标签:
7种结构型模式:适配器模式、装饰模式、代理模式、外观模式、桥接模式、组合模式、享元模式。其中对象的适配器模式是各种模式的起源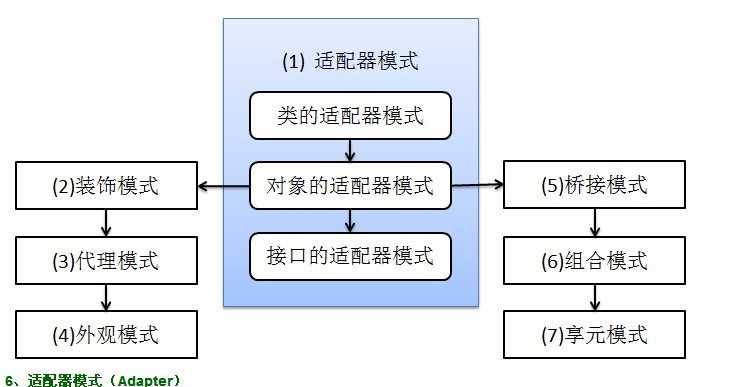
/**
* @author liubo
*
*/
public class Source {
public void method1() {
System.out.println("thid is original method1");
}
}
/**
* @author liubo
*
*/
public class Source {
public void method1() {
System.out.println("thid is original method1");
}
}
/**
* @author liubo
*
*/
public class Adapter extends Source implements Targetable {
public void method2() {
System.out.println("this is the targetable method");
}
}
/**
* @author liubo
*
*/
public class AdapterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Targetable target = new Adapter();
target.method1();
target.method2();
}
}
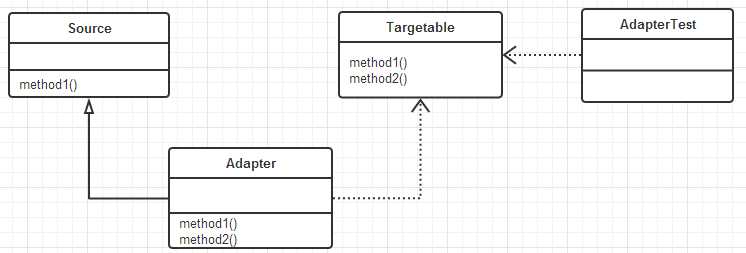
对象的适配器模式
基本思路和类的适配器模式相同,只是将Adapter类作修改,这次不继承Source类,而是持有Source类的实例,以达到解决兼容性的问题。看图:

只需要修改Adapter类的源码即可:
测试类:
输出与第一种一样,只是适配的方法不同而已。
第三种适配器模式是接口的适配器模式,接口的适配器是这样的:有时我们写的一个接口中有多个抽象方法,当我们写该接口的实现类时,必须实现该接口的所有方法,这明显有时比较浪费,因为并不是所有的方法都是我们需要的,有时只需要某一些,此处为了解决这个问题,我们引入了接口的适配器模式,借助于一个抽象类,该抽象类实现了该接口,实现了所有的方法,而我们不和原始的接口打交道,只和该抽象类取得联系,所以我们写一个类,继承该抽象类,重写我们需要的方法就行。看一下类图:

这个很好理解,在实际开发中,我们也常会遇到这种接口中定义了太多的方法,以致于有时我们在一些实现类中并不是都需要。看代码:
抽象类Wrapper2:
测试输出:
the sourceable interface‘s first Sub1!
the sourceable interface‘s second Sub2!
达到了我们的效果!
讲了这么多,总结一下三种适配器模式的应用场景:
类的适配器模式:当希望将一个类转换成满足另一个新接口的类时,可以使用类的适配器模式,创建一个新类,继承原有的类,实现新的接口即可。
对象的适配器模式:当希望将一个对象转换成满足另一个新接口的对象时,可以创建一个Wrapper类,持有原类的一个实例,在Wrapper类的方法中,调用实例的方法就行。
接口的适配器模式:当不希望实现一个接口中所有的方法时,可以创建一个抽象类Wrapper,实现所有方法,我们写别的类的时候,继承抽象类即可。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/liubo6/p/4526532.html