标签:des style blog http color get
dict 是redis中最重要的数据结构,存放结构体redisDb中。
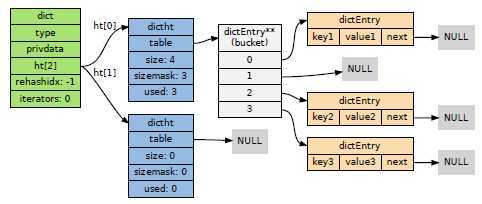
typedef struct dict { dictType *type; void *privdata; dictht ht[2]; int rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */ int iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */ } dict;
其中type是特定结构的处理函数
typedef struct dictType { unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key); void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key); void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj); int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2); void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key); void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj); } dictType;
privdata就是上述函数的参量,dict中定义了两个哈希表dictht,作为rehash使用,一开始加入的键值对放入ht[0]中,它像普通的hash表一样使用链表法来避免冲突,当ht中的加入的数据个数超过他的容量,就开始rehash,将数据转移到容量更大的ht[1]中,rehash的过程并不是上来就把整个ht[0]一次性的放到ht[1]中,它使用的是渐进式的转移。
渐进式rehash 主要由_dictRehashStep 和dictRehashMilliseconds 两个函数进行:
• _dictRehashStep 用于对数据库字典、以及哈希键的字典进行被动rehash ;
• dictRehashMilliseconds 则由Redis 服务器常规任务程序(server cron job)执行,用于对数据库字典进行主动rehash ;
主要操作在dictRehash中进行。
/* Performs N steps of incremental rehashing. Returns 1 if there are still * keys to move from the old to the new hash table, otherwise 0 is returned. * Note that a rehashing step consists in moving a bucket (that may have more * than one key as we use chaining) from the old to the new hash table. */ int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) { if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0; while(n--) { dictEntry *de, *nextde; /* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */ if (d->ht[0].used == 0) { zfree(d->ht[0].table); d->ht[0] = d->ht[1]; _dictReset(&d->ht[1]); d->rehashidx = -1; return 0; } /* Note that rehashidx can‘t overflow as we are sure there are more * elements because ht[0].used != 0 */ assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned)d->rehashidx); while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) d->rehashidx++; de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx]; /* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */ while(de) { unsigned int h; nextde = de->next; /* Get the index in the new hash table */ h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask; de->next = d->ht[1].table[h]; d->ht[1].table[h] = de; d->ht[0].used--; d->ht[1].used++; de = nextde; } d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL; d->rehashidx++; } return 1; }
dict中的iterators有两种,安全迭代器和不安全迭代器。这相当于c++中的const_iterator和iterator。用来遍历字典中的数据,即dictEntry。
typedef struct dictEntry { void *key; union { void *val; uint64_t u64; int64_t s64; } v; struct dictEntry *next; } dictEntry;
dictEntry可以看做是链表的节点,存放于dictht->table中。如果发生key的哈希值碰撞,则在将发生碰撞的key插入到next上形成链表结构。上面讲的rehash操作就是为了避免链表过长,增加bucket的容量。
redis源码解析之dict数据结构,布布扣,bubuko.com
标签:des style blog http color get
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/loujiayu/p/3797792.html