标签:style class blog code http color
STL中的每个算法都非常精妙,
ForwardIter lower_bound(ForwardIter first, ForwardIter last,const _Tp& val)算法返回一个非递减序列[first, last)中的第一个大于等于值val的位置。
ForwardIter upper_bound(ForwardIter first, ForwardIter last, const _Tp& val)算法返回一个非递减序列[first, last)中第一个大于val的位置。
lower_bound和upper_bound如下图所示:
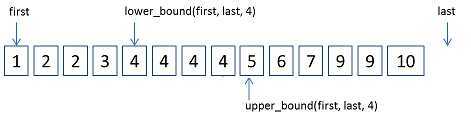
1, lower_bound
这个序列中可能会有很多重复的元素,也可能所有的元素都相同,为了充分考虑这种边界条件,STL中的lower_bound算法总体上是才用了二分查找的方法,但是由于是查找序列中的第一个出现的值大于等于val的位置,所以算法要在二分查找的基础上做一些细微的改动。
1 int my_lower_bound(int *array, int size, int key) 2 { 3 int first = 0, last = size-1; 4 int middle, pos=0; //需要用pos记录第一个大于等于key的元素位置 5 6 while(first < last) 7 { 8 middle = (first+last)/2; 9 if(array[middle] < key){ //若中位数的值小于key的值,我们要在右边子序列中查找,这时候pos可能是右边子序列的第一个 10 first = middle + 1; 11 pos = first; 12 } 13 else{ 14 last = middle; //若中位数的值大于等于key,我们要在左边子序列查找,但有可能middle处就是最终位置,所以我们不移动last, 15 pos = last; //而是让first不断逼近last。 16 } 17 } 18 return pos; 19 }
2, upper_bound
upper_bound返回的是最后一个大于等于val的位置,也是有一个新元素val进来时的插入位置
1 int my_upper_bound(int *array, int size, int key) 2 { 3 int first = 0, last = size-1; 4 int middle, pos = 0; 5 6 while(first < last) 7 { 8 middle = (first+last)/2; 9 if(array[middle] > key){ //当中位数大于key时,last不动,让first不断逼近last 10 last = middle; 11 pos = last; 12 } 13 else{ 14 first = middle + 1; //当中位数小于等于key时,将first递增,并记录新的位置 15 pos = first; 16 } 17 } 18 return pos; 19 }
[STL] lower_bound和upper_bound,布布扣,bubuko.com
标签:style class blog code http color
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/diegodu/p/3795077.html