标签:
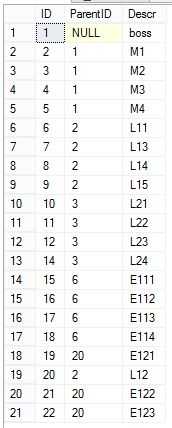
1,传统的分层结构是父子结构,表结构中有一个ParentID字段自引用表的主键,表示“归属”关系,例如
create table dbo.emph ( ID int not null primary key, ParentID int foreign key references dbo.emph(id), Descr varchar(100) not null )
示例数据是一个简单的HR职称结构,Boss,M表示的Mananger,L表示的是Leader,E表示的是Employee。
2,将父子结构转换为使用HierarchyID的结构
2.1 首先创建一个新表 dbo.emph2,代码以下
create table dbo.emph2 ( idpath hierarchyid not null primary key, id int not null, --parentpath as idpath.GetAncestor(1) persisted foreign key references dbo.emph2(idpath), descr varchar(100) ) create unique nonclustered index idx_emph2_unique on dbo.emph2(id)
代码分析:
2.2 将父子结构的数据填充到使用HierarchyID构建的表中
;with cte(idpath,id,descr) as ( select cast(HierarchyID::GetRoot().ToString() as Varchar(max)) as idpath,ID,Descr from dbo.emph where ParentID is null union all select cast(c.idpath+cast(e.id as varchar)+‘/‘ as varchar(max)) as idpath,e.id,e.descr from dbo.emph e inner join cte c on e.parentid=c.id ) insert dbo.emph2 (idpath,id,descr) select idpath,id,descr from cte
HierarchyID类型的字符串格式如:‘/1/2/3/’,字符串以‘/’开头,并以‘/’结尾;
HierarchyID类型不会自动生成节点的位置,需要在代码中将父子关系拼接成字符串,
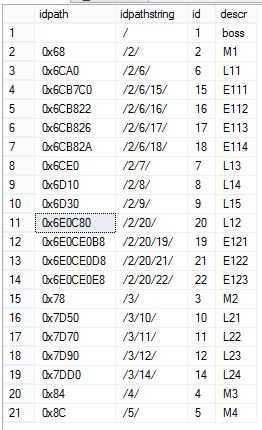
2.3 查询新表dbo.emph2,将HierarchyID类型转换为字符串,能更直观地看出其结构和位置。例如,idpathstring=‘/2/6/15/‘的上一级父节点的path是‘/2/6/’,idpath=‘/2/6/’的ID是6。
select idpath, idpath.ToString() as idpathstring,id,descr from dbo.emph2
2.4 查看某一个节点的父节点,@NodeID是一个节点ID,@Upcnt是指@Node向上的第几个父节点,如果为Null,那么查询出所有的父节点。
alter procedure dbo.usp_GetAncestor @NodeID int, @Upcnt int=null as begin declare @node HierarchyID select @node=idpath from dbo.emph2 where id=@NodeID --get all ancestors if @Upcnt is null begin set @Upcnt=@node.GetLevel() --;with cte(idpath,id,descr,Level) as --( -- select idpath,id,descr, 0 as Level -- from dbo.emph2 -- where id=@NodeID -- union all -- select e.idpath,e.id,e.descr,c.Level+1 as Level -- from dbo.emph2 e -- inner join cte c on e.idpath=c.idpath.GetAncestor(1) -- where c.Level<@Upcnt --) --select idpath,idpath.ToString() as idpathstring,id,descr --from cte declare @rt table(idpath hierarchyid,idpathstring varchar(max),id int ,descr varchar(100)) declare @i int=0 while @i<=@Upcnt begin insert into @rt select idpath, idpath.ToString() as idpathstring,id,descr from dbo.emph2 where idpath=@node.GetAncestor(@i); set @i=@i+1 end select idpath, idpath.ToString() as idpathstring,id,descr from @rt end else begin select idpath, idpath.ToString() as idpathstring,id,descr from dbo.emph2 where idpath=@node.GetAncestor(@Upcnt); end end
2.5 查询子节点
alter procedure dbo.usp_GetDescendant @NodeID int, @Downcnt int=null as begin declare @Node hierarchyid select @node=idpath from dbo.emph2 where id=@NodeID select idpath, idpath.ToString() as idpathstring,id,descr from dbo.emph2 where idpath.IsDescendantOf(@Node)=1 and (@Downcnt is null or (idpath.GetLevel()=@Node.GetLevel()+@Downcnt)) end
2.6 增加一个节点,有时节点的idpath是有顺序的,为了保证顺序,必须使用GetDescendant函数。
--在子节点序列的末尾加入新节点 create procedure dbo.usp_addnode @parentid int, @id int, @descr varchar(100) as begin declare @parentnode hierarchyid declare @maxchildnode hierarchyid select @parentnode=idpath from dbo.emph2 where id=@parentid select @maxchildnode=max(idpath) from dbo.emph2 where idpath.GetAncestor(1)=@parentnode insert into dbo.emph2(idpath,id,descr) select @parentnode.GetDescendant(@maxchildnode,null),@id,@descr end
--按照一定的顺序插入子节点 alter procedure dbo.usp_addnode_order @parentid int, @childleft int, @childright int, @id int, @descr varchar(100) as begin declare @childrightnode hierarchyid declare @childleftnode hierarchyid declare @parentnode hierarchyid select @childleftnode=idpath from dbo.emph2 where id=@childleft select @childrightnode=idpath from dbo.emph2 where id=@childright select @parentnode=idpath from dbo.emph2 where id=@parentid insert into dbo.emph2(idpath,id,descr) select @parentnode.GetDescendant(@childleftnode,@childrightnode),@id,@descr end
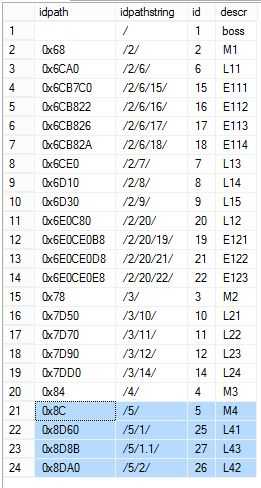
对stored procedure 进行测试,并对查询结果进行排序,如下图
exec dbo.usp_addnode 5,25,‘L41‘ exec dbo.usp_addnode 5,26,‘L42‘ exec dbo.usp_addnode_order 5,25,26,27,‘L43‘ select idpath, idpath.ToString() as idpathstring,id,descr from dbo.emph2 order by idpath
2.7 删除一个节点
如果删除的是叶子节点,非常简单,删除叶子节点不会影响其他节点,但是,如果删除的是非叶子节点,必须处理好其子节点,否则,其子节点将会从层次结构游离出来,成为非法存在,所以在删除一个节点的同时,必须为其可能存在的子节点指定一个新的父节点。
alter procedure dbo.usp_deletenode @deleteid int, @childnewparentid int as begin declare @deletenode hierarchyid select @deletenode=idpath from dbo.emph2 where id=@deleteid declare @id int declare @descr varchar(100) declare cur_child cursor for select id,descr from dbo.emph2 where idpath.IsDescendantOf(@deletenode)=1 and id!=@deleteid open cur_child fetch next from cur_child into @id,@descr while @@FETCH_STATUS=0 begin delete dbo.emph2 where id=@id exec dbo.usp_addnode @childnewparentid,@id,@descr fetch next from cur_child into @id,@descr end close cur_child deallocate cur_child delete dbo.emph2 where id=@deleteid end
注意:IsDescendantOf函数包含当前节点,要想获取当前节点的所有子孙节点,必须将当前节点过滤掉。
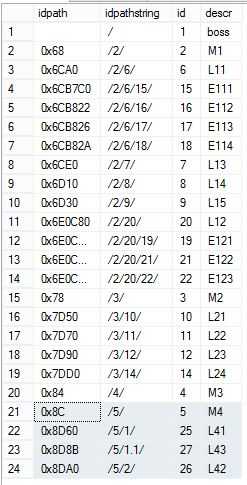
测试,将id=5的节点删除,并将其子节点挂在id=4的节点下。
exec dbo.usp_deletenode 5,4
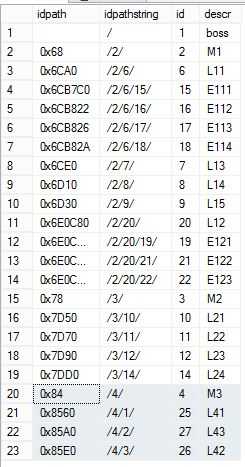
查询结果
select idpath, idpath.ToString() as idpathstring,id,descr from dbo.emph2 order by idpath
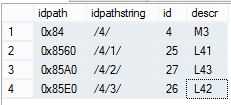
使用存储过程查询id=4的子孙节点
exec dbo.usp_getdescendant 4
2.8 更新一个节点
更新一个节点,变更其父节点,同样面临如何处理其子节点的问题。
create procedure dbo.usp_updatenode @id int, @parentid int, @childnewparentid int as begin --获取节点的idpath declare @deletenode hierarchyid select @deletenode=idpath from dbo.emph2 where id=@id --删除旧节点,并变更节点的父节点 declare @descr varchar(100) select @descr=descr from dbo.emph2 where id=@id delete dbo.emph2 where id=@id exec dbo.usp_addnode @parentid,@id,@descr --逐个变更子节点的父节点 declare @childid int declare @childdescr varchar(100) declare cur_child cursor for select id,descr from dbo.emph2 where idpath.IsDescendantOf(@deletenode)=1 and id!=@id open cur_child fetch next from cur_child into @childid,@childdescr while @@FETCH_STATUS=0 begin delete dbo.emph2 where id=@childid exec dbo.usp_addnode @childnewparentid,@childid,@childdescr fetch next from cur_child into @childid,@childdescr end close cur_child deallocate cur_child end
测试数据如下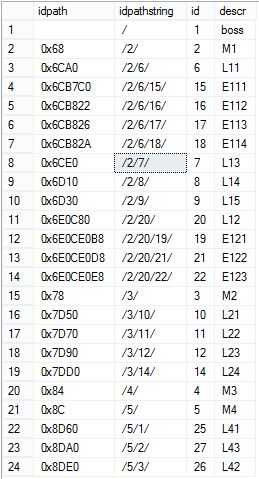
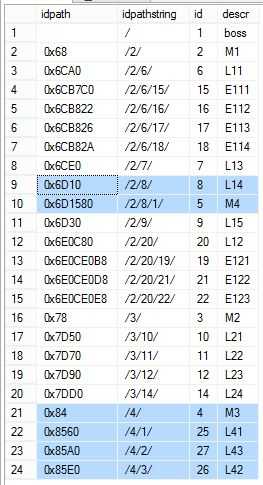
测试的目的是将id=5的所有子节点挂在id=4的节点下,并强id=5的父节点变更为id=8的节点
exec dbo.usp_updatenode 5,8,4
查询结果
select idpath, idpath.ToString() as idpathstring,id,descr from dbo.emph2 order by idpath
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ljhdo/p/4585528.html