标签:
当需要为服务器增加一个自定义的扩展功能时,需要用到模块,相当于Nginx给开发者提供的一个模板范式。
比如现在实现一个书签收藏网站的signin功能,用Flask框架可以这样实现:
@app.route(‘/signin‘, methods=[‘GET‘, ‘POST‘])
def web_signin():
if request.method == ‘GET‘:
return redirect(url_for(‘web‘))
if request.method == ‘POST‘:
name = request.form.get(‘username‘, None)
session[‘username‘] = name
password = request.form.get(‘password‘, None)
db = LinkDB()
if name.strip()==‘‘ or password.strip()==‘‘:
return redirect(url_for(‘web‘))
if db.has_user(name, password):
return render_template(‘page.html‘)
else:
return ‘用户名或密码错误‘
它实现的功能就是解析用户GET和POST过来的数据,然后构造相应的响应。这和Nginx的handler模块所做的工作相似。
Nginx本身做的工作实际很少,当它接到一个HTTP请求时,它仅仅是通过查找配置文件将此次请求映射到一个location block,而此location中所配置的各个指令则会启动不同的模块去完成工作,因此模块可以看做Nginx真正的劳动工作者。下图表示一次请求和相应的完整过程。
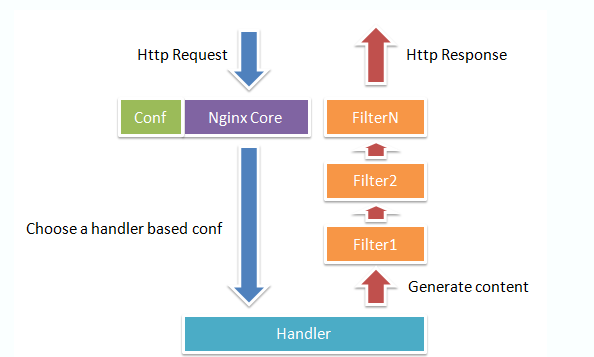
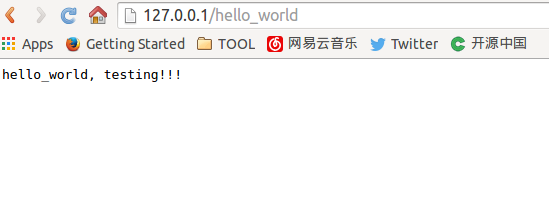
现在在浏览器中输入http://127.0.0.1/hello_world,让浏览器显示hello_world, testing!!!怎么实现呢?这需要我们编写一个hello handler模块。
开发一个模块,需要定义一个ngx_module_t类型的变量来说明这个模块的信息。它定义在/nginx/src/core/ngx_config_file中。
struct ngx_module_s {
ngx_uint_t ctx_index;
ngx_uint_t index;
ngx_uint_t spare0;
ngx_uint_t spare1;
ngx_uint_t spare2;
ngx_uint_t spare3;
ngx_uint_t version;
void *ctx;
ngx_command_t *commands;
ngx_uint_t type;
ngx_int_t (*init_master)(ngx_log_t *log);
ngx_int_t (*init_module)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
ngx_int_t (*init_process)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
ngx_int_t (*init_thread)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
void (*exit_thread)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
void (*exit_process)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
void (*exit_master)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
//...
};
hello模块定义如下:
ngx_module_t ngx_http_hello_world_module = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_http_hello_world_module_ctx,
ngx_http_hello_world_commands,
NGX_HTTP_MODULE,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};
模块的编写步骤是:
ngx_http_hello_world_handler中实现。static ngx_int_t ngx_http_hello_world_handler(ngx_http_request_t* r) {
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_buf_t* b;
ngx_chain_t out[2];
ngx_http_hello_world_loc_conf_t* hlcf;
hlcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_hello_world_module);
// 设置 request 的 header
r->headers_out.content_type.len = sizeof("text/plain") - 1;
r->headers_out.content_type.data = (u_char*)"text/plain";
// 分配缓冲区的内存空间
b = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_buf_t));
// 第 1 块缓冲区
out[0].buf = b;
out[0].next = &out[1];
// 本模块中,缓冲区只需要写入数据,所以只设置 pos 和 last
b->pos = (u_char*)"hello_world, ";
b->last = b->pos + sizeof("hello_world, ") - 1;
b->memory = 1; // 标示缓冲区是内存缓冲
// 分配缓冲区的内存空间
b = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_buf_t));
// 第 2 块缓冲区
out[1].buf = b;
out[1].next = NULL;
// 本模块中,缓冲区只需要写入数据,所以只设置 pos 和 last
b->pos = hlcf->output_words.data;
b->last = hlcf->output_words.data + (hlcf->output_words.len);
b->memory = 1; // 标示缓冲区是内存缓冲
b->last_buf = 1; // 标示整个响应最后一个缓冲区,nginx会立即发送缓冲的所有数据
// 设置 request 的 header
r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_OK;
r->headers_out.content_length_n = hlcf->output_words.len + sizeof("hello_world, ") - 1;
// 发送 request
rc = ngx_http_send_header(r);
if (rc == NGX_ERROR || rc > NGX_OK || r->header_only) {
return rc;
}
return ngx_http_output_filter(r, &out[0]);
}
在Nginx文件夹下
mkdir ngx_http_hello_world_module
cd ngx_http_hello_world_module
touch ngx_http_hello_world_module.c
touch config
ngx_http_hello_world_module.c是主要的函数,
config是配置文件。
在配置文件中加入
ngx_addon_name=ngx_http_hello_module
HTTP_MODULES="$HTTP_MODULES ngx_http_hello_world_module"
NGX_ADDON_SRCS="$NGX_ADDON_SRCS $ngx_addon_dir/ngx_http_hello_world_module.c"
这个config文件的内容就是告诉nginx的编译脚本,该如何进行编译。
./configure --add-module=/home/hy/Desktop/nginx/ngx_http_hello_world_module
make
make install
add-module后接上文中新建目录的路径。
在/usr/local/nginx/conf路径下的nginx.conf文件中加入
location /hello_world
{
hello_world testing!!!;
}
访问http://127.0.0.1/hello_world即可看见成功的页面。
http://blog.csdn.net/poechant/article/details/7627828
http://kb.cnblogs.com/page/98352/
http://wiki.nginx.org/3rdPartyModules
标签:
原文地址:http://my.oschina.net/lvyi/blog/423842