标签:
可以直接调用,也可以通过window来调用,接收一个函数作为回调,返回一个ID值,通过把这个ID值传给window.cancelAnimationFrame()可以取消该次动画。
requestAnimationFrame(callback)//callback为回调函数
模拟一个进度条动画,初始div宽度为1px,在step函数中将进度加1然后再更新到div宽度上,在进度达到100之前,一直重复这一过程。
为了演示方便加了一个运行按钮(看不到例子请刷新)。
<div id="test" style="width:1px;height:17px;background:#0f0;">0%</div>
<input type="button" value="Run" id="run"/>
复制代码
window.requestAnimationFrame = window.requestAnimationFrame || window.mozRequestAnimationFrame || window.webkitRequestAnimationFrame || window.msRequestAnimationFrame;
var start = null;
var ele = document.getElementById("test");
var progress = 0;
function step(timestamp) {
progress += 1;
ele.style.width = progress + "%";
ele.innerHTML=progress + "%";
if (progress < 100) {
requestAnimationFrame(step);
}
}
requestAnimationFrame(step);
document.getElementById("run").addEventListener("click", function() {
ele.style.width = "1px";
progress = 0;
requestAnimationFrame(step);
}, false); 下面是由Paul Irish及其他贡献者放在GitHub Gist上的代码片段,用于在浏览器不支持requestAnimationFrame情况下的回退,回退到使用setTmeout的情况。当然,如果你确定代码是工作在现代浏览器中,下面的代码是不必的。
(function() {
var lastTime = 0;
var vendors = [‘ms‘, ‘moz‘, ‘webkit‘, ‘o‘];
for (var x = 0; x < vendors.length && !window.requestAnimationFrame; ++x) {
window.requestAnimationFrame = window[vendors[x] + ‘RequestAnimationFrame‘];
window.cancelAnimationFrame = window[vendors[x] + ‘CancelAnimationFrame‘] || window[vendors[x] + ‘CancelRequestAnimationFrame‘];
}
if (!window.requestAnimationFrame) window.requestAnimationFrame = function(callback, element) {
var currTime = new Date().getTime();
var timeToCall = Math.max(0, 16 - (currTime - lastTime));
var id = window.setTimeout(function() {
callback(currTime + timeToCall);
}, timeToCall);
lastTime = currTime + timeToCall;
return id;
};
if (!window.cancelAnimationFrame) window.cancelAnimationFrame = function(id) {
clearTimeout(id);
};
}());
CSS3支持的动画效果有限
由于CSS3动画的贝塞尔曲线是一个标准3次方曲线(详见:贝塞尔曲线与CSS3动画、SVG和canvas的基情),因此,只能是:Linear,Sine,Quad,Cubic,Expo等,但对于Back,Bounce等缓动则只可观望而不可亵玩焉。
下面这张图瞅瞅,那些波澜壮阔的曲线都是CSS3木有的~~
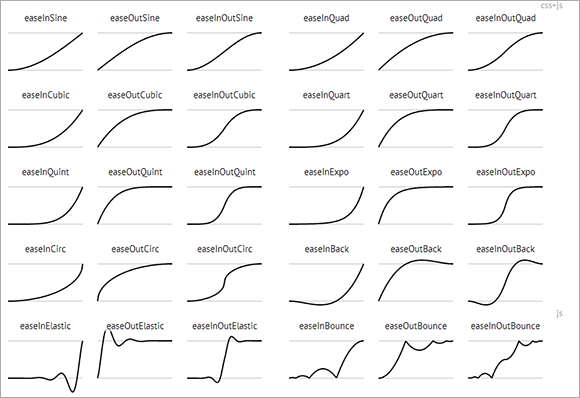
先给大家普及下缓动(Tween)知识吧:
每个效果都分三个缓动方式,分别是(可采用后面的邪恶记忆法帮助记忆):
每周动画效果都有其自身的算法。我们都知道jQuery UI中就有缓动,As脚本也内置了缓动,其中的运动算法都是一致的。我特意弄了一份,哦呵呵呵~~(因为较高,滚动显示),或GitHub访问:
/*
* Tween.js
* t: current time(当前时间)
* b: beginning value(初始值)
* c: change in value(变化量)
* d: duration(持续时间)
*/
var Tween = {
Linear: function(t, b, c, d) { return c*t/d + b; },
Quad: {
easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) {
return c * (t /= d) * t + b;
},
easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
return -c *(t /= d)*(t-2) + b;
},
easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * t * t + b;
return -c / 2 * ((--t) * (t-2) - 1) + b;
}
},
Cubic: {
easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) {
return c * (t /= d) * t * t + b;
},
easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
return c * ((t = t/d - 1) * t * t + 1) + b;
},
easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * t * t*t + b;
return c / 2*((t -= 2) * t * t + 2) + b;
}
},
Quart: {
easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) {
return c * (t /= d) * t * t*t + b;
},
easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
return -c * ((t = t/d - 1) * t * t*t - 1) + b;
},
easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * t * t * t * t + b;
return -c / 2 * ((t -= 2) * t * t*t - 2) + b;
}
},
Quint: {
easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) {
return c * (t /= d) * t * t * t * t + b;
},
easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
return c * ((t = t/d - 1) * t * t * t * t + 1) + b;
},
easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * t * t * t * t * t + b;
return c / 2*((t -= 2) * t * t * t * t + 2) + b;
}
},
Sine: {
easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) {
return -c * Math.cos(t/d * (Math.PI/2)) + c + b;
},
easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
return c * Math.sin(t/d * (Math.PI/2)) + b;
},
easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
return -c / 2 * (Math.cos(Math.PI * t/d) - 1) + b;
}
},
Expo: {
easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) {
return (t==0) ? b : c * Math.pow(2, 10 * (t/d - 1)) + b;
},
easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
return (t==d) ? b + c : c * (-Math.pow(2, -10 * t/d) + 1) + b;
},
easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
if (t==0) return b;
if (t==d) return b+c;
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * Math.pow(2, 10 * (t - 1)) + b;
return c / 2 * (-Math.pow(2, -10 * --t) + 2) + b;
}
},
Circ: {
easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) {
return -c * (Math.sqrt(1 - (t /= d) * t) - 1) + b;
},
easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
return c * Math.sqrt(1 - (t = t/d - 1) * t) + b;
},
easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return -c / 2 * (Math.sqrt(1 - t * t) - 1) + b;
return c / 2 * (Math.sqrt(1 - (t -= 2) * t) + 1) + b;
}
},
Elastic: {
easeIn: function(t, b, c, d, a, p) {
var s;
if (t==0) return b;
if ((t /= d) == 1) return b + c;
if (typeof p == "undefined") p = d * .3;
if (!a || a < Math.abs(c)) {
s = p / 4;
a = c;
} else {
s = p / (2 * Math.PI) * Math.asin(c / a);
}
return -(a * Math.pow(2, 10 * (t -= 1)) * Math.sin((t * d - s) * (2 * Math.PI) / p)) + b;
},
easeOut: function(t, b, c, d, a, p) {
var s;
if (t==0) return b;
if ((t /= d) == 1) return b + c;
if (typeof p == "undefined") p = d * .3;
if (!a || a < Math.abs(c)) {
a = c;
s = p / 4;
} else {
s = p/(2*Math.PI) * Math.asin(c/a);
}
return (a * Math.pow(2, -10 * t) * Math.sin((t * d - s) * (2 * Math.PI) / p) + c + b);
},
easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d, a, p) {
var s;
if (t==0) return b;
if ((t /= d / 2) == 2) return b+c;
if (typeof p == "undefined") p = d * (.3 * 1.5);
if (!a || a < Math.abs(c)) {
a = c;
s = p / 4;
} else {
s = p / (2 *Math.PI) * Math.asin(c / a);
}
if (t < 1) return -.5 * (a * Math.pow(2, 10* (t -=1 )) * Math.sin((t * d - s) * (2 * Math.PI) / p)) + b;
return a * Math.pow(2, -10 * (t -= 1)) * Math.sin((t * d - s) * (2 * Math.PI) / p ) * .5 + c + b;
}
},
Back: {
easeIn: function(t, b, c, d, s) {
if (typeof s == "undefined") s = 1.70158;
return c * (t /= d) * t * ((s + 1) * t - s) + b;
},
easeOut: function(t, b, c, d, s) {
if (typeof s == "undefined") s = 1.70158;
return c * ((t = t/d - 1) * t * ((s + 1) * t + s) + 1) + b;
},
easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d, s) {
if (typeof s == "undefined") s = 1.70158;
if ((t /= d / 2) < 1) return c / 2 * (t * t * (((s *= (1.525)) + 1) * t - s)) + b;
return c / 2*((t -= 2) * t * (((s *= (1.525)) + 1) * t + s) + 2) + b;
}
},
Bounce: {
easeIn: function(t, b, c, d) {
return c - Tween.Bounce.easeOut(d-t, 0, c, d) + b;
},
easeOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
if ((t /= d) < (1 / 2.75)) {
return c * (7.5625 * t * t) + b;
} else if (t < (2 / 2.75)) {
return c * (7.5625 * (t -= (1.5 / 2.75)) * t + .75) + b;
} else if (t < (2.5 / 2.75)) {
return c * (7.5625 * (t -= (2.25 / 2.75)) * t + .9375) + b;
} else {
return c * (7.5625 * (t -= (2.625 / 2.75)) * t + .984375) + b;
}
},
easeInOut: function(t, b, c, d) {
if (t < d / 2) {
return Tween.Bounce.easeIn(t * 2, 0, c, d) * .5 + b;
} else {
return Tween.Bounce.easeOut(t * 2 - d, 0, c, d) * .5 + c * .5 + b;
}
}
}
}
Math.tween = Tween; 看个球的动画效果
http://www.zhangxinxu.com/study/201309/requestanimationframe-tween-easeoutbounce.html
相关源代码可以参见demo页面源代码
funFall = function() {
var start = 0, during = 100;
var _run = function() {
start++;
var top = Tween.Bounce.easeOut(start, objBall.top, 500 - objBall.top, during);
ball.css("top", top);
shadowWithBall(top); // 投影跟随小球的动 if (start < during) requestAnimationFrame(_run);
};
_run();
};
requestanimationframe用法一二(总结别人的)
标签:
原文地址:http://my.oschina.net/u/2328177/blog/464516