标签:style class blog code java http
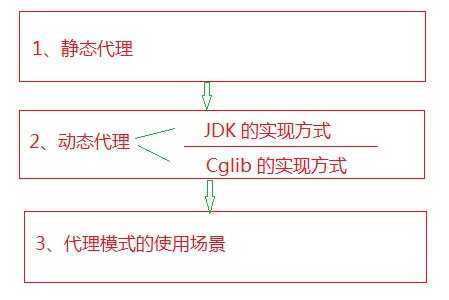
java 的代理模式可以有静态代理模式和动态代理模式。下面的内容,大体的流程如下:
所谓代理模式,就是代理处理其他类的操作。具体点就是,类似于北京的中介公司一样,自己没有实际的房屋和出租权,而是通过跟真正的房东商谈,代理出租房屋,从中谋取利益。这种模式的好处是,隐藏了真正的处理类,可以使代理类的操作简单化,而代理的操作可以复杂和有更多的操作。就如中介公司如果把房东透漏给你了,你就不会再经过中介去租房屋了,中介也不能再中介抽取钱了。
(I)静态代理模式
首先,看一下简单的静态代理模式。静态代理模式的类图如下:
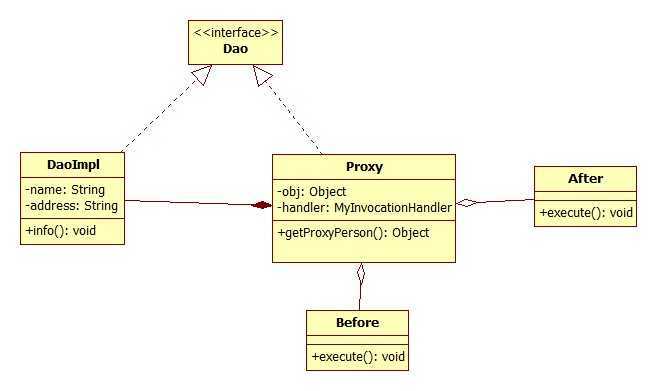
其中,我定义了接口 PersonDao,实现类 PersonDaoImpl,代理类 PersonProxy,另外两个 After、Before 是我设置的后置方法类和前置方法的封装类。具体的代码如下:
(1)Dao 接口:
1 /** 2 * 0.0.0.1 3 */ 4 package com.gaoqing.common.mode; 5 6 /** 7 * Person 到 接口 8 * @author gaoqing 9 * 2014-6-17 10 */ 11 public interface PersonDao { 12 13 public void info(); 14 15 }
上述 Dao 接口,只是定义了一个简单的 info() 方法,打印出用户信息的操作。
(2)DaoImpl 实现类:
1 /** 2 * 0.0.0.1 3 */ 4 package com.gaoqing.common.mode; 5 6 /** 7 * Person dao 的实现类 8 * @author gaoqing 9 * 2014-6-17 10 */ 11 public class PersonDaoImpl implements PersonDao { 12 13 private String name; 14 private String address; 15 /** 16 * 构造方法 17 */ 18 public PersonDaoImpl() { 19 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * 构造方法 24 */ 25 public PersonDaoImpl(String name, String address) { 26 super(); 27 this.name = name; 28 this.address = address; 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * @see com.gaoqing.common.mode.PersonDao#info() 33 */ 34 @Override 35 public void info() { 36 37 System.out.println("姓名:" + name + "," + "地址:" + address); 38 39 } 40 41 /** 42 * @return the name 43 */ 44 public String getName() { 45 return name; 46 } 47 48 /** 49 * @param name the name to set 50 */ 51 public void setName(String name) { 52 this.name = name; 53 } 54 55 /** 56 * @return the address 57 */ 58 public String getAddress() { 59 return address; 60 } 61 62 /** 63 * @param address the address to set 64 */ 65 public void setAddress(String address) { 66 this.address = address; 67 } 68 }
(3)代理类如下:
1 /** 2 * 0.0.0.1 3 */ 4 package com.gaoqing.common.mode; 5 6 /** 7 * 静态代理方法 8 * @author gaoqing 9 * 2014-6-21 10 */ 11 public class StaticProxyTest implements PersonDao{ 12 13 /** PersonDao 方法 */ 14 private PersonDao personDao; 15 /** 前置方法对象 */ 16 private Before before; 17 /** 后置方法对象 */ 18 private After after; 19 20 /** 21 * 构造方法 22 */ 23 public StaticProxyTest() { 24 25 } 26 27 /** 28 * 构造方法 29 * @param personDao PersonDao 对象 30 * @param before 前置方法对象 31 * @param after 后置方法对象 32 */ 33 public StaticProxyTest(PersonDao personDao, Before before, After after) { 34 super(); 35 this.personDao = personDao; 36 this.before = before; 37 this.after = after; 38 } 39 40 /** 41 * @see com.gaoqing.common.mode.PersonDao#info() 42 */ 43 @Override 44 public void info() { 45 //执行前置方法 46 before.execute(); 47 48 //执行具体的请求方法 49 personDao.info(); 50 51 //执行后置方法 52 after.execute(); 53 } 54 55 /** 56 * @return the personDao 57 */ 58 public PersonDao getPersonDao() { 59 return personDao; 60 } 61 62 /** 63 * @param personDao the personDao to set 64 */ 65 public void setPersonDao(PersonDao personDao) { 66 this.personDao = personDao; 67 } 68 69 /** 70 * @return the before 71 */ 72 public Before getBefore() { 73 return before; 74 } 75 76 /** 77 * @param before the before to set 78 */ 79 public void setBefore(Before before) { 80 this.before = before; 81 } 82 83 /** 84 * @return the after 85 */ 86 public After getAfter() { 87 return after; 88 } 89 90 /** 91 * @param after the after to set 92 */ 93 public void setAfter(After after) { 94 this.after = after; 95 } 96 }
上面的代理类的特点是:和 DaoImpl 的实现类一样,都实现了 PersonDao 接口,只是在自己的 info() 方法,调用实现类的具体方法,而在自己的操作中,添加了更多别的附加的操作。
(II)动态代理模式
如果只是仅仅使用简单的静态代理也可以实现某些面向切面的编程,比如插入日志什么的,可以将插入的内容放到 Before 和 After 类中。但是,如果我需要很多的代理类的时候,就需要像上面一样,写很多的类似的 PersonProxy 类,这样就很类了。随之产生的一种处理方式就出现了--动态代理。这样就可以只编写一个代理类,去代理所有自己想要代理类,更可以把那些相同的代码,分离到某些类中,集中进行管理,方便而且优雅。
(II.1)JDK 实现
我依旧使用上面的 PersonDao 和 PersonDaoImpl,具体的类图如下:
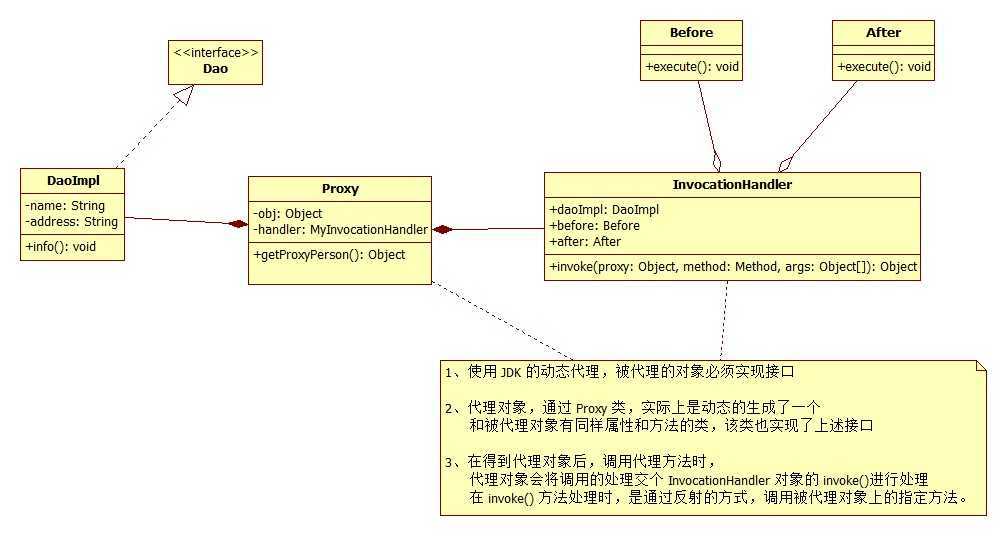
正如,在类图中的注释,这种动态代理的方式,是在 JDK 中,动态的生成一个类,该类和代理类一样,实现了相同的接口,拥有和代理类同样的方法。
(4)动态代理类如下:
1 /** 2 * 0.0.0.1 3 */ 4 package com.gaoqing.common.mode; 5 6 import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; 7 8 /** 9 * 代理类 10 * @author gaoqing 11 * 2014-6-17 12 */ 13 public class ProxyPerson { 14 15 /** 被代理对象 */ 16 private Object obj; 17 18 /** 调用处理类对象 */ 19 private MyInvocationHandler handler; 20 21 /** 22 * 构造方法 23 */ 24 public ProxyPerson() { 25 26 } 27 28 /** 29 * 构造方法 30 * @param obj 被代理的对象 31 * @param handler 具体的调用处理类 32 */ 33 public ProxyPerson(Object obj, MyInvocationHandler handler) { 34 super(); 35 this.obj = obj; 36 this.handler = handler; 37 } 38 39 /** 40 * 生成代理类 41 * @author 高青 42 * 2014-6-17 43 * @return obj 代理类 44 */ 45 public Object getProxyPerson(){ 46 47 return Proxy.newProxyInstance(obj.getClass().getClassLoader(), obj.getClass().getInterfaces(), handler); 48 } 49 50 /** 51 * @return the obj 52 */ 53 public Object getObj() { 54 return obj; 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * @param obj the obj to set 59 */ 60 public void setObj(Object obj) { 61 this.obj = obj; 62 } 63 64 /** 65 * @return the handler 66 */ 67 public MyInvocationHandler getHandler() { 68 return handler; 69 } 70 71 /** 72 * @param handler the handler to set 73 */ 74 public void setHandler(MyInvocationHandler handler) { 75 this.handler = handler; 76 } 77 }
(4)具体的调用处理类如下:
1 /** 2 * 0.0.0.1 3 */ 4 package com.gaoqing.common.mode; 5 6 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; 7 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 8 9 /** 10 * 自定义的调用处理器 11 * @author gaoqing 12 * 2014-6-17 13 */ 14 public class MyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { 15 16 /** 被代理的类 */ 17 private Object obj; 18 19 /** 方法前对象 */ 20 private Before before; 21 22 /** 方法后对象 */ 23 private After after; 24 25 /** 26 * 构造方法 27 */ 28 public MyInvocationHandler() { 29 30 } 31 32 /** 33 * 构造方法 34 */ 35 public MyInvocationHandler(Object obj) { 36 super(); 37 this.obj = obj; 38 } 39 40 /** 41 * 构造方法 42 */ 43 public MyInvocationHandler(Object obj, Before before, After after) { 44 super(); 45 this.obj = obj; 46 this.before = before; 47 this.after = after; 48 } 49 50 /** 51 * @see java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler#invoke(java.lang.Object, java.lang.reflect.Method, java.lang.Object[]) 52 */ 53 @Override 54 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) 55 throws Throwable { 56 /* 57 * 代理的具体处理方式 58 */ 59 60 //方法前操作 61 before.execute(); 62 63 Object invokeValue = method.invoke(obj, args); 64 65 //方法后操作 66 after.execute(); 67 68 return invokeValue; 69 } 70 71 /** 72 * @return the obj 73 */ 74 public Object getObj() { 75 return obj; 76 } 77 78 /** 79 * @param obj the obj to set 80 */ 81 public void setObj(Object obj) { 82 this.obj = obj; 83 } 84 85 /** 86 * @return the before 87 */ 88 public Before getBefore() { 89 return before; 90 } 91 92 /** 93 * @param before the before to set 94 */ 95 public void setBefore(Before before) { 96 this.before = before; 97 } 98 99 /** 100 * @return the after 101 */ 102 public After getAfter() { 103 return after; 104 } 105 106 /** 107 * @param after the after to set 108 */ 109 public void setAfter(After after) { 110 this.after = after; 111 } 112 }
(II.2)Cglib 实现
从上面可以看到,使用 JDK 自带的接口实现动态代理的话,需要被代理的对象必须实现一个接口。这样,就存在了一种限制,如果我需要代理那些普通的类那该怎么办呢?这个时候可以使用 cglib 类库,它可以实现代理那些没有实现接口的类。Cglib 是一个优秀的动态代理框架,它的底层使用 ASM 在内存中动态的生成被代理类的一个子类。具体的 ASM 的使用,目前还没用过啊,现在只是简单的使用以下 cglib 。
使用 cglib 框架实现动态代理时,需要导入两个包,一个是其依赖的 asm.jar,一个是 cglib.jar。注意:需要导入合适的包,如果包的版本不对,是会报错的,如果报错了,可以试着换下 cglib 的 jar 包。在这个代理的过程中,主要用到了 cglib 的:
(1)Enhancer – 主要的增强类,类似于 JDK 的 Proxy 类,产生具体的代理类
(2)MethodInterceptor – 主要的方法拦截类,它是Callback接口的子接口,需要用户实现,就是将代理类请求的方法,进行拦截到被代理类对象进行处理,类似于 JDK 的 InvocationHandler 接口的 invoke()方法
(3)MethodProxy – JDK的java.lang.reflect.Method类的代理类,可以方便的实现对源对象方法的调用
具体的实现如下:
1 /** 2 * 0.0.0.1 3 */ 4 package com.gaoqing.common.mode; 5 6 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 7 8 import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer; 9 import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor; 10 import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy; 11 12 /** 13 * 使用 Cglib 框架实现的代理类 14 * @author gaoqing 15 * 2014-6-19 16 */ 17 public class DynamicProxyByCGLIBTest { 18 19 /** 20 * 构造方法 21 */ 22 public DynamicProxyByCGLIBTest() { 23 24 } 25 26 /** 27 * 主线程方法 28 * @author 高青 29 * 2014-6-19 30 * @param args 参数字符串集 31 * @return void 空 32 */ 33 public static void main(String[] args) { 34 35 //代理类 36 final PersonDaoImpl personDaoImpl = new PersonDaoImpl("gaoqing", "beijing"); 37 38 //得到增强类 39 Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer(); 40 41 //设置增强类的父类 42 enhancer.setSuperclass(PersonDaoImpl.class); 43 44 enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptor() { 45 46 @Override 47 public Object intercept(Object target, Method method, Object[] args, 48 MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable { 49 50 Object invoke = method.invoke(personDaoImpl, args); //也可以使用 proxy 的 invokeSupre(target, args) 51 52 return invoke; 53 } 54 }); 55 PersonDaoImpl personDaoImplProxy = (PersonDaoImpl) enhancer.create(); 56 57 personDaoImplProxy.info(); 58 59 } 60 }
(III)代理模式的使用场景
上述就是简单的代理模式的实现。动态代理的方式,可以实现面向 AOP 的编程,具体的使用是大家知道的动态的插入日志,添加事物,记录用户的操作记录等。具体的框架应用就是 Spring 的 AOP 实现,为它们提供为方法的Interception(拦截),在 hibernate 中,使用 Cglib 来代理单端single-ended(多对一和一对一)关联等等。
标签:style class blog code java http
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/gaoqing/p/3801679.html