标签:
黑马程序员------IO(五)
1.1 操作对象(示例1)
ObjectInputStream与ObjectOutputStream
被操作的对象需要实现Serializable。
Serializable:用于给被序列化的类加入ID号,用于判断类和对象是否是同一个版本
类通过实现java.io.Serializable接口以启用序列化功能,Serializable只是一个标记接口。
1 示例1:
2 import java.io.*;
3
4 class ObjectStreamDemo
5 {
6 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
7 {
8 //writeObj();
9 readObj();
10 }
11 public static void readObj()throws Exception
12 {
13 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("obj.txt"));
14
15 Person p = (Person)ois.readObject();
16
17 System.out.println(p);
18 ois.close();
19 }
20
21 public static void writeObj()throws IOException
22 {
23 ObjectOutputStream oos =
24 new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("obj.txt"));
25
26 oos.writeObject(new Person("lisi0",399,"kr"));
27
28 oos.close();
29 }
30 }
2.1 管道流(示例2)
PipedInputStream和PipedOutputStream:输入输出可以直接进行连接,通过结合线程使用。
1 示例2:
2 import java.io.*;
3
4 class Read implements Runnable
5 {
6 private PipedInputStream in;
7 Read(PipedInputStream in)
8 {
9 this.in = in;
10 }
11 public void run()
12 {
13 try
14 {
15 byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
16
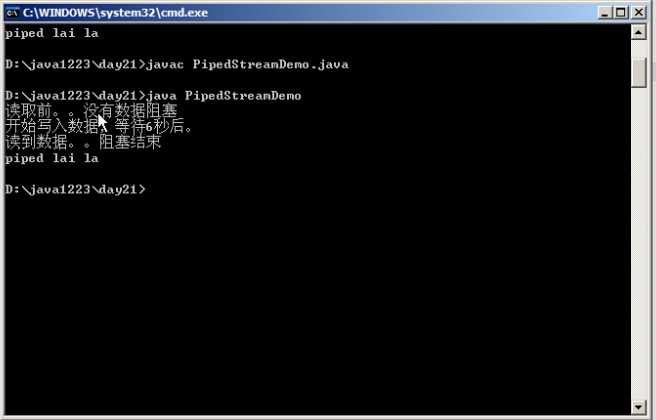
17 System.out.println("读取前。。没有数据阻塞");
18 int len = in.read(buf);
19 System.out.println("读到数据。。阻塞结束");
20
21
22
23 String s= new String(buf,0,len);
24
25 System.out.println(s);
26
27 in.close();
28
29 }
30 catch (IOException e)
31 {
32 throw new RuntimeException("管道读取流失败");
33 }
34 }
35 }
36
37 class Write implements Runnable
38 {
39 private PipedOutputStream out;
40 Write(PipedOutputStream out)
41 {
42 this.out = out;
43 }
44 public void run()
45 {
46 try
47 {
48 System.out.println("开始写入数据,等待6秒后。");
49 Thread.sleep(6000);
50 out.write("piped lai la".getBytes());
51 out.close();
52 }
53 catch (Exception e)
54 {
55 throw new RuntimeException("管道输出流失败");
56 }
57 }
58 }
59
60 class PipedStreamDemo
61 {
62 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
63 {
64
65 PipedInputStream in = new PipedInputStream();
66 PipedOutputStream out = new PipedOutputStream();
67 in.connect(out);
68
69 Read r = new Read(in);
70 Write w = new Write(out);
71 new Thread(r).start();
72 new Thread(w).start();
73
74
75 }
76 }
输出结果:
3.1 RandomAccessFile(示例3)
随机访问文件,自身具备读写的方法。
通过skipBytes(int x),seek(int x)等方法来达到随机访问。
该类不是算是IO体系中子类。
而是直接继承自Object。
但是它是IO包中成员。因为它具备读和写功能。
内部封装了一个数组,而且通过指针对数组的元素进行操作。
可以通过getFilePointer获取指针位置,
同时可以通过seek改变指针的位置。
其实完成读写的原理就是内部封装了字节输入流和输出流。
通过构造函数可以看出,该类只能操作文件。
而且操作文件还有模式:只读r,,读写rw等。
如果模式为只读 r。不会创建文件。会去读取一个已存在文件,如果该文件不存在,则会出现异常。
如果模式rw。操作的文件不存在,会自动创建。如果存则不会覆盖。
1 示例3:
2 class RandomAccessFileDemo
3 {
4 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
5 {
6 //writeFile_2();
7 //readFile();
8
9 //System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(258));
10
11 }
12
13 public static void readFile()throws IOException
14 {
15 RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("ran.txt","r");
16
17 //调整对象中指针。
18 //raf.seek(8*1);
19
20 //跳过指定的字节数
21 raf.skipBytes(8);
22
23 byte[] buf = new byte[4];
24
25 raf.read(buf);
26
27 String name = new String(buf);
28
29 int age = raf.readInt();
30
31
32 System.out.println("name="+name);
33 System.out.println("age="+age);
34
35 raf.close();
36
37
38 }
39
40 public static void writeFile_2()throws IOException
41 {
42 RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("ran.txt","rw");
43 raf.seek(8*0);
44 raf.write("周期".getBytes());
45 raf.writeInt(103);
46
47 raf.close();
48 }
49
50 public static void writeFile()throws IOException
51 {
52 RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("ran.txt","rw");
53
54 raf.write("李四".getBytes());
55 raf.writeInt(97);
56 raf.write("王五".getBytes());
57 raf.writeInt(99);
58
59 raf.close();
60 }
61 }
4.1 DataInputStream与DataOutputStream
可以用于操作基本数据类型的数据的流对象。
5.1 用于操作字节数组的流对象(示例4):
ByteArrayInputStream :在构造的时候,需要接收数据源,。而且数据源是一个字节数组。
ByteArrayOutputStream: 在构造的时候,不用定义数据目的,因为该对象中已经内部封装了可变长度的字节数组。
这就是数据目的地。
因为这两个流对象都操作的数组,并没有使用系统资源。
所以,不用进行close关闭。
在流操作规律讲解时:
源设备,
键盘 System.in,硬盘 FileStream,内存 ArrayStream。
目的设备:
控制台 System.out,硬盘FileStream,内存 ArrayStream。
用流的读写思想来操作数据。
1 示例4:
2 import java.io.*;
3 class ByteArrayStream
4 {
5 public static void main(String[] args)
6 {
7 //数据源。
8 ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream("ABCDEFD".getBytes());
9
10 //数据目的
11 ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
12
13 int by = 0;
14
15 while((by=bis.read())!=-1)
16 {
17 bos.write(by);
18 }
19
20
21
22 System.out.println(bos.size());
23 System.out.println(bos.toString());
24
25 // bos.writeTo(new FileOutputStream("a.txt"));
26
27 }
28 }
编码表的由来
计算机只能识别二进制数据,早期由来是电信号。为了方便应用计算机,让它可以识别各个国家的文字。
就将各个国家的文字用数字来表示,并一一对应,形成一张表,这就是编码表。
常见的编码表
ASCII:美国标准信息交换码,用一个字节的7位可以表示。
ISO8859-1:拉丁码表。欧洲码表,用一个字节的8位表示。
GB2312:中国的中文编码表。
GBK:中国的中文编码表升级,融合了更多的中文文字符号。
Unicode:国际标准码,融合了多种文字。
所有文字都用两个字节来表示,Java语言使用的就是unicode
UTF-8:最多用三个字节来表示一个字符。
......
示例5:
编码:字符串变成字节数组。
解码:字节数组变成字符串。
String-->byte[]; str.getBytes(charsetName);
byte[] -->String: new String(byte[],charsetName);
1 示例5:
2 import java.util.*;
3 class EncodeDemo
4 {
5 public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
6 {
7 String s = "哈哈";
8
9 byte[] b1 = s.getBytes("GBK");
10
11 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b1));
12 String s1 = new String(b1,"utf-8");
13 System.out.println("s1="+s1);
14
15 //对s1进行iso8859-1编码。
16 byte[] b2 = s1.getBytes("utf-8");
17 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b2));
18
19 String s2 = new String(b2,"gbk");
20
21 System.out.println("s2="+s2);
22
23
24
25 }
26 }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/jiandonn/p/4579357.html