标签:style class blog code java http
ArrayList是实现了List接口的动态数组.与java中的数组相比,它的容量能动态增长.ArrayList的三大特点:
① 底层采用数组结构
② 有序
③ 非同步
下面我们从ArrayList的增加元素、获取元素、删除元素三个方面来学习ArrayList。
ArrayList添加元素
因为ArrayList是采用数组实现的,其源代码比较简单.首先我们来看ArrayList的add(E e).以下代码版本是jdk7。
public boolean add(E e) { // 检查数组容量 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); elementData[size++] = e; return true; } private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { // 计算数组长度 if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { // 模数自增,fail-fast机制 modCount++; // 如果超过当前数组的长度,调用grow()方法增加数组长度 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } private void grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 新的容量=oldCapacity+oldCapacity/2,这里相比jdk6有变化 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // 创建新的数组,把原数组的数据添加到新数组里面 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
从上面的代码可以看到,add()方法关键点在于数组容量的处理,添加元素只是将在elementData[size++]处保存e的引用.从grow()方法中我们看到,数组的动态增长时的新长度=原长度+原长度/2.这里和jdk6中有点区别,具体可以查看下jdk6的源码.
ArrayList中还可以添加元素到指定位置.add(index,element):
public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // 将index之后的元素往后挪一个位置,腾出elementData[i]的位置 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; }
代码中看到,add(index,element)方法会造成element[index+1]到element[size]的元素往后挪动,极端情况下(size+1>element.length),要新建数组并且挪动所有元素.这会带来额外的开销,所以,如果不是特别需要,建议使用add(e)方法添加元素.
ArrayList获取元素
ArrayList底层是采用数组存储,所以最简单也最快的获取方式是通过脚标访问.
public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); }
接下来,我们看下ArrayList的遍历.ArrayList有三种遍历方式:脚标访问,foreach循环遍历,迭代器遍历.下面我们来对比下三种方式的效率.
public class ArrayListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for(int i = 0;i<10000000;++i){ list.add(i); } System.out.println("access by index spend time : "+printListByIndex(list)); System.out.println("access by for spend time : "+printListByFor(list)); System.out.println("access by iterator spend time : "+printListByIterator(list)); } public static long printListByIndex(List list) { if(checkList(list)){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("list is null or list.size=0"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i=0;i<list.size();++i){ list.get(i); } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); return endTime - startTime; } public static long printListByFor(List list) { if(checkList(list)){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("list is null or list.size=0"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(Object obj : list){ // } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); return endTime - startTime; } public static long printListByIterator(List list) { if(checkList(list)){ throw new IllegalArgumentException("list is null or list.size=0"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Iterator iterator = list.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ // iterator.next(); } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); return endTime - startTime; } public static boolean checkList(List list){ return null==list || list.size()<1; } }
运行结果如图:
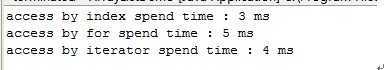
ps:每次运行的结果可能不同,但在我的几次试验中,用脚标访问的方式是最快的,使用foreach循环是相对而言最慢的.
由上面的运行结果,建议遍历ArrayList时使用脚标遍历,这样效率最高.
ArrayList删除元素
public E remove(int index) { //检查index合法性 rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); // 如果移除最后一个元素,则elementData[--size]==null, // 如果不是最后一个元素,则将index之后的元素往前挪一个位置 int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; }
由上面的代码,可以知道,如果删除的元素不是最后一个元素,会造成元素的移动.这也会带来额外的开销.
由上面的学习和分析,我们可以得出如下结论:ArrayList底层采用的数组结构,对get(index)、set(index,element)操作具备很好的性能,但频繁的增删会影响ArrayList的性能(数组中元素位置移动的开销或者新建数组转移元素带来的开销).所以ArrayList并不适合频繁增删元素的应用场景,另外,在初始化ArrayList时,如果能够预估ArrayList容量来设置初始容量,会减少ArrayList转移元素时的开销,从而提升应用程序的性能.
以上就是本人对ArrayList源码的学习,欢迎大家一起交流讨论!
由JDK源码学习ArrayList,布布扣,bubuko.com
标签:style class blog code java http
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/heavenyes/p/3791937.html