if(!visited[q.x][q.y][q.z]){ 142 Q.push(q); 143 visited[q.x][q.y][q.z]=true; 144 } 145 } 146 } 147 } 148 } 149 } 150 151 main() 152 { 153 int i, j, k; 154 int len1, len2; 155 while(scanf("%d %d %d %d",&stx,&sty,&endx,&endy)==4){ 156 if(!stx&&!sty&&!endx&&!endy) break; 157 len1=len2=0; 158 llx[len1++]=stx; 159 llx[len1++]=endx; 160 lly[len2++]=sty; 161 lly[len2++]=endy; 162 scanf("%d",&n); 163 for(i=0;i<n;i++){ 164 scanf("%d %d %d %d",&a[i].x1,&a[i].y1,&a[i].x2,&a[i].y2); 165 llx[len1++]=a[i].x1; 166 llx[len1++]=a[i].x2; 167 lly[len2++]=a[i].y1; 168 lly[len2++]=a[i].y2; 169 } 170 sort(llx,llx+len1); 171 sort(lly,lly+len2); 172 lx=ly=1; 173 mapx.clear(); 174 mapy.clear(); 175 for(i=0;i<len1;i++){ 176 if(mapx.find(llx[i])==mapx.end()){ 177 mapx[llx[i]]=lx;lx+=2; 178 } 179 } 180 for(i=0;i<len2;i++){ 181 if(mapy.find(lly[i])==mapy.end()){ 182 mapy[lly[i]]=ly;ly+=2; 183 } 184 } 185 creat(); 186 /* for(i=0;i<len1;i++) printf("%d ",mapx[llx[i]]); 187 cout<<endl; 188 for(i=0;i<=lx;i++){ 189 for(j=0;j<=ly;j++){ 190 printf("%d ",g[i][j]); 191 } 192 cout<<endl; 193 }*/ 194 sx=mapx[stx];ex=mapx[endx]; 195 sy=mapy[sty];ey=mapy[endy]; 196 bfs(); 197 int ans=inf; 198 for(i=0;i<4;i++){ 199 ans=min(ans,dp[ex][ey][i]); 200 } 201 if(ans!=inf) printf("%d\n",ans); 202 else printf("-1\n"); 203 } 204 }
O5YBIE)DJ(TD~SJ`5E309C.png)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/qq1012662902/p/4511997.html