标签:
网络拓扑:参考:http://blog.csdn.net/lastsweetop/article/details/9065667
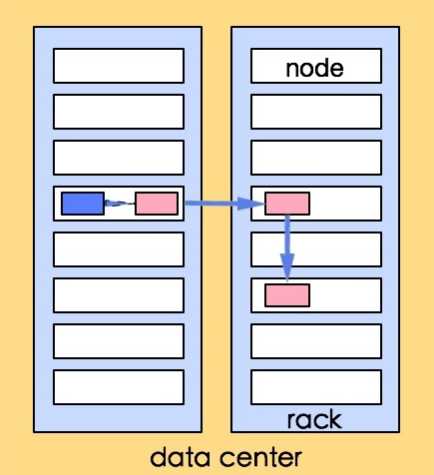
分布式的集群通常包含非常多的机器,由于受到机架槽位和交换机网口的限制,通常大型的分布式集群都会跨好几个机架,由多个机架上的机器共同组成一个分布式集群。机架内的机器之间的网络速度通常都会高于跨机架机器之间的网络速度,并且机架之间机器的网络通信通常受到上层交换机间网络带宽的限制。
在Hadoop中把网络看做一个树,两个节点之间的距离是它们到最近的共同祖先的距离总和。该树中的层次是没有预先设定的,但是对于数据中心、机架和正在运行的节点通常可以设定等级的。
distance(/D1/R1/H1,/D1/R1/H1)=0 同一节点中的进程(相同的datanode)
distance(/D1/R1/H1,/D1/R1/H2)=2 同一机架上的不同节点(同一rack下的不同datanode)
distance(/D1/R1/H1,/D1/R1/H4)=4 同一数据中心中不同机架上的节点(同一IDC下的不同datanode)
distance(/D1/R1/H1,/D2/R3/H7)=6 不同数据中心中的节点(不同IDC下的datanode)
Hadoop无法自行定义网络拓扑结构,它需要我们能够理解并辅助定义。(如果网络是平铺的(仅有单一层次),可以不需要进行配置)。
The HDFS and the Map/Reduce components are rack-aware.
The NameNode and the JobTracker obtains the rack id of the slaves in the cluster by invoking an API resolve in an administrator configured module. The API resolves the slave‘s DNS name (also IP address) to a rack id. What module to use can be configured using the configuration item topology.node.switch.mapping.impl. The default implementation of the same runs a script/command configured using topology.script.file.name. If topology.script.file.name is not set, the rack id /default-rack is returned for any passed IP address. The additional configuration in the Map/Reduce part is mapred.cache.task.levels which determines the number of levels (in the network topology) of caches. So, for example, if it is the default value of 2, two levels of caches will be constructed - one for hosts (host -> task mapping) and another for racks (rack -> task mapping).
副本存放:
namenode节点选择一个datanode节点去存储block副本得过程就叫做副本存放,这个过程的策略其实就是在可靠性和读写带宽间得权衡。
那么我们来看两个极端现象:
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/java-cjt/p/4524701.html