标签:style class blog code java http
先验算法是实现频繁项挖掘的一种经典算法,利用关联式规则不断扩展频繁项子集以获得全部的频繁项集合。解释一下关联式规则,所谓关联式是指在大量的数据中找出的项与项之间的关系。例如消费者购买了产品A,一般都会购买产品B,这就是一条关联式。
先验算法被设计用来处理包含事务的数据库,这里的每一个事务都被当成是一组项集,给定一个阈值C,我们需要找出至少出现C次的事务子集(即子项)。这边这个C值就是最小支持度,规定了一个项集出现多少次才能被认为是一个频繁项。
先验算法的核心思想基于以下一个事实:一个项集是频繁项集,其所有子集一定是频繁项集;一个项集不是频繁项,其超集一定不是频繁项集。那么我们在寻找事务中的最大频繁项的过程中,只需要扩展是频繁项的子集,这就大大地缩减了搜索空间。下面是该算法的伪代码实现:

其中T代表的是事务集合,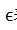 表示最小支持度,Li对应的是第i次迭代得到的频繁项集,Ci表示对于第i次迭代的候选项集。伪代码的第一行遍历了事务中的所有项,统计每一项出现的频数,保留所有出现次数高于最小支持度的项。
表示最小支持度,Li对应的是第i次迭代得到的频繁项集,Ci表示对于第i次迭代的候选项集。伪代码的第一行遍历了事务中的所有项,统计每一项出现的频数,保留所有出现次数高于最小支持度的项。
优点:
缺点:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.HashMap; 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.List; 6 import java.util.Map; 7 import java.util.Set; 8 9 /** 10 * 这是一个简单的先验算法的实现,包含了如下假设: 11 * 1.事务对应一个TID和一个项集合,每个项对应一个int类型的数值,保证同一个事务内部的项唯一 12 * 2.算法在实现方式上还存在很多可以优化剪枝的部分,这里省略了优化,是结构更加清晰 13 * 3.这只是一个样例程序 14 * @author LuZhou 15 * @email 448287076@qq.com 16 */ 17 public class Aprior { 18 19 20 public static class TransactionItem { 21 22 private Integer itemValue; 23 24 public TransactionItem( int i ){ 25 itemValue = i; 26 } 27 28 @Override 29 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 30 TransactionItem it = (TransactionItem) obj; 31 return this.itemValue == it.itemValue; 32 } 33 34 35 @Override 36 public String toString() { 37 return itemValue.toString(); 38 } 39 40 @Override 41 public int hashCode() { 42 return itemValue % 31; 43 } 44 } 45 46 47 public static class ItemCollection{ 48 private Set<TransactionItem> items = new HashSet<Aprior.TransactionItem>(); 49 50 public ItemCollection(){ 51 } 52 53 public ItemCollection(int[] items){ 54 for (int i = 0; i < items.length; i++) { 55 this.add(new TransactionItem(items[i])); 56 } 57 } 58 59 public boolean itemContains(Set<TransactionItem> sub){ 60 return items.containsAll(sub); 61 } 62 63 @Override 64 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 65 ItemCollection ic = (ItemCollection) obj; 66 return ic.items.containsAll(items) && 67 items.containsAll(ic.items); 68 } 69 70 @Override 71 public int hashCode() { 72 int v = 0; 73 for (TransactionItem ts : items) { 74 v = ( v + ts.hashCode() ) % 31; 75 } 76 return v; 77 } 78 79 public boolean contains(ItemCollection sub){ 80 return items.containsAll(sub.items); 81 } 82 83 public boolean containItem(TransactionItem item){ 84 return items.contains(item); 85 } 86 87 public Set<TransactionItem> getItems(){ 88 return items; 89 } 90 91 public void add(TransactionItem item){ 92 items.add(item); 93 } 94 95 @Override 96 public String toString() { 97 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 98 sb.append("{"); 99 for (TransactionItem item : getItems()) { 100 sb.append( item.toString() ); 101 sb.append(","); 102 } 103 sb.append("}"); 104 return sb.toString(); 105 } 106 107 } 108 109 public static class Transaction{ 110 private int id; 111 private ItemCollection ic; 112 113 public Transaction(int id , ItemCollection itemCollection){ 114 this.id = id; 115 this.ic = itemCollection; 116 } 117 118 public boolean itemContains(ItemCollection sub){ 119 return ic.contains(sub); 120 } 121 122 public Set<TransactionItem> getItems(){ 123 return ic.getItems(); 124 } 125 126 } 127 128 private Set<TransactionItem> restItems = new HashSet<Aprior.TransactionItem>(); 129 private List<Transaction> transactions = new ArrayList<Aprior.Transaction>(); 130 131 //统计一项的出现次数 132 private int itemsFrequency( ItemCollection sub ){ 133 int frequency = 0 ; 134 135 for (Transaction t : transactions) { 136 if(t.itemContains(sub)){ 137 frequency ++; 138 } 139 } 140 141 return frequency; 142 } 143 144 //确定扩展项是否为频繁项 145 private Set< ItemCollection > filterWithThreadshold( 146 Set< ItemCollection > items, int threadshold ){ 147 148 Set< ItemCollection > result = new HashSet<ItemCollection>(); 149 for (ItemCollection subItems : items) { 150 if( threadshold <= itemsFrequency(subItems)) 151 result.add(subItems); 152 } 153 154 return result; 155 } 156 157 //根据现有的子项集获取所有的可能扩展 158 private Set< ItemCollection > extendItems( Set< ItemCollection > current){ 159 Set< ItemCollection > extend = new HashSet<Aprior.ItemCollection>(); 160 161 //找出剩余的项集 162 restItems.clear(); 163 for (ItemCollection ic : current) { 164 for (TransactionItem item : ic.getItems()) { 165 restItems.add(item); 166 } 167 } 168 169 //需要找到当前频繁项子集 170 for (ItemCollection itemCollection : current) { 171 for (TransactionItem rest : restItems) { 172 if( ! itemCollection.containItem(rest) ){ 173 //找到一个b 不属于 频繁项集 A 但是存在于剩余项中 用其构造其余的子项 174 extend.add( buildCollection( itemCollection, rest )); 175 } 176 } 177 178 } 179 180 return extend; 181 } 182 183 //result = ic.items & item 184 private ItemCollection buildCollection(ItemCollection ic,TransactionItem item){ 185 ItemCollection ex = new ItemCollection(); 186 187 Iterator<TransactionItem> it = ic.getItems().iterator(); 188 while(it.hasNext()){ 189 ex.add( it.next() ); 190 } 191 192 ex.add(item); 193 194 return ex; 195 } 196 197 198 //初始化剩余项 199 private Set<ItemCollection> initCollection( int threadshold ){ 200 201 Map<TransactionItem , Integer> tc = new HashMap<Aprior.TransactionItem, Integer>(); 202 203 for ( Transaction t : transactions ) { 204 205 for ( TransactionItem item : t.getItems() ) { 206 207 if( !restItems.contains(item) ){ 208 restItems.add(item); 209 tc.put(item, 1); 210 }else 211 tc.put( item, 1 + tc.get(item) ); 212 213 } 214 } 215 216 217 Set<ItemCollection> collection = new HashSet<Aprior.ItemCollection>(); 218 219 Iterator< TransactionItem > it = tc.keySet().iterator(); 220 while( it.hasNext() ){ 221 TransactionItem item = it.next(); 222 if( threadshold <= tc.get( item ) ){ 223 ItemCollection ic = new ItemCollection(); 224 ic.add( item ); 225 collection.add( ic ); 226 } 227 } 228 229 return collection; 230 } 231 232 233 /** 234 * 找出频繁项 235 * @param threadshold 最小支持度 236 * @return 237 */ 238 public Set< ItemCollection > frequentItem( int threadshold ){ 239 240 Set< ItemCollection > current = initCollection( threadshold ); 241 Set< ItemCollection > result = new HashSet<Aprior.ItemCollection>(); 242 243 while( current.size() > 0 ){ 244 245 result.addAll( current ); 246 247 Set<ItemCollection> extendList = extendItems( current ); 248 249 current = filterWithThreadshold( extendList, threadshold ); 250 251 } 252 253 254 return result; 255 } 256 257 public void addTransaction(Transaction ts){ 258 transactions.add(ts); 259 } 260 261 262 public static void main(String args[]){ 263 264 final int MINSUPPROT = 2; 265 Aprior aprior = new Aprior(); 266 /** 267 * 数据集包括 268 * T1 {1,3,4} 269 * T2 {2,3,5} 270 * T3 {1,2,3,5} 271 * T4 {2,5} 272 * 最小支持度为2,请最大频繁项 273 */ 274 aprior.addTransaction(new Transaction(1, new ItemCollection(new int[]{1,3,4}))); 275 aprior.addTransaction(new Transaction(2, new ItemCollection(new int[]{2,3,5}))); 276 aprior.addTransaction(new Transaction(3, new ItemCollection(new int[]{1,2,3,5}))); 277 aprior.addTransaction(new Transaction(4, new ItemCollection(new int[]{2,5}))); 278 279 System.out.println(aprior.frequentItem( MINSUPPROT )); 280 281 } 282 283 284 }
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apriori_algorithm
http://rakesh.agrawal-family.com/papers/vldb94apriori.pdf
http://www.cnblogs.com/gaizai/archive/2010/03/31/1701573.html
标签:style class blog code java http
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yahokuma/p/3769969.html