标签:
原文:索引键的唯一性(4/4):非唯一聚集索引上的唯一和非唯一非聚集索引在上一篇文章里,我谈了唯一聚集索引上的唯一和非唯一非聚集索引的区别。在这篇文章里,我想谈下非唯一聚集索引上的唯一和非唯一聚集索引的区别。我们都知道,SQL Server内部把非唯一聚集索引当作唯一聚集索引处理的。如果你定义了一个非唯一聚集索引,SQL Server会增加叫做uniquifier到你的索引记录,它导致你聚集索引的导航结构(B树的非叶子层)里,每条索引行都要用到4 bytes的开销。
下列代码再次创建我们的Customers表,这次在它上面定义非唯一聚集索引,最后定义2个非聚集索引,1个是唯一的,另1个是非唯一的。
1 -- Create a table with 393 length + 7 bytes overhead = 400 bytes 2 -- Therefore 20 records can be stored on one page (8.096 / 400) = 20,24 3 CREATE TABLE Customers 4 ( 5 CustomerID INT NOT NULL, 6 CustomerName CHAR(100) NOT NULL, 7 CustomerAddress CHAR(100) NOT NULL, 8 Comments CHAR(189) NOT NULL 9 ) 10 GO 11 12 -- Create a non unique clustered index on the previous created table 13 CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX idx_Customers ON Customers(CustomerID) 14 GO 15 16 -- Insert 80.000 records 17 DECLARE @i INT = 1 18 WHILE (@i <= 20000) 19 BEGIN 20 DECLARE @j INT = 1 21 INSERT INTO Customers VALUES 22 ( 23 @i, 24 ‘CustomerName‘ + CAST(@i AS CHAR) + CAST(@j AS CHAR), 25 ‘CustomerAddress‘ + CAST(@i AS CHAR), 26 ‘Comments‘ + CAST(@i AS CHAR) 27 ) 28 29 SET @j += 1; 30 31 INSERT INTO Customers VALUES 32 ( 33 @i, 34 ‘CustomerName‘ + CAST(@i AS CHAR) + CAST(@j AS CHAR), 35 ‘CustomerAddress‘ + CAST(@i AS CHAR), 36 ‘Comments‘ + CAST(@i AS CHAR) 37 ) 38 39 SET @j += 1; 40 41 INSERT INTO Customers VALUES 42 ( 43 @i, 44 ‘CustomerName‘ + CAST(@i AS CHAR) + CAST(@j AS CHAR), 45 ‘CustomerAddress‘ + CAST(@i AS CHAR), 46 ‘Comments‘ + CAST(@i AS CHAR) 47 ) 48 49 SET @j += 1; 50 51 INSERT INTO Customers VALUES 52 ( 53 @i, 54 ‘CustomerName‘ + CAST(@i AS CHAR) + CAST(@j AS CHAR), 55 ‘CustomerAddress‘ + CAST(@i AS CHAR), 56 ‘Comments‘ + CAST(@i AS CHAR) 57 ) 58 59 SET @i += 1 60 END 61 GO 62 63 -- Create a unique non clustered index on the clustered table 64 CREATE UNIQUE NONCLUSTERED INDEX idx_UniqueNCI_CustomerID 65 ON Customers(CustomerName) 66 GO 67 68 -- Create a non-unique non clustered index on the clustered table 69 CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX idx_NonUniqueNCI_CustomerID 70 ON Customers(CustomerName) 71 GO
我们通过DMV sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats查看索引的相关信息。
1 -- Retrieve physical information about the unique non-clustered index 2 SELECT * FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats 3 ( 4 DB_ID(‘ALLOCATIONDB‘), 5 OBJECT_ID(‘Customers‘), 6 2, 7 NULL, 8 ‘DETAILED‘ 9 ) 10 GO 11 12 -- Retrieve physical information about the non-unique non-clustered index 13 SELECT * FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats 14 ( 15 DB_ID(‘ALLOCATIONDB‘), 16 OBJECT_ID(‘Customers‘), 17 3, 18 NULL, 19 ‘DETAILED‘ 20 ) 21 GO
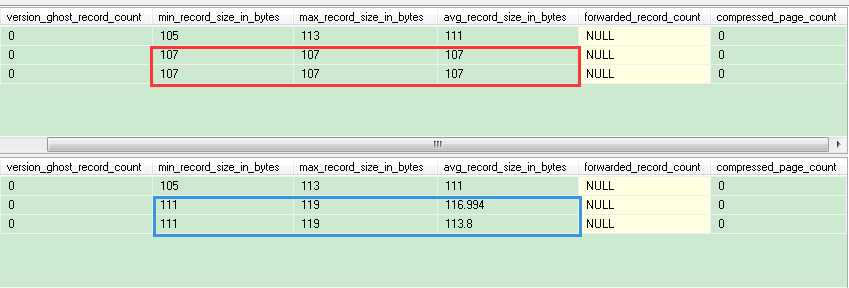
从图中我们可以看到,在导航层的唯一非聚集索引每个索引行占用107 bytes,而非唯一非聚集索引每个索引行平均占用117 bytes(最小111 bytes,最大119 bytes)。我们用DBCC PAGE分析下各自的根页。
1 TRUNCATE TABLE dbo.sp_table_pages 2 INSERT INTO dbo.sp_table_pages 3 EXEC(‘DBCC IND(ALLOCATIONDB, Customers, -1)‘) 4 5 SELECT * FROM dbo.sp_table_pages ORDER BY IndexLevel DESC
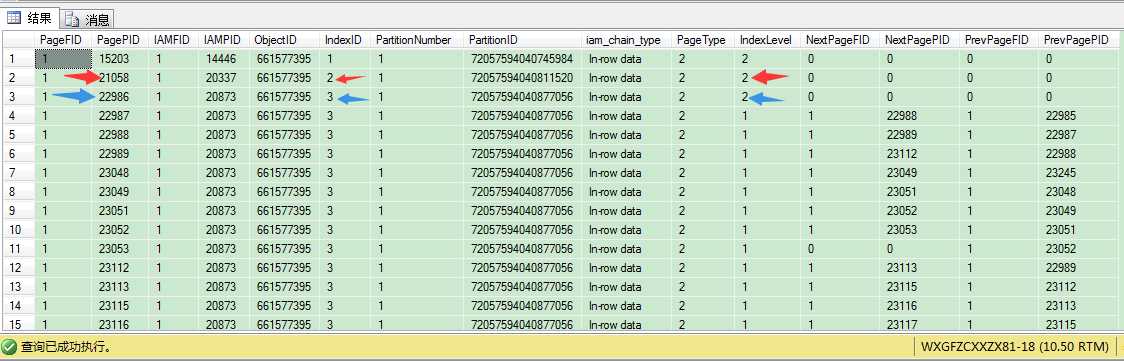
首先是唯一非聚集索引,它的根页是21058。
1 DBCC PAGE(ALLOCATIONDB, 1, 21058, 3) 2 GO 3 4 DBCC PAGE(ALLOCATIONDB, 1,21057,3) 5 GO
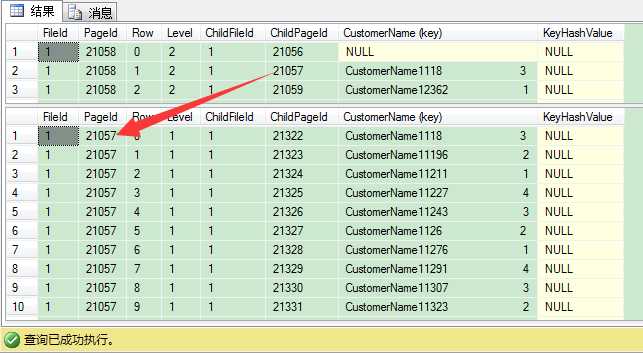
从图中我们可以看出,唯一非聚集索引在索引根层(还有中间层)只保存了唯一非聚集键,因为非聚集键本身就已经唯一了。
我们换参数1再来看看根页信息:
1 DBCC TRACEON(3604) 2 DBCC PAGE(ALLOCATIONDB, 1, 21058, 1) 3 GO
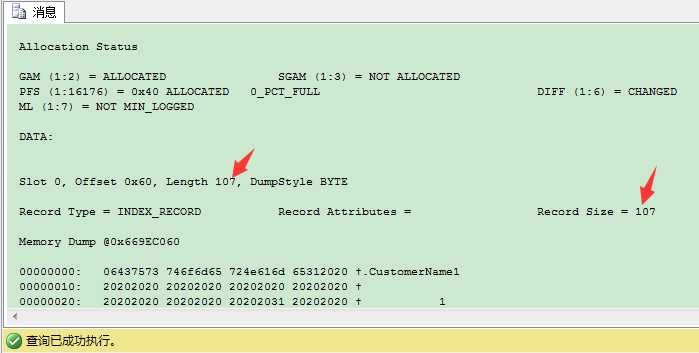
这107 bytes包含下列信息:
我们再来看看唯一非聚集索引的叶子页。
1 DBCC PAGE(ALLOCATIONDB, 1,21322,3) 2 GO
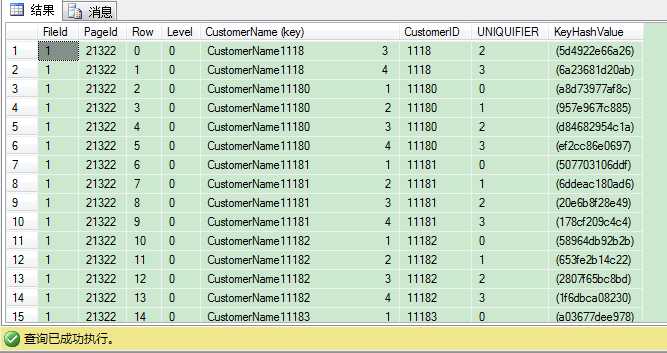
我们可以看出SQL Server通过非唯一聚集键和uniquifier来指向聚集表的对应记录。
这里我们可以得出结论:在非唯一聚集索引上的唯一非聚集索引只在叶子层使用4 bytes的uniquifier,因为这里SQL Server使用聚集键和uniquifier直接指向对应的记录。这个4 bytes的uniquifier在唯一非聚集索引的非叶子层(根层和中间层)不存在。
我们再来看看非唯一非聚集索引的根页,它的根页是22986。
1 DBCC PAGE(ALLOCATIONDB, 1, 22986, 3) 2 GO
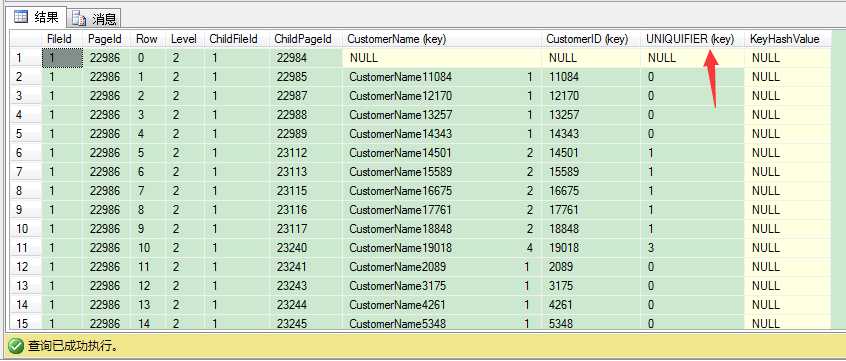
这里的根页输出信息非常有意思!索引记录的键必须设计为唯一。SQL Server如何让非唯一非聚集索引键唯一呢?非常简单——加下聚集键(CustomerID (key))(4 bytes)。但是聚集键这里默认还是不唯一的,因此SQL Server又加了uniquifier(4 bytes),因次当你uniquifier不为0的时候,每个索引行都有8 bytes的开销。当uniquifier为0时,你只要4 bytes的开销,因为这个情况下uniquifier并不物理保存在索引记录里,0是SQL Server自动假定的值。
我们再看看参数为1的信息:
1 DBCC TRACEON(3604) 2 DBCC PAGE(ALLOCATIONDB, 1, 22986, 1) 3 GO
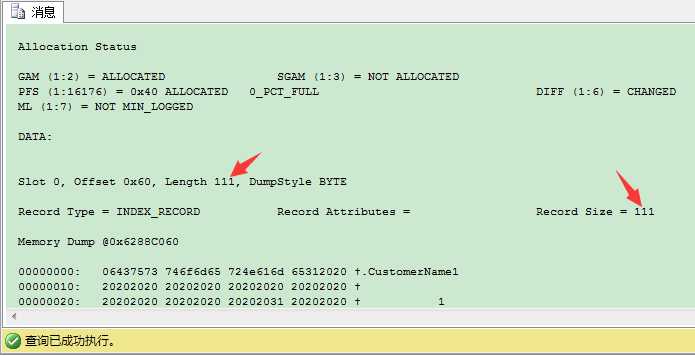
这111 bytes 包含下列信息:
刚才我们通过sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats知道非唯一非聚集索引的索引记录是111 bytes,最长是117 bytes。
我们来看看非唯一非聚集索引的叶子页:
1 DBCC PAGE(ALLOCATIONDB, 1,23308,3) 2 GO
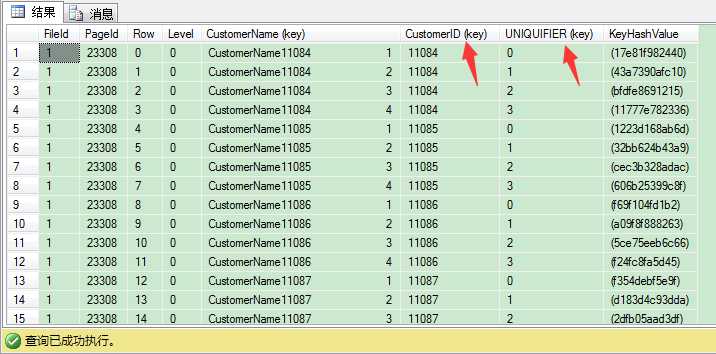
这和非唯一聚集索引上定义的唯一非聚集索引是一样的。叶子层通过聚集键(CustomerID)和uniquifier指向聚集表的对应记录。从这个例子我们可以看出,当你在非唯一聚集索引上定义非唯一非聚集索引时,会有巨大的开销(每个索引行 8 bytes),因为SQL Server内部要保证非聚集键唯一,这就需要大量的存储开销。
索引键的唯一性(4/4):非唯一聚集索引上的唯一和非唯一非聚集索引
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lonelyxmas/p/4576717.html