标签:
Financial Terminology
Capital Market,资本市场,主要用于大于一年的投资。
(Financing, 融资,资本市场存在的目的。
Security, 证券。
Securities Act (1933), 证券法案,
Senior Security, 优先级证券,包括债券和优先股。
Stock, 股票
(Preferred Stock, 优先股
间于Bond和Common Stock
红利,由董事会决定是否分发当年红利,董事会可决定将优先股的红利用于再投资,在资金充足时再发放。
索偿权,债券持有人对不按时支付利息的,可以通过法律来强制索取,优先股不可。
Common Stock, 普通股
Convertible Preferred Stock,可转换优先股,可转换成普通股。
Growth Stock,成长股
连续几个会计周期持续成长的股票,可能目前业绩并不出色,但每个会计周期的利润收益都在稳定增长.
公司从股东权益上赚取较高的收益率,并将全部/大部分用于再投资,短期风险较大,长期(4—5年)较佳。
当年微软政策,将所有利润用于再投资,而不支付红利,目的是培育日后更高的红利支付能力。
Short Sale, 卖空,
投资者看跌,卖空者预计某股票会跌,但他手中现在没有那支股票, 所以他会向经纪人借用这支股票,以当前价格将其卖出,并在以后以下跌的价格再次 买入该股票,并还给经纪人
A trading technique typically used when a stock is expected to decline in price. A short sale involves selling borrowed stock anticipating that the same number of shares will be repurchased later at a lower price. The repurchase shares are then returned to the owner from whom they were borrowed.
Buy Long, 买空,
投资者看涨,看好某只股票要涨,但手头没钱买,于是就借经纪人的钱,买进股票。等股票价格上涨后,卖掉股票,换上债务,剩余的,便是自己的利润。
Dividend, 红利
Stock Dividend, 股息,以股票的形式发放红利。
DRIP, Dividend reinvestment plan, 红利再投资计划。
Volume, 交易量,
The total number of shares traded, of an individual security or in the entire market, in a given period of time.
Price Earning rate, 市盈率
反映股票收益与风险的重要指标
市盈率=每股市价/每股税后净利润。
当市盈率(P/E)高于30时,要小心股市泡沫。
Odd lot, 零股,散股,
Normally, an odd lot is 1 to 99 shares.
Round lot, 整股
A round lot is 100 shares or a multiple of 100 shares.
Odd lot differential, 零股差价
购买零碎股票时支付的额外费用,一般是每股0.125$。
Margin,保证金, Margin Account,保证金账户
保证金维持要求:
NYSE 最低要求是2000$.
1974年,联储委员会将保证金从65%调低至50%。要购买10000$的股票,投资者必须在5天内向自己的账户中至少存入5000$。
投资者权益任何时候不得低于25%(经纪公司通常设置为30%--35%),一旦过低,账户会“保证金不足”(Under-Margined),经纪公司则会发出“追缴保证金通知”,(Margin Call)。若客户不追缴保证金,则自动出售证券。
例:要求保证金50%,我在账户存入了6000$,然后买入了9000$的股票。
则: 9000$ 现有市场价值 (Current Market Value)
9000-6000 =3000$ 借方余额,既我欠经纪人的钱 (Debit Balance)
------------------
6000$ 现有权益 (Current Equity)
9000×50% = 4500$ 要求的保证金 (Required Margin)
------------------
1500$ 超额保证金 (Excess Margin)
1500$/50% = 3000$ 购买力 (Buying Power)
Credit Balance,一个帐户中所收到的钱。
(Current Equity)现有权益=现有保证金比例×市场价值。
现有保证金比例=(卖空收入+账户存款)/ 当前市场价值 - 1。(低于一定比例则margin call)
例,我存入5000,以每股70$,卖空100股。
若,价格不变,
则,现在保证金比例=(7000+5000)/7000 - 1 = 5000/7000=0.71 大于则赚,小于则亏
则,现有权益=5/7 × 7000=5000,
若,跌至55$:
则,现有保证金比例=(7000+5000)/5500 – 1 = 1.182
则现有权益=1.18×5500=6500赚
若,涨至92$,
则,现有保证金比例=(7000+5000)/9200 – 1 = 0.304 低于35%,Margin Call
则,现有权益=0.30×9200=2760 亏
Option,期权
一个合约,允许投资者在一定时间,一定价格买/卖一定数量(100)的股票。
A contract allowing an investor to purchase or sell 100 shares of stock at a predetermined price any time up to expiration date.
Underlying Security 基础股票。可以进行期权交易的股票。
Premium,权酬,期权的价格(权利的价格),The market price of an option.
Striking Price,股票的预订价格,predetermined price.又称执行价格,exercise price.
Call Option,买权(于买方角度,想以当前低价买入未来高价的股票的权力),卖方看跌,买方看涨。
A contract giving the holder a right to buy 100 shares of stock at a striking price any time up to expiration date. A Call Option is bought to profit by a rise in the stock price.
Put Option,卖权(于买方角度,想以当前高价在未来低价卖出股票的权力),卖方看涨,买方看跌。
A contract giving the holder a right to sell 100 shares of stock at a predetermined price any time up to expiration date. A put option is bought to profit by a decline in the stock price.
Expiration date,到期日,
Exercise,行权。
To make use of the right possessed by the holder of an option. The option holder notifies the writer that they wish to exercise or assign their option. The writer is then obliged to the holder on the terms already agreed – they must buy or sell the underlying asset.
指方即须按约定条件,向期权持有人买进或卖出合约指定的资产。
Writer,立权方,出售期权的一方。
Covered,备兑期权,
如果一手期权的卖主在标的证券中还一股对一股地持有同该期权相反的市场头寸,这个售出的期权就是持保的。也就是说,如果一手空头的看涨期权的卖主拥有其标的股票,该期权是持保的;如果一手空头的看跌期权其标的股票在该帐户中也是卖空,该期权也是持保的(为保证金的目的)。此外,一手空头的看涨期权是持保的,如果它的帐户同时也按与空头看跌期权相同的或更低的定约价买进另一手同一标的证券的看涨期权。一手空头的看跌期权是持保的,如果在它的帐户里还买有一手定约价与空头看跌期权相同或更高的看跌期权。
Uncovered,非备兑期权,裸型期权,无担保期权
如果投资者在出售期权时在其标的证券中没有对冲的头寸,该期权就是无担保的。
例,我手中股票100股,现价50$,我估计要跌,所以,卖出执行价格(striking price)50$ 的此股票(Underlying Stock)的期权(买权)给张三,到期日(Expiration Date)是2010.1.1。权酬(Premium)为每股5$。
若,价格没变,则我赚5$×100(权酬)。张三亏了所有权酬,不管他是否行权。
若,价格下跌,则我依然赚5$×100。即便张三没有行买权,我赚的权酬依然可以提供给我下跌至45$的对冲空间。若低于45$,则亏。张三现在行权,则亏的就不止是权酬,还有低于50$的部分。
若,价格上涨,则我以50$每股卖给张三,还是赚5$×100。但最大利润也就只有这些。在未涨到55$前,张三都是亏的,一旦涨过55$则我亏,比如涨到60$,张三行权,意味着,张三以55$买了我60$ 的股票,稳赚。
Future,期货,Future Contract,期货合约
所谓期货,一般指期货合约,就是指由期货交易所统一制定的、规定在将来某一特定的时间和地点交割一定数量标的物的标准化合约。交易双方不必在买卖发生时就交收实货,而是共同约定在未来的某一时候交收实货,期货是保证金交易,用5%的资金可以做100%的交易,资金放大20倍,杠杆作用十分明显。
Underlying Assets,基础资产。
是期货合约所对应的现货,这种现货可以是某种商品,如铜或原油,也可以是某个金融工具,如外汇、债券。
Bond,债券,
债券发行人(即借款人)承诺向债券持有人在约定时间内按约定的利率支付利息,并在债券到期时按面额赎回债券。
A certificate of indebtedness extending over a period of more than one year from the time it is issued. A debt of less than one year is usually called a “Note”( 票据)。A bond is an obligation that must be repaid at a certain time. Meanwhile, the borrower pays interest to the bondholder for the use of the money。
Note
A debt security, usually maturing in one to 10 years.
Investopedia Says:
In comparison, bills mature in less than one year and bonds typically mature in more than 10 years.
Coupon,息票,债券的利息。
Junk bonds,垃圾债券,极少抵押物,高利息,高风险。收购,兼并时常用。
Bonds that are issued having little or no collateral or liquidation value.
Debenture,信用债券,无抵押物,靠承诺和整体的信誉来发行的债券。
An unsecured (without collateral) bond issued on the good word and general credit of the borrower.
Convertible debenture,可转换信用债券,可转换为普通股。
Fund
Open-end Fund,开放式基金,
Mutual Fund,共同基金,中小投资者将资金以买入基金的方式投入到基金公司,由基金公司以不同的投资组合,投资到不同地方。分散风险。属于开放基金
Close-end Fund,封闭式基金,
Hedge Fund,对冲基金,为超级富有的少数几个客户创建投资组合,提供多种抵消 风险的投资组合,涉及卖空。
Money Market,货币市场,短期借贷市场,期限小于一年,大多在90天内完成。
1.CUSIP
证券统一辨识码。
Committee on Uniform Securities Identification Procedures(证券统一辨识程序委员会)的缩写。美国各种联邦政府债券、市政及公司债券均会获得一个CUSIP码,作为辨识的统一代码。
Symbol,Stock Symbol,Ticker Symbol
A short and convenient way of identifying a stock,
代表上市股票的字母代码,是辨认股票的简便方法,
2.OTC
Over-The-Counter,相对于Exchange traded market交易所场内市场
场外交易市场,柜台市场,和交易所市场完全不同,OTC没有固定的场所,没有规定的成员资格,没有严格可控的规则制度,场外交易包括通常的市场行情清单上没有包含的证券,因此也未受到证券交易所严格规则的约束。
3.Third Market
三板市场,在场外市场买卖已经上市的股票,
The buying and selling of exchange-listed stocks in the OTC market.
4.DTC, Depository Trust Corporation 全美证券托管公司。
5.NSCC,National Security Clearance Corporation 全美证券清算公司。
DTCC,Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation 全美证券托管清算公司
<![if !vml]>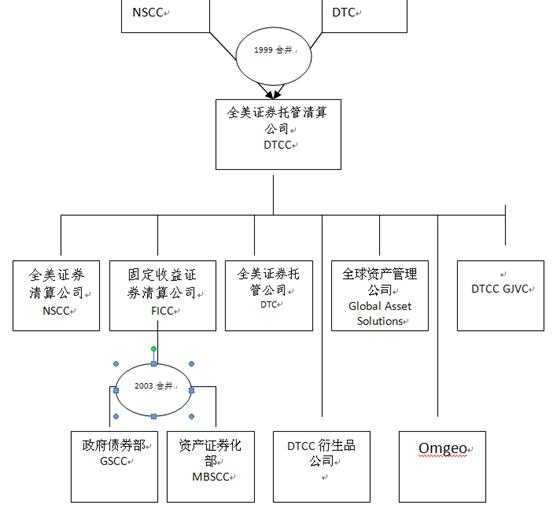 <![endif]>
<![endif]>
市政债券、公司债券等则由DTC集中托管,由NSCC办理结算;
<![if !vml]> <![endif]>
<![endif]>
FICC负责政府债券和资产支持证券的结算。
6.Dow Jones Index
道琼斯,股票价格平均指数。
共有四组,工业业(30),交通运输业(20),公用事业(6),综合(以上三组,共56)。
通常指第一组,(Dow Jones Industrial Average)工业平均指数。
大约每2年更新一家公司,在纽约证交所每半小时公布一次。
计算,入选的所有股票的总价格/入选股票的总股数。
其成分股声誉好,具有行业代表性,但不包括新兴行业(高科,服务,金融)
7.NASDAQ [‘næz?dæk] 始于1971年
National Association of Securities Dealers‘ Automated Quotations System,全美证券商协会自动报价系统。
特点:收集并发布OTC交易的非上市股票的证券商报价。允许电话,网络直接交易,内容以新兴技术为主,尤其是与计算机相关行业。有属于自己的做市商。
Nasdaq Index 反映Nasdaq的市场变化。
8.Market Maker
做市商,专家经纪人。经纪人的经纪人。投资人找经纪人,经纪人找做市商。
一些独立的证券交易商,为投资者承担某一只证券的买卖,买卖者不需要等待对家的出现即可交易。在Nasdaq 称为“Specialist”,专家,在香港称“庄家”。
NYSE的经纪人鲍德,意外摔伤双腿,于是坐在一把椅子上,只买卖西方联合公司的股票,成为第一个做市商。
9.Arbitrage
套利。
在一个市场低价买入,去另一市场高价卖出。
在不同利息率的市场之间买、卖。不同国家,利息率不同,资本从低利率流向高利息率的国家,涉及国际汇率。
在NYSE是指,同时买卖密切相关的证券(如,可相互转换),
好处,消除价差的主要途径。
10. Repo
Repurchase agreement
证券回购协议,允许borrower(借入人)立即将自己的股票卖给lender(出借人),并承诺在一段时间后以规定价格再次买回来。
例如,账户B急需用钱,他希望以100$每股卖掉手上股票,但现在市场上他的股票只值80$,他估计股票会一直上涨,两个月后会涨到120。所以不舍得卖掉,故以REPO形式,以每股100$卖给账户L,并承诺2个月后以105$买回股票(回购)。
It allows a borrower to use a financial security as collateral for a cash loan at a fixed rate of interest. In a repo, the borrower agrees to sell immediately a security to a lender and also agree to buy the same security from the lender at a fixed price at some later date.
Reverse repo, Reverse Repurchase Agreement
The purchase of securities with the agreement to sell them at a higher price at a specific future date.
For the party selling the security (and agreeing to repurchase it in the future) it is a repo; for the party on the other end of the transaction (buying the security and agreeing to sell in the future) it is a reverse repurchase agreement.
Investopedia Says:
Repos are classified as a money-market instrument. They are usually used to raise short-term capital.
赚取上例中账户B的钱。稳赚。
11.Exchange-Listed,上市股票。
12.Listed,上市。
13.Speculator, investor 区别
投机者,投资者
投机,是买了上市公司的股票后,见涨就卖出,马上获利,是短期炒作行为;一般的散户为了赚钱,基本都是投机行为。
投资,是买了上市公司的股票长期持有,等待公司有了利润后,通过配股或者分红获得利润,一般不做短期炒作;
股票的参与者基本上以投机者居多,投机者被套住时就成了投资者。
14.Option, Future 区别
期货交易的标的物是商品或期货合约,而期权交易的标的物则是一种商品或期货合约选择权的买卖权利
期权是单向合约,期权的买方在支付保险金后即取得履行或不履行买卖期权合约的权利,而不必承担义务;期货合同则是双向合约,交易双方都要承担期货合约到期交割的义务。如果不愿实际交割,则必须在有效期内对冲。可以用对冲的方式解除履约责任。
15.Bond, Debenture 区别
Bond 有抵押物,Debenture是信誉债券,仅靠信誉,无抵押物。
16.Bond , Stock 区别
Stock代表所有权,参与公司利润变化,公司兴隆,则股价上涨。
Bond不参与,只回收“本金”和利息。
公司破产后,债券和优先股(Preferred Stock)可优先得到本金,又称为“优先级证券”(Senior Security)。
17. Position
头寸
头寸,是一种市场约定,承诺买卖外汇合约的最初部位,买进外汇合约者是多头long,处于盼涨部位;卖出外汇合约为空头short,处于盼跌部位。头寸可指投资者拥有或借用的资金数量。
就证券投资而言,头寸是指在一项资产上做多(即拥有)或做空(即借入待还)的数量。
投资者买入了一笔欧元多头头寸合约,就称这个投资者持有了一笔欧元多头头寸;如果做空了一笔欧元,则称这个投资者持有了一笔欧元空头头寸。当投资者将手里持有的欧元空头头寸卖回给市场的时候,就称之为平仓(Closing a Position)。
18.平仓(Closing a Position)
是指将交易头寸结清,即以卖出来结清多头头寸,以回补(即买入)来结清空头头寸。在期货或期权市场,平仓亦指在合约到期时交付标的金融工具或实物商品以供交割。
The delivery of underlying financial instruments or commodities against a future or option contract. The offsetting of a long or short position in a market by making an offsetting trade in the other direction. A trader would close a short position by buying the same instrument, or close a long position by selling it.
19. Short
空头/做空
借入证券。
就是比如说当你预期某一股票未来会跌,就在当期价位高时卖出你并不拥有的股票(借来卖),再在股价跌到一定程度是买进,这样差价就是你的利润。
In finance, short selling is the practice of selling securities that have been borrowed from a broker, with the intention of buying identical assets back at a later date to return to the lender. The short seller hopes to profit from a decline in the price of the assets between the sale and the repurchase
20. Long
多头/做多
持有证券。
看好股票未来的上涨前景就会立即买入股票,所以做多就是买入股票。
In finance, a long position in a security means the holder of the position owns the security and will profit if the price of the security goes up. Going long is the more conventional practice of investing and is contrasted with going short.
Similarly, a long position in a futures contract or similar derivative means that the holder of the position will profit if the price of the futures contract or derivative goes up. Note that it is important to consider the value of the option, not the value of the underlying instrument, as the value of a put option will increase when the value of the underlying instrument decreases.
General Ledger,
A company‘s accounting records. This formal(正式的) ledger contains all the financial accounts and statements of a business.
Investopedia Says:
The ledger uses two columns: one records debits, the other has offsetting credits.
Also commonly referred to as an accounting ledger, a general ledger is a primary accounting record used by a business to keep track of all the financial transactions the company makes. All financial transactions, debits and credits, are recorded, or "posted," in the general ledger, regardless of whether or not they also post to a subsidiary ledger (sub-ledger), such as accounts receivable or cash. These values can provide the information used to generate all of a company‘s financial statements. When the idea of ledgers was first created, physical ledgers were manually kept, usually in books; with the advancement of technology, most general ledgers are now computerized using accounting software. Such software programs can be purchased over the Internet or from most stores that sell computer software products.
Credit,
. A contractual agreement in which a borrower receives something of value now and agrees to repay the lender at some date in the future, generally with interest. The term also refers to the borrowing capacity of an individual or company.
. An accounting entry that either decreases assets or increases liabilities and equity on the company‘s balance sheet. On the company‘s income statement, a debit will reduce net income, while a credit will increase net income.
Investopedia Says:
. The amount of money available to be borrowed by an individual or a company is referred to as credit because it must be paid back to the lender at some point in the future. For example, when you make a purchase at your local mall with your VISA card it is considered a form of credit because you are buying goods with the understanding that you‘ll need to pay for them later.
. For example, on a company‘s balance sheet, a debit will increase the inventory account (an asset) if the company buys merchandise for resale on credit. On the other hand, a credit will increase the company‘s accounts payable (a liability).
Debit,
An accounting entry which results in either an increase in assets or a decrease in liabilities on a company‘s balance sheet or in your bank account.
Investopedia Says:
The opposite transaction is called a credit.
Account Balance帐户结余含义同"结余”
The net of debits and credits for an account at the end of a reporting period.
Investopedia Says:
This applies for all types of accounts. A bank account balance shows the amount owed to you by the bank while a credit card balance shows the amount you owe to the credit card company.
Savings Account储蓄存款户头
A deposit account held at a bank or other financial institution that provides principal security and a modest interest rate. Depending on the specific type of savings account, the account holder may not be able to write checks from the account (without incurring extra fees or expenses) and the account is likely to have a limited number of free transfers/transactions. Savings account funds are considered one of the most liquid investments outside of demand accounts and cash.
Investopedia Says:
Because savings accounts almost always pay lower interest rates than Treasury bills and certificates of deposit, they should not be used for long-term holding periods. Their main advantages are liquidity and superior rates compared to checking accounts. Most modern savings accounts offer access to funds through visits to a local branch, over the internet and through automated teller machines.
Accounting
To provide a record such as funds paid or received for a person or business. Accounting summarizes and submits this information in reports and statements. The reports are intended both for the firm itself and for outside parties.
Investopedia Says:
Concise accounting helps management make accurate decisions.
Journal
1. In accounting, a first recording of financial transactions as they occur in time, so that they can then be used for future reconciling and transfer to other official accounting records such as the general ledger. A journal will state the date of the transaction, which account(s) were affected and the amounts, usually in a double-entry bookkeeping簿记, 记账 method.
2. For an individual investor or professional manager, a detailed record of trades occurring in the investor‘s own accounts, used for tax, evaluation and auditing purposes.
Investopedia Says:
Journaling is an essential part of objective record-keeping and allows for concise review and records transfer later in the accounting process. Journals are often reviewed as part of a trade or audit process, along with the general ledger(s).
Trial Balance[会计]试算表
A bookkeeping worksheet in which the balances of all ledgers are compiled into debit and credit columns. A company prepares a trial balance periodically, usually at the end of every reporting period. The general purpose of producing a trial balance is to ensure the entries in a company‘s bookkeeping system are mathematically correct.
Investopedia Says:
Preparing a trial balance for a company serves to detect any mathematical errors that have occurred in the double-entry accounting system. Provided the total debts equal the total credits, the trial balance is considered to be balanced, and there should be no mathematical errors in the ledgers.
However, this does not mean there are no errors in a company‘s accounting system. For example, transactions classified improperly or those simply missing from the system could still be material accounting errors that would not be detected by the trial balance procedure.
Back Office后勤部门
金融机构的后勤支持部门,负责处理交易的结算、交割、记录保存及监督程序等工作。参见Front Office (前线部门)和Middle Office (中后勤部门)。
"The department in a financial institution that processes deals and handles delivery, settlement and regulatory procedures. See also: Office"
Administration and support personnel(人员, 职员)in a financial services company. They carry out functions like settlements, clearances, record maintenance, regulatory (管理的, 控制的, 调整的)compliance, and accounting. When order processing is slow due to high volume, it is commonly referred to as "back office crunch(咬碎; 扎扎地踏; 咬碎声;处理(数据))."
Investopedia Says:
A financial services company is logically broken up into three parts: the front office includes sales personnel and corporate finance, the middle office manages risk and IT resources, and the back office provides administrative and support services.
Front OfficeFront Office
前线部门
金融机构中最接近市场买卖操作的交易人员及助理。
参见Back Office(后勤部门、后台业务部),Middle Office(中后勤部门)。
"The Front Office describes the dealing and support staff in a financial institution who are closest to the buying and selling operations of a market.See also: Back Office, Middle Office"
The sales personnel and corporate finance employees in a financial services company. It‘s in the front office where revenues are generated.
Investopedia Says:
A financial services company is logically broken up into three parts: the front office includes sales personnel and corporate finance, the middle office manages risk and IT resources, and the back office provides administrative and support services.
Middle Office中间部门
"就金融机构而言,通常是指负责计算交易盈亏以及风险管理的部门.参见Front Office(前线部门),Back Office(后勤部门)。"
"The part of a financial institution‘s settlement process that most closely liaises with the front office, recording trades and trading positions. See also: Front Office, Back Office"
The group of employees in a financial services company that manages risk, calculates profits and losses, and (generally) is in charge of information technology. The middle office draws on the resources of both the front and the back offices.
Investopedia Says:
A financial services company is logically broken up into three parts: the front office includes sales personnel and corporate finance; the middle office manages risk and IT resources; and the back office provides administrative and support services.
Internal Revenue Service (IRS)美国国税局
A United States government agency that is responsible for the collection and enforcement of taxes. The IRS was established in 1862 by President Lincoln and operates under the authority of the United States Department of the Treasury. It is primarily engaged in the collection of individual income taxes and employment taxes, but also handles corporate, gift, excise and estate taxes.
The IRS is sometimes referred to as the "tax man".
Investopedia Says:
The IRS is headquartered in Washington, D.C. It is an expansive organization that services the taxation of all Americans. In 2006, the IRS processed about 133 million personal income tax returns and almost six million corporate income tax returns, bringing in trillions of dollars of tax revenue.
Fail
A transaction that has not been settled before a deadline.
Investopedia Says:
Presently, firms have three days after the date of a trade to settle stock transactions. Within this timeframe, securities and cash must be delivered to the clearing house for settlement. If firms are unable to meet this deadline a fail will occur.
Settlement requirements for stock, options, futures contracts, forwards, and fixed-income securities differ. In common trading terms, if a seller does not deliver securities or a buyer does not pay owed funds by the settlement date, then the transaction is said to fail. In a stock exchange, this occurs if a stockbroker does not deliver or receive securities, within a specified time after a security sale or a security purchase. When a seller cannot deliver the contracted securities, this is called a short fail. If a buyer is unable to pay for the securities, this is called a long fail.
Presently, firms have three days after the date of a trade to settle stock transactions. Within this time frame, securities and cash must be delivered to the clearing house for settlement. If firms are unable to meet this deadline, a fail will occur. Settlement requirements for stock, options, futures contracts, forwards and fixed-income securities differ.
Fail is also used as a bank term when a bank is unable to pay its debt to other banks. The inability of one bank to pay its debt to other banks in interbank fund transfer systems, can potentially lead to a domino effect, causing several banks to become insolvent.
Insolvent
无力偿付
"指公司无力偿还到期的债务,亦指公司的债务超过资产价值的情况.参见Solvent(有偿债能力)。"
"A company becomes insolvent when it is either unable to pay its debts as and when they fall due, or when its liabilities, including contingent and prospective liabilities, exceed the value of its assets. The opposite of solvent."
See also: Solvent
Liabilities
负债
"就公司而言,负债是指公司运作所产生的债务以及偿付责任. 负债须透过向债权人转移经济利益来偿还,比如支付现金或提供商品或服务. 在公司的资产负债表上,资产等于负债加股东资金,换着话说,资产的资金来源不外乎负债以及股东资金. 负债的形式包括贷款、应付帐款、应计费用、预收收入以及或有负债等.参见Assets(资产)以及Company(公司)。"
Liabilities are debts arising from borrowing and credits used to finance assetsSee also: Assets
Settlement Date结算日
1. The date by which an executed security trade must be settled. That is, the date by which a buyer must pay for the securities delivered by the seller.
2. The payment date of benefits from a life insurance policy.
Investopedia Says:
The settlement date for stocks and bonds is usually three business days after the trade was executed. For government securities and options, the settlement date is usually the next business day.
Trade Date交易日
The date on which a security trade occurs.
Investopedia Says:
This differs from the settlement date, which is usually between one and five days after the trade date, depending on the transaction type.
Delivery Date交割日
1. The final date by which the underlying commodity for a futures contract must be delivered in order for the terms of the contract to be fulfilled.
2. The maturity date of a currency forward contract.
Investopedia Says:
All futures and forward contracts have a delivery date upon which the underlying must be transferred to the contract holder if he or she holds the contract until maturity instead of offsetting it.
Value Date起息日
A future date used in determining the value of a product that fluctuates in price. Typically, you will see the use of value dates in determining the payment of products and accounts where there is a possibility for discrepancies due to differences in the timing of valuation. Such products include forward currency contracts, option contracts, and the interest payable or receivable on personal accounts. Also referred to as "valuta".
Investopedia Says:
For example, in the case of savings bonds, the interest is compounded semi-annually so the value date is every six months. This removes any uncertainty for investors because their calculations of interest payments will be the same as the government‘s.
Reconciliation .[会]对账
An accounting process used to compare two sets of records to ensure the figures are in agreement and are accurate. Reconciliation is the key process used to determine whether the money leaving an account matches the amount spent, ensuring that the two values are balanced at the end of the recording period.
Investopedia Says:
At the end of every month it is a good idea to reconcile your checkbook by comparing your receipts with your bank statement. Among other advantages, this type of account reconciliation makes it possible to determine whether money is being fraudulently withdrawn from an account.
Consolidate
consolidate [con·sol·i·date || k?n‘s?l?de?t]
v. 巩固, 统一, 使联合; 巩固
To combine the assets(资产), liabilities(负债) and other financial items of two or more entities into one.
Investopedia Says:
This term is generally used in the context of consolidated financial statements. When statements are consolidated, all subsidiaries report under the umbrella of the parent company.
Clearing Member Trade Agreement (CMTA)
An agreement by which an investor may enter derivative trades with a limited number of different brokers and later consolidate these trades with one brokerage house for clearing.
Investopedia Says:
When the position is consolidated, some brokers will ‘give up‘ their position to the clearing firm. The positions should be cleared through the Options Clearing Corporation.
Derivative
In finance, a security whose price is dependent upon or derived from one or more underlying assets. The derivative itself is merely a contract between two or more parties. Its value is determined by fluctuations in the underlying asset. The most common underlying assets include stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, interest rates and market indexes. Most derivatives are characterized by high leverage.
Investopedia Says:
Futures contracts, forward contracts, options and swaps are the most common types of derivatives. Because derivatives are just contracts, just about anything can be used as an underlying asset. There are even derivatives based on weather data, such as the amount of rain or the number of sunny days in a particular region.
Derivatives are generally used to hedge risk, but can also be used for speculative purposes. For example, a European investor purchasing shares of an American company off of an American exchange (using American dollars to do so) would be exposed to exchange-rate risk while holding that stock. To hedge this risk, the investor could purchase currency futures to lock in a specified exchange rate for the future stock sale and currency conversion back into euros.
Haircut
1. The difference between prices at which a market maker can buy and sell a security.
2. The percentage by which an asset‘s market value is reduced for the purpose of calculating capital requirement, margin and collateral levels.
Investopedia Says:
1. The term haircut comes from the fact that market makers can trade at such a thin spread.
2. When they are used as collateral, securities will generally be devalued(贬值) since a cushion(缓冲物,垫子) is required by the lending(出借,) parties in case the market value falls.
Spread
1. The difference between the bid(买家出价) and the ask(卖家出价) price of a security or asset.
2. An options position established by purchasing one option and selling another option of the same class but of a different series.
Prospectus
招股书
一份正式文件,由发行证券或基金的机构提供给潜在投资者,说明发行的细节,一般会包括发行条款、筹集资金的用途、发行人介绍以及相关的财务报表。英文亦称为offering circular。
"A document produced by the issuing company, which provides detailed terms and conditions of a new equity or debt offering."
A formal legal document, which is required by and filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, that provides details about an investment offering for sale to the public. A prospectus should contain the facts that an investor needs to make an informed investment decision.
Also known as an "offer document".
POP
公开发行价格
英文Public Offering Price的缩写,指证券向公众发行的售价,承销商会将佣金计入发行价内。就共同基金而言,若采用单一报价方式,公开发售价等同基金的单位净值(NAV),认购费另外支付;若采双向报价,发售价等于基金单位净值加上认购费。
参见Mutual Fund(共同基金)及One-way Quote/Two-way Quote(单一报价/双向报价)。
Synonym: Public Offering Price
The issue price of a new share that is fixed by the underwriter on behalf of a company. The underwriter‘s commission is built into the price. Shares in a mutual fund may be purchased at the POP.See also: Fund
Facility
A term used to describe financial assistance programs offered by lending institutions to help companies requiring capital
Investopedia Says:
These financial assistance programs are merely another name for loans taken on by companies. Examples of such facilities include swingline loans and lines of credit. Often you will hear of companies obtaining different credit facilities, as they can vary between committed or uncommitted.
Depository Trust Company (DTC)
One of the world‘s largest securities depositories, it holds in excess of US$10 trillion worth of securities in custody托管. The DTC acts like a clearinghouse(票据交换所) to settle trades in corporate and municipal securities.
Depository
受托人
受托保管金钱或有价证券等贵重财物的个人或机构。
A storage facility for securities registration and ownerships.
Custody
托管
证券托管是指妥善保管证券,以及保持证券所有权的准确记录。跨境交易使得市场对本地及全球证券托管服务的需求日增。
参见Clearstream(国际结算系统),Euroclear(欧洲结算系统)。
"The storage and safekeeping of securities, and the maintenance of accurate records of their ownership. Cross-border trading has produced a growing need for custody services both within countries and globally. See also: Clearstream, Euroclear"
DeliveryInstruction,发运通知单
An order by a client to a broker as to where the broker should place securities or other assets once they are received from a seller. They could be given directly to the customer, placed in a brokerage account, or put somewhere else entirely.
A customer‘s directions to a broker as to the disposition of funds and securities in the customer‘s account. For example, a customer must instruct the broker whether securities placed in the account should be sent to the customer or kept in street name in the account.
options delivery instruction: 期权交付指令
Receive Versus Payment (RVP)
An instruction accompanying sell orders, stating that only cash will be accepted in exchange for delivery of the securities.
Investopedia Says:
Institutions are usually required by law to only accept cash.
DVP
券款对付
英文Delivery Versus Payment的缩写,指债券交易的结算方式,即买卖双方在约定的结算日,债券与资金同步进行交收。
Synonym: Delivery Versus Payment
The normal method of settling bond trades whereby delivery of the security is made on the same day as payment is effected.
A securities industry procedure in which the buyer‘s payment for securities is due at the time of delivery. Security delivery and payment are simultaneous.
Investopedia Says:
Also known as delivery against payment, delivery against cash, or from the sell side.
Mismatch
错配
"1. 指债务期限与投资期限之间的显著差异,比如以短期债务为长期投资融资,即存在期限错配的问题,会有资金周转不灵的风险."
"2. 指空头交易头寸与多头头寸不相配的情况.参见Matched Book(对应账簿), Long(多头), Short(空头)。"
"1. A difference between the length of time for which money is borrowed and the length of time for which it is invested, or the difference between the maturities of borrowing and investments. One example is when a bank borrows money for a C1125short time but lends it for a longer period, so there is a mismatch between its source and use of funds. 2. A mismatched book, or a mismatch in an overall trading position, occurs when short and long positions do not complement each other."
"See also: Mismatch, Long, Short"
Matched Book
对应账簿
"指银行的资产与负债的期限结构基本相同,换句话说,即短、中、长期的资产与负债规模相当. 亦指贷款利息收入与资金成本相当的情形."
参见Book(账簿)。
"A book where the maturity dates for a bank or trader‘s liabilities match those of the assets. Also, where borrowing costs equal the interest earned on investments.See also: Book"
Matched Book
A bank is running a matched book when the maturities of its assets and liabilities are equally distributed. Also known as "asset/liability management".
Investopedia Says:
A risk management technique for banks that ensures they have equal valued liabilities and assets with equal maturities.
TIPS
美国通膨保值公债
"英文Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities的缩写, 是美国财政部发行的一种特殊公债. TIPS持有人除享有一般美国公债零信贷风险的好处外,还可回避通货膨胀侵蚀债券价值的风险. TIPS派发的票息及偿还的本金会经通膨调整—按消费者物价指数加以调整,令投资人得以享有某一水平的实质回报. 参见Index-linked Bonds(与指数挂钩的债券)."
Treasury Inflation Protected Securities (TIPS)
A special type of Treasury note or bond that offers protection from inflation. Like other Treasuries, an inflation-indexed security pays interest every six months and pays the principal when the security matures. The difference is that the coupon payments and underlying principal are automatically increased to compensate for inflation as measured by the consumer price index (CPI).
Also referred to as "Treasury inflation-indexed securities".
Investopedia Says:
If U.S. Treasuries are the world‘s safest investments, then you might say that TIPS are the safest of the safe. This is because your real rate of return, which represents the growth of your purchasing power, is guaranteed. The downside is that, because of this safety, TIPS offer a low return.
Other countries have similar securities. For example, in Canada this is known as a "real return bond" (RRB).
Syndicate
银团
指负责发行债务的金融机构所组成的团体。组成银团的目的是要分散发行的风险,并将之分割成可控制的量。
A group of institutions responsible for issuing debt. A syndicate is formed to share the risk of an issue and split it into manageable amounts.
Syndicate
A group of bankers, insurers, etcetera, who work together on a large project.
Investopedia Says:
A syndicate only works together temporarily. They are commonly used for large loans or underwritings to reduce the risk that each individual firm must take on.
When Issued (WI)
A transaction which is made conditionally because a security has been authorized, but not yet issued.
Investopedia Says:
Treasury(国库) securities, splits, and new issues are all traded on a when-issued basis. The term is actually short for "when, as, and if issued."
What is the purpose of a ‘when-issued‘ market?
Today, a bidder(出价人,投标人) at a government security auction(拍卖) can only second(支持) guess what the demand for a bond will be. This uncertainity leads to a volatility whenever there is a large auction. A when-issued market will enable bidders to get an idea of how many investors are interested in buying. Reduced volatility will draw more investors and lead to further development of the bond market.
How does the when-issued market work?
Jul 31, 2006, 12.02am IST
A "when, as and if issued" (commonly known as ‘when-issued‘) security refers to a bond whose issue has been announced but not yet taken place.
By inference a `when-issued‘ market is one where such ‘when-issued‘ instruments are traded. In India the ‘when-issued‘ market in government securities is expected to take off in few days with transactions taking place on RBI‘s Negotiated Dealing System - Open Markets (NDS-OM), an on-line trading platform for government securities.
In a when-issued market trade can take place only from the day an auction of government securities is notified upto the date of the auction.
During this period there will be a kind of a book-building with buying and selling of the to-be-issued security going on simultaneously. Once the securites are issued through the auction there will be a settlement of all these buy-sell transactions that has taken place earlier.
Who can participate in a when-issued market?
Broadly a when-issued market is open to those institutions which participate in the government bonds market. The RBI notification describes the participants as banks, primary dealers or any other entities it notifies.
Since institutional trade in government bonds takes place in demat form with RBI acting as the depository, RBI allows only those entities to trade those who can hold goverment securities in dematerialised form. Primary dealers can participate upto 10% of the size of the forthcoming(即将来临的) auction. Others can trade for a value upto 5% of the auction.
Reserve Bank Of India (RBI)
The central bank of India, which was established on April 1, 1935, under the Reserve Bank of India Act. The RBI uses monetary policy to create financial stability in India and is charged with regulating the country‘s currency and credit systems.
Investopedia Says:
Located in Mumbai, the Reserve Bank of India serves the financial market in many ways. One of its most important functions is establishing an overnight interbank lending rate. The Mumbai Interbank Offer Rate, or MIBOR, serves as a benchmark for interest rate related financial instruments in India.
Authorized Stock
The maximum number of shares that a corporation is legally permitted to issue, as specified in its articles of incorporation. This figure is usually listed in the capital accounts section of the balance sheet.
Also known as "authorized shares" or "authorized capital stock".
Investopedia Says:
This number can be changed only by a vote of all the shareholders. Management will typically keep the number of authorized shares higher than those actually issued. This allows the company to sell more shares if it needs to raise additional funds.
Bloomberg
A major global provider of 24-hour financial news and information including real-time and historic price data, financials data, trading news and analyst coverage, as well as general news and sports. Its services, which span their own platform, television, radio and magazines, offer professionals analytic tools.
Investopedia Says:
One of its key revenue earners and what they are well known for is the Bloomberg Terminal - an integrated platform that streams together price data, financials, news, trading data, and much more to more than 250,000 customers worldwide.
Delivery Versus Payment (DVP),
付款交割,指买方需要在交付证券当时支付有关款项。证券的交付及付款必须同时进行
A securities industry procedure in which the buyer‘s payment for securities is due at the time of delivery. Security delivery and payment are simultaneous.
Investopedia Says:
Also known as delivery against payment, delivery against cash, or from the sell side.
Redemption
The return of an investor‘s principal in a security, such as a stock, bond, or mutual fund.
Investopedia Says:
Redemption of mutual fund shares from a mutual fund company must occur within seven days of receiving a request for redemption from the investor.
赎回指债券发行人在债券到期时赎回债券。参见Warrant(认股权证)。
The repurchase of a bond at maturity by the issuer.
Warrant
认股权证
一种衍生工具,持有人有权在一定的期限内按约定的认购价向发行人购进一家公司的普通股,认购价通常高于发行时标的股票的市价。认股权证的有效期通常较长,可以是数年至永久有效。认股权证通常依附公司债或优先股发行,作为吸引投资人认购的“赠品”,但认股权证有其独立的价值,可自由转让、单独买卖。认股权证的标的股票通常是发行公司自身的股票,但也可以是子公司的股票。
参见Covered Warrant (备兑认股证)。
"A type of financial instrument attached to a security that has a separate life and value. A warrant allows the investor to purchase ordinary shares at a fixed price over a period of time (years) or to perpetuity. The price of the shares is usually higher than the market price at the time of issue. A warrant is freely transferable and can be traded separately. Warrants are usually issued by companies for their own shares, or the shares of a subsidiary. Covered warrants are issued by banks, for the shares of other companies, or for use as a trading instrument."
Warrant
A derivative security that gives the holder the right to purchase securities (usually equity) from the issuer at a specific price within a certain time frame. Warrants are often included in a new debt issue as a "sweetener" to entice investors.
Investopedia Says:
The main difference between warrants and call options is that warrants are issued and guaranteed by the company, whereas options are exchange instruments and are not issued by the company. Also, the lifetime of a warrant is often measured in years, while the lifetime of a typical option is measured in months.
RR, Registered Representative
A person who works for a brokerage company that is licensed by the Security and Exchange Commission (SEC) and acts as an account executive for clients trading investment products such as stocks, bonds and mutual funds. Also known as an "account executive".
It is also refers to a person registered with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) who works for a commission house or a futures commission merchant.
Investopedia Says:
To become licensed as a Registered Representative to act as agent in the buying and selling of securities, a person must pass the Series 7 and Series 63 securities examinations. Also, the person must work for a brokerage licensed by the SEC, NYSE and NASD.
Dealer,经销商,自营商,是交易市场的主体,本身具有资金及帐户,自己在市场中进行有价证券的买卖,盈亏与风险自负。政府也要求这些自营商必须负起一些社会责任,包括维持交易市场的活络以及在必要时刻稳定市场等等。
1. An individual or firm willing to buy or sell securities for their own account.
2. One who purchases goods or services for resale to consumers.
Investopedia Says:
A dealer differs from an agent in that a dealer acts as a principal in a transaction. That is, a dealer takes ownership of assets and is exposed to inventory risk, while an agent only facilitates a transaction on behalf of a client.
Broker-Dealer
A person or firm in the business of buying and selling securities operating as both a broker and a dealer depending on the transaction.
Investopedia Says:
Technically, a broker is only an agent who executes orders on behalf of clients, whereas a dealer acts as a principal and trades for his or her own account. Because most brokerages act as both brokers and principals, the term broker-dealer is commonly used to describe them.
Shareholder
Any person, company, or other institution that owns at least one share in a company.
指持有机构或公司股票者。
A shareholder may also be referred to as a "stockholder".
Investopedia Says:
Shareholders are the owners of a company. They have the potential to profit if the company does well, but that comes with the potential to lose if the company does poorly.
Pairoff
1. A purchase of securities to offset a previously transacted sale of the same security.
2. A transaction in securities markets where off-setting buy and sell trades are settled in cash, based on the difference in the prices between the off-setting trades. No securities trade hands; instead the settlement difference between the trades is calculated, and a money wire is sent to the appropriate party.
Investopedia Says:
1. The offsetting position is usually transacted within the same day of the original purchase. This is also referred to as crystallization.
2. Matching trades for pairoff can reduce settlement risks and security wire transfer fees. It is ultimately a form of speculation.
Offset抵销, 弥补, 补偿
1. To liquidate a futures position by entering an equivalent, but opposite, transaction which eliminates the delivery obligation.
2. To reduce an investor‘s net position in an investment to zero, so that no further gains or losses will be experienced from that position.
Investopedia Says:
1. Investors will offset futures contracts and other investment positions in order to remove themselves from any associated liabilities. Almost all futures positions are offset before the terms of the futures contract are realized. Despite the fact that most positions are offset near the delivery term, the benefits of the futures contract as a hedging mechanism are still realized.
2. If the initial investment was a purchase, a sale is made to neutralize the position; to offset an initial sale, a purchase is made to neutralize the position. For example, if you wanted to offset a long position in a stock, you could short sell an identical number of shares. By doing so, your net ownership of the stock would be zero, and you would not incur any further gains or losses from the position.
Liquidate [‘likwideit]清算, 清偿, 消除
1. To convert assets into cash or equivalents by selling them on the open market.
2. When an entity chooses or is forced by a legal judgment or contract to turn assets into a "liquid" form (cash).
Investopedia Says:
1. An individual may choose to liquidate his or her possessions or investments to pay off creditors, convert assets to cash for spending or because the investments are not going to increase in value and the investor wants to re-allocate funds.
2. Businesses are best known to liquidate assets as a part of bankruptcy procedure, but the process can also be used by businesses to free up cash, even in the absence of financial hardship.
To Be Announced (TBA)
A term used to describe a forward mortgage-backed securities trade. Pass-through securities issued by Freddie Mac, Fannie Mae and Ginnie Mae trade in the TBA market. The term TBA is derived from the fact that the actual mortgage-backed security that will be delivered to fulfill a TBA trade is not designated at the time the trade is made. The securities are "to be announced" 48 hours prior to the established trade settlement date.
Investopedia Says:
The settlement procedures of mortgage-backed securities TBA trades are established by the Bond Market Association. Each type of agency pass-through security is given a specific trade settlement date for each month. Trade counterparties are required to exchange pool information by 3:00 pm (EST) 48 hours prior to the established settlement date. Trades are allocated in $1 million lots.
Flip
A point when traders shift from having more long positions to having more short positions, or vice versa. A flip can be described as a situation when a trader decides that their outlook or strategy is no longer a winning one, and begins to take steps to reverse their positions. This may involve selling long equity positions in favor of short positions, or through the use of derivative instruments.
Investopedia Says:
This can be a very effective tool for determining the trend of a certain currency. A shift from long to short positions indicates that the market‘s bullish outlook on a specific currency could be coming to an end. Another such example could be the market for crude oil, which has been known to be a very volatile trade, with traders often "flipping" positions numerous times over the course of a contract.
Point
点
价格波动以“点”(point)及“点子/跳动点”(pip)表示,视乎市场及金融工具而定,1点可以折合成若干点子,比如100点子,不过有时1点就是指1个跳动点。就债券及贷款而言,1点是指债券面额或贷款本金的1%。就股票而言,1点通常是指1元。
Bullish
看涨
相信价格将上涨。因此,如果市场浮现看涨的气氛,价格会走高。与看跌或看空(bearish)相反。参见Bearish(看跌/看空/熊市的)。
Holding a belief that prices will rise. A bullish sentiment(观点) in the market will therefore push prices higher. The opposite of bearish.See also: Bearish
The general direction of a market or of the price of an asset. Trends can vary in length from short, to intermediate, to long term. If you can identify a trend, it can be highly profitable, because you will be able to trade with the trend.
<![if !vml]> <![endif]>
<![endif]>
Investopedia Says:
As a general strategy, it is best to trade with trends, meaning that if the general trend of the market is headed up, you should be very cautious about taking any positions that rely on the trend going in the opposite direction.
A trend can also apply to interest rates, yields, equities and any other market which is characterized by a long-term movement in price or volume.
Equity,
The term‘s meaning depends very much on the context. In finance, in general, you can think of equity as ownership in any asset after all debts associated with that asset are paid off. For example, a car or house with no outstanding debt is considered the owner‘s equity because he or she can readily sell the item for cash. Stocks are equity because they represent ownership in a company.
FX
外汇市场
FX是外汇市场的缩写。外汇市场是各种货币的存款(绝大多数的期限在12个月以内)互相交换的场所,以现货、远期、期货和期权等形式进行。汇率(FX rates)是两种货币进行交换的比率,例如欧元兑美元的汇率是指1欧元可兑换到多少美元。参见Spot Market(现货市场),Forwards(远期合约),Futures(期货合约),Option(期权)。
Forex (FX)
The market in which currencies are traded. The forex market is the largest, most liquid market in the world with an average traded value that exceeds $1.9 trillion per day and includes all of the currencies in the world.
Investopedia Says:
There is no central marketplace for currency exchange; trade is conducted over the counter. The forex market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, and currencies are traded worldwide among the major financial centers of London, New York, Tokyo, Zürich, Frankfurt, Hong Kong, Singapore, Paris and Sydney - spanning most time zones.
The forex is the largest market in the world in terms of the total cash value traded, and any person, firm or country may participate in this market.
Fail to deliver
[经] 未能交付
situation where the broker-dealer on the sell side of a contract has not delivered securities to the broker-dealer on the buy side. A fail to deliver is usually the result of a broker not receiving delivery from its selling customer. As long as a fail to deliver exists, the seller will not receive payment.
If Party A fail to deliver the finished products in time, all loss thus incurred should be borne by Party A .
若甲方不能按期交货,由此而造成的一切损失都将由甲方负担
An outcome in a transaction where one of the counterparties in the transaction fails to meet their respective obligations. When failure to deliver occurs, either the party with the long position does not have enough money to pay for the transaction, or the party in the short position does not own the underlying assets that are to be delivered. Failure to deliver can occur in both equity and derivatives markets.
Whenever a trade is made, both parties in the transaction will have to transfer the cash and assets before the settlement date. Subsequently, if the transaction is not settled, one side of the transaction has failed to deliver. Failure to deliver also can occur if there is a technical problem in the settlement process carried out by the respective clearing house.
For forward contracts, a party with the short position‘s failure to deliver can cause significant problems for the party with the long position, because these contracts often involve significant volumes of commodities that are pertinent to long position‘s business operations.
Failure to deliver is also important when discussing naked short selling. When naked short selling occurs an individual agrees to sell a stock that they neither own nor have borrowed. Subsequently, the failure to deliver creates what are called "phantom shares" in the market which may dilute the price of the underlying stock.
<![if !supportLineBreakNewLine]>
<![endif]>
fail to receive
未能接收
situation where the broker-dealer on the buy side of a contract has not received delivery of securities from the brokerdealer on the sell side. As long as a fail to receive exists, the buyer will not make payment for the securities.
Derivative衍生物
In finance, a security whose price is dependent upon or derived from one or more underlying assets. The derivative itself is merely a contract between two or more parties. Its value is determined by fluctuations in the underlying asset. The most common underlying assets include stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, interest rates and market indexes. Most derivatives are characterized by high leverage.
Investopedia Says:
Futures contracts, forward contracts, options and swaps are the most common types of derivatives. Because derivatives are just contracts, just about anything can be used as an underlying asset. There are even derivatives based on weather data, such as the amount of rain or the number of sunny days in a particular region.
Derivatives are generally used to hedge risk, but can also be used for speculative purposes. For example, a European investor purchasing shares of an American company off of an American exchange (using American dollars to do so) would be exposed to exchange-rate risk while holding that stock. To hedge this risk, the investor could purchase currency futures to lock in a specified exchange rate for the future stock sale and currency conversion back into euros.
SEC(Securities And Exchange Commission) Fee
A nominal fee that was created by the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 to be an additional transaction cost attached to the selling of exchange-listed equities. This fee is usually listed as a separate fee, independent of any associated brokerage commissions or fees.
Up until 2007, the fee is 1% of one three-hundredth of the dollar value of the equities sold. After 2007, the fee will be 1% of one eight-hundredth of the dollar value of the equities sold.
<![if !supportLineBreakNewLine]>
<![endif]>
The proceeds of the SEC fee are collected from the brokerage firms and are eventually returned to the U.S. Treasury. This fee provides the necessary capital for the government to pay for the costs involved in the SEC‘s regulation of equity dealers and the equities market.
Note that this fund only applies to the selling of most classes of equities and equity-related options. Debt instruments, such as bonds, are not charged this fee.
Correspondent
The name given to a bank, broker, dealer, or financial institution that acts on behalf of another financial institution with limited or restricted access to the financial markets where a transaction must occur.
Commonly done by smaller financial corporations that don‘t necessarily have the capital to enter into foreign markets and set up new operations. This is a cheaper method of providing international services to clients through agreements and partnerships.
Broker vs Dealer, Broker buys/sells securties on his/her clients behalf and dealer buys/sells securties for his/her accounts.
Brokers and dealers are terms associated with securities. Though both have almost the same work, they are different in many aspects. The main difference between a broker and a dealer is in respect of their role in the market, as well as the capital required. A broker is a person who executes the trade on behalf of others, whereas a dealer is a person who trades business on their own behalf.
A dealer is a person who will buy and sell securities on their account. On the other hand, a broker is one who will buy and sell securities for their clients.
When dealing with securities, dealers make all decisions in respect of purchases. On the other hand, a broker will only make purchases as per the client’s wishes. While dealers have all the rights and freedom regarding the buying and selling of securities, brokers seldom have this freedom and these rights.
When talking about their experience, a broker has only a little experience in the field compared to dealers. It has also been seen that brokers become dealers once they get experience.
A broker is normally paid a commission for transacting the business. Brokers do not have any assets, but only act as middlemen between sellers and buyers. On the other hand, a dealer is not paid a commission, and he or she is a primary principal. Dealers will have assets of their own which they sell at a later stage.
Brokers and dealers have to adhere to certain guidelines and regulations. Both brokers and dealers have certain financial responsibilities.
Summary:
1. A broker is a person who executes the trade on behalf of others, whereas a dealer is a person who trades business on their own behalf.
2. A dealer is a person who will buy and sell securities on their account. On the other hand, a broker is one who will buy and sell securities for their clients.
3. While dealers have all the rights and freedom regarding the buying and selling of securities, brokers seldom seldom have this freedom and these rights.
4. A broker has only a little experience in the field compared to dealers. It has also been seen that brokers become dealers once they get experience.
5. A broker is normally paid a commission for transacting the business. A dealer is not paid a commission, and he or she is a primary principal.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
A corporate structure whereby the shareholders of the company have a limited liability to the company‘s actions.
Investopedia Says:
Basically, an LLC is a hybrid between a partnership and a corporation.
Inventory,库存
"也称为存货(stock),指公司贮存的原材料、半成品和成品。"
"A company‘s stock of raw materials, semi-finished and finished goods. Also known simply as stock."
The raw materials, work-in-process goods and completely finished goods that are considered to be the portion of a business‘s assets that are ready or will be ready for sale. Inventory represents one of the most important assets that most businesses possess, because the turnover of inventory represents one of the primary sources of revenue generation and subsequent earnings for the company‘s shareholders/owners.
Possessing a high amount of inventory for long periods of time is not usually good for a business because of inventory storage, obsolescence and spoilage costs. However, possessing too little inventory isn‘t good either, because the business runs the risk of losing out on potential sales and potential market share as well.
Inventory management forecasts and strategies, such as a just-in-time inventory system, can help minimize inventory costs because goods are created or received as inventory only when needed.
Turnover
营业额
1. 营业额是公司在一段时间内出售的商品或服务的总金额,也称“营业收入”(revenue)或“销售额”(sales)。
2. 成交额指一段时间内某一市场的交易总量。
1.The amount of goods or services sold by a company in a given period. Also known as revenue or sales. 2. Total volume of trades in a market during a given period.
Revenue
营业收入
指公司在某一段时间内销售产品或服务的金额,也称“销售额”(sales)或“营业额”(turnover)。
RR,
Registered Representative
A person who works for a brokerage company that is licensed by the Security and Exchange Commission (SEC) and acts as an account executive for clients trading investment products such as stocks, bonds and mutual funds. Also known as an "account executive".
It is also refers to a person registered with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) who works for a commission house or a futures commission merchant.
Investopedia Says:
To become licensed as a Registered Representative to act as agent in the buying and selling of securities, a person must pass the Series 7 and Series 63 securities examinations. Also, the person must work for a brokerage licensed by the SEC, NYSE and NASD.
Flat
持平
1.指股票或金融工具的价格既不上升也不下跌,也称sideways(横向波动)。
2.形容债券以不带应计利息的条件买卖,例如遭违约的债券。
3.形容头寸既非做多头亦非做空头。
"The price of a share or financial instrument that is neither rising nor falling; also called sideways. Also, a bond that is trading without accrued interest, such as a bond in default and a position in a market, or a financial instrument, which is balanced, neither long nor short."
1. A price that is neither rising nor declining.
2. In forex, the condition of being neither long nor short in a particular currency. Also referred to as ‘being square‘.
3. A bond that is trading without accrued interest.
Investopedia Says:
1. If a stock over the last month has been trading around $30, it can be thought of as trading flat.
2. If you had no positions in the U.S. dollar or your long and short positions canceled each other out, you would be flat or have a flat book.
3. A bond is trading flat if the buyer of the bond is not responsible for paying the interest that has accrued since the last payment (accrued interest is usually part of the bond purchase price). Bonds that are in default trade flat.
The Small Business Administration (SBA) is an autonomous U.S. government agency that was established in 1953 to promote and strengthen the overall economy by assisting small businesses. The SBA provides counseling to help people start and grow businesses. Their website (www.sba.gov) has tools to aid businesses, such as the Small Business Planner, and online training programs. Local offices throughout the United States and its territories provide in-person counseling services, such as assistance with business-plan writing or small-business loans.
The SBA provides a great deal of information to assist with small-business startup and growth, as well as online educational events. Local offices provide support through counseling and special events. The SBA provides a network of professionals who have volunteered their expertise to aid small businesses.
美国中小企业管理局的使命是:为小企业的创业发展提供技术援助、保贷款融资服务,解决小企业发展过程中的资金短缺问题,
为小企业投资基金(公司)提供资金和人才方面的支持。对符合国家产业、经济政策的方向进行风险投资,加速小企业的成长,
为了小企业能够规避市场的风险,以政府项目承包来拉动小企业的发展。在风险投资市场的发展过程中,美国政府意识到,
仅依赖于自由市场来满足高技术企业的资金需求是不够的,市场未能自身有效地分配资金。因此提出了州政府介入风险资金市场的必要性。
自20世纪80年代初以来,美国有超过25个州建立或正在筹建某种形式的州政府资助的风险基金。其特点为:
第一,基金项目的设计。在设立基金前,州政府进行详尽的研究,确定基金是否符合本地区的需求。
州政府重点考虑当地经济发展中基金的作用和基金拟达到的规模以及产业发展的最终目标。更重要的是,州风险投资项目只能被看做是
在当地发展高科技产业整体计划中的一部分。因此州风险投资计划不仅包括设立基金,还包括资助企业“孵化器”和风险投资网络。
第二,确立基金目标。州政府十分重视基金结构设计,包括基金的最终目标和评价指标。因此,州政府所面临的最根本问题是
基金应当注重投资回报率还是投资经济指标。投资回报率是投资额收益值的客观的业绩衡量指标,是私人风险投资公司评价自身业绩的而衡量尺度;
投资经济指标是以创造就业职位、社区福利等因素来衡量。
第三,风险投资经济。州政府风险投资基金可以多种方式进行投资,如直接投资于企业或作为私人基金的有限合伙人,
或两者的结合。为积极参与和更好地监督管理投资的企业,大基金倾向于将它们的投资组合限定相对较少数量的企业,
基金规模和基金所投的创业期企业数目之间呈负相关的关系。如,1亿美元的资金平均投资在25家企业,每家企业平均投资400万美元,
这个数字大大超过了种子期阶段和早期创业阶段企业融资的需求。结果基金公司可能偏向于投资企业的而后期阶段。州政府必须制定投资标准,
防止上述倾向发生。
第四,利用州退休基金。基金的来源可以多种形式,如州的税收、彩票所得、州退休金。州政府比较慎用州退休金。
较为合理的措施是州政府仅动用很小比例的退休基金注入风险投资基金。
总体说,美国各州政府基金所采用的管理模式各异,且成功率差别也很大。比较成功的是马赛诸萨州技术发展公司和密歇根州风险投资基金,
在州政府设立的基金中堪称典范。
Loan
The act of giving money, property or other material goods to another party in exchange for future repayment of the principal amount along with interest or other finance charges. A loan may be for a specific, one-time amount or can be available as open-ended credit up to a specified ceiling amount.
Investopedia Says:
The terms of a standardized loan are formally presented (usually in writing) to each party in the transaction before any money or property changes hands. If a lender出借方 requires any collateral, this will be stipulated规定 in the loan documents as well. Most loans also have legal stipulations regarding the maximum amount of interest that can be charged, as well as other covenants契约 such as the length of time before repayment is required.
Loans can come from individuals, corporations, financial institutions and governments. They are a way to grow the overall money supply in an economy as well as open up competition, introduce new products and expand business operations. Loans are a primary source of revenue for many financial institutions such as banks, as well as some retailers through the use of credit facilities.
<![if !supportLists]>· <![endif]>Loan Servicer
贷款服务
Prepayment
提前偿付
泛指在债务到期前已偿还。就抵押贷款而言,这是指在原定偿还计划以外的额外还款。有时贷款合约会规定,提前还款须向放款人缴付提前还款罚金(prepayment penalty)。如果提前偿还毋须支付罚金,借款人即拥有提前还款权(prepayment privilege或prior redemption privilege)。参见Amortization(1。分期偿还)。
"In mortgages, any unscheduled principal payment made in addition to the normal amortization.See also: Amortization"
Underlying
1. In derivatives, the security that must be delivered when a derivative contract, such as a put or call option, is exercised.
2. In equities, the common stock that must be delivered when a warrant is exercised, or when a convertible bond or convertible preferred share is converted to common stock.
Investopedia Says:
The price of the underlying is the main factor that determines prices of derivative securities, warrants and convertibles. Thus, a change in an underlying results in a simultaneous change in the price of the derivative asset that is linked to it. In most cases, the underlying is a security such as a stock (in the case of options) or a commodity (in the case of futures).
Prime
A classification类别 of borrowers, rates or holdings in the lending market that are considered to be of high quality. This classification is placed on those borrowers that are deemed视为 to be the most credit-worthy, and the prime rate is the rate that a lender will lend to its high quality borrowers.
Investopedia Says:
Lenders use a credit scoring system to determine which loans a borrower may qualify. A major variable in this credit scoring system is a borrower’s FICO score (which may range from 300 to 850). In general a borrower with a FICO score greater than 620 is considered to be eligible for a prime loan; however, other variables such as a past payment history, a record of bankruptcy破产, foreclosure抵押品赎回权的取消and the loan-to-value(LTV)ratio质押率 are also considered.
Since a lender’s incentives are not always aligned with a borrower’s incentives, it is important for consumers to shop for the best loan at the best rate.
Basis Points
基点
100个基点等于1个百分点,即1基点等于0.01个百分点。基点是市场谈论利率和债券收益率的标准计量单位。
"One hundredth of a percentage point, or 0.01, the standard market measure for interest rates and bond yields债券收益."
Interest Rate
利率
"利率是资金的价格,反映借贷的成本. 利率一般按年计算,比如年息5%(5厘),是指借款人一年需向放款人支付本金的5%,作为占用资金的代价. 支付利息是为了补偿放款人牺牲使用资金的权利、贷款期间因通货膨胀导致资金购买力下降的损失以及因放贷所承担的其它风险."
"The cost paid by a borrower to a lender over a period of time, often calculated annually. It is intended to compensate lenders for the sacrifice of losing the immediate use of their money, for the inflationary erosion of buying power over the life of the loan, and for the risk involved in lending."
A unit that is equal to 1/100th of 1%, and is used to denote指示 the change in a financial instrument. The basis point is commonly used for calculating changes in interest rates, equity indexes and the yield of a fixed-income security.
The relationship between percentage changes and basis points can be summarized as follows: 1% change = 100 basis points, and 0.01% = 1 basis point.
So, a bond whose yield increases from 5% to 5.5% is said to increase by 50 basis points; or interest rates that have risen 1% are said to have increased by 100 basis points.
<![if !supportLineBreakNewLine]>
<![endif]>
A lending risk assessment ratio that financial institutions and others lenders examine before approving a mortgage. Typically, assessments with high LTV ratios are generally seen as higher risk and, therefore, if the mortgage is accepted, the loan will generally cost the borrower more to borrow or he or she will need to purchase mortgage insurance.
Calculated as:
<![if !vml]>![]() <![endif]>
<![endif]>
For example, Jim needs to borrow $92,500 to purchase a $100,000 property. The LTV ratio yields a value of about 92.5%. Since bankers usually require a ratio at a maximum of 75% for a mortgage to be approved, it may prove difficult for Jim to get a mortgage.
Similar to other lending risk assessment ratios, the LTV ratio is not comprehensive全面 enough to be used as the only criteria in assessing mortgages
<![if !supportLineBreakNewLine]>
<![endif]>
Collateralized Mortgage Obligation (CMO)
A type of mortgage-backed security that creates separate pools of pass-through rates for different classes of bondholders with varying maturities, called tranches. The repayments from the pool of pass-through securities are used to retire the bonds in the order specified by the bonds‘ prospectus.
Investopedia Says:
Here is an example how a very simple CMO works: The investors in the CMO are divided up into three classes. They are called either class A, B or C investors. Each class differs in the order they receive principal payments, but receives interest payments as long as it is not completely paid off. Class A investors are paid out first with prepayments and repayments until they are paid off. Then class B investors are paid off, followed by class C investors. In a situation like this, class A investors bear most of the prepayment risk, while class C investors bear the least.
CMOs usually offer low returns because they are very low risk and are sometimes backed by government securities.
Basis
基差
基差为期货价格与标的资产现货价格的差距,通常是指最近月期货价减去现货价的结果。现货价与期货价有高度的相关性,但基差并非一成不变。基差交易(basis trade)就是根据对基差变动的预期而进行的买卖。随着期货趋近到期日,基差一般会逐渐缩窄,最终归于零
accrual basis权责发生制,应计制,权责发生基础,应计基础
确认收入和费用的一种会计方法。即根据商品的销售(或发货)和劳务的提供来确认收入,不论在什么时候收到现金;根据发生应付账款来确认费用,而不论什么时期支付现金
从会计的历史发展过程来看,权责发生制会计是从现金收付制会计的基础上发展起来的。现金收付制会计之所以没落,权责发生制之所以兴起,是出于对递延、应计项目和会计期假设的认识。目前,大多数企业采用权责发生制。因为权责发生制可以反映企业本期盈亏的实际情况。但是,近年来经济发达国家又逐渐重视现金流量报表(cash flow statement)。与现金收付制会计(cash basis accounting)的词义相对照
亦称应计基础,是指以是滞取得收到现金的权利或支付现金的责任权责的发生为标志来确认本期收入和费用及债权和债务。即收入按现金收入及未来现金收入――债权 扫生来确认;费用按现金支出及未来现金支出――债务的发生进行确认。而不是以现金的收入与支付来确认收入费用。按照权责发生制原则,凡是本期已经实现的收入和已经发生或应当负担的费用,不论其款项是否已经收付,都应作为当期的收入和费用处理;凡是不属于当期的收入和费用,即使款项已经在当期收付,都不应作为当期的收入和费用。因此,权责发生制属于会计要素确认计量方面的要求,它解决收入和费用何时予以确认及确认多少的问题。
权责发生制的实践依据是,在会计主体的经济活动中,经济业务的发生和货币的收支不是完全一致的,即存在着现金流动与经济活动的分离。由此而产生两个确诊和记录会计要素的标准,一个标准是根据货币收支是否来作为收入和费用确认和记录的依据,称为收付实现制;另一个标准是以取得收款权利付款责任作为记录收入或费用的依据,称为权责发生制。
权责发生制是依据持续经营和会计分期两个基本前提来正确划分不同会计期间资产、负债、收入、费用等会计要素的归属。并运用一些诸如应收、应付、预提、待摊等项目来记录由此形成的资产和负债等会计要素。企业经营不是一次而是多次,而其损益的记录又要分期进行,每期的损益计算理应反映所有属于本期的真实经营业绩,收付实现制显然不能完全做到这一点。因此,权责发生制能更加准确地反映特定会计期间实际的财务状况和经营业绩。
权责发生制大反映企业的经营业绩时有其合理性,几乎完全取代了收付实现制;但在反映企业的财务状况时却有其局限性:一个在损益表上看来经营很好,效率很高的企业,在资产负债表上却可能没有相应的变现资金而陷入财务困境。这是由于权责发生制把应计的收入和费用都反映在损益表上,而其在资产负债表上则部分反映为现金收支,部分反映为债权债务。为提示这种情况,应编制以收付实现制为基础的现金流量或财务状况变动表。弥补权责发生制的不足。
cash basis现金制(以现金为依据的记帐法)
Accruals
Accounts on a balance sheet that represent liabilities and non-cash-based assets used in accrual-based accounting. These accounts include, among many others, accounts payable, accounts receivable, goodwill, future tax liability and future interest expense.
Investopedia Says:
The use of accrual accounts has greatly increased the amount of information on accounting statements. Before the use of accruals only cash transactions were recorded on these statements. But cash transactions don‘t give information about other important business activities, such as revenue based on credit and future liabilities. By using accruals, a company can measure what it owes looking forward and what cash revenue it expects to receive. It also allows a company to show assets that do not have a cash value, such as goodwill.
Accruedinterest应计利息receivable应收款/ payable应付
Receivable 、Payable和 Prepaid
将Receivable 和Payable 两个词稍加比较,不难发现它们后面的四个字母相同,都有-able ,这是英语词汇构成的后缀之一。
这个词缀紧接在动词之后,使动词变成形容词,表示“能够…、适于…、可…、应…”。
Receive(收到、接受)加上- able 成为receivable,其意义也相应成为“能收的、应收的”;
同样pay(付款、支付)加上-able 也相应成为“应付的”。
这里要特别提到的是,动词后缀有-able 所形成的形容词,和一般形容词不同,在修饰名词时,它不在名词之前而在名词之后。
例如:
accounts receivable(应收帐款)、accounts payable (应付帐款)、notes receivable(应收票据)、notes payable(应付票据)。
下面举出几个句子来操练一下这几个会计词汇:
1、A business with many credit customers would set up the general ledger Accounts Receivable account for all credit customers
and a separate account for each credit customer.
有很多赊购客户的企业应设置一个应收帐款总分类帐户,登记所有赊购客户欠的货款,并为每个赊购客户设置一个明细帐户。
2、Accounts Receivable are often classified as current assets.
应收帐款通常归入流动资产。
3、Accounts receivable arise when a business sells goods and service on credit.
当企业以赊帐方式销售产品或提供服务时,就产生应收帐款。
4、A promissory note is regarded as notes receivable for the payee and notes payable for the maker.
本票对受款人来说是应收票据,对出票人来说则是应付票据。
5、Notes receivable which can be collected and converted into cash during next accounting year or operating cycle are classified
as current assets and are recorded at face value.
能在下一个会计年度或下一个经营周期收回和转换成现金的应收票据,归入流动资产,并按面值入帐。
6、Accounts payable and notes payable are typical example of current liabilities.
应付帐款和应付票据是流动负债的典型例子。
7、As stated above, accounts payable and notes payable are usually created by a company‘s economic activities, such as
purchases of merchandise and services received in the normal course of business.
如前所述,应付帐款和应付票据通常产生于企业的经营活动,例如在正常经营过程中的赊帐购买商品和接受服务。
Prepaid(预付的)这个词和前面的Pay 关系非常密切,实际上就是在pay 的过去分词paid 前加上一个前缀pre-,这个前缀表示“前、预
先”之意,合起来就是“预付的”。例如:
8、Assume that a business paid a $1200 premium on April 1 for one year‘s insurance in advance. This represents an increase in
one asset (prepaid expense) and a decrease in another asset (cash). Thus, the entry would be :
Dr. Prepaid Expenses—Prepaid Insurance $1200
Cr. Cash $1200
假设,一个公司4月1日支付了1200美圆的保险费预付一年的保险费。这意味着一种资产(预付费用)的增加,另一种资产(现金)的
减少。因此,会计分录应为:
借:预付费用—预付保险费 1200美圆
贷:现金 1200美圆
在进行对帐(Reconciliation)时,系统提供一个手边现金帐簿以核对凭证。通过输入银行凭证文件,用户可以进行人工或自动核对。
Bank reconciliation(银行存款余额调节表):对于银行对账单中现金余额与企业现金账户中现金余额之间存在差异的项目进行详细分析。
FOR 2012/04/10,
Trade-for-Trade Settlement
A securities transaction that the buyer and seller settledirectly, without recourse to a clearing house.
RR Registered Representative,
also called a general securities representative, a stock broker, or an account executive,
is an individual who is licensed to sell securities and has the legal power of an agent
in the USA.
Registered representatives usually work for broker-dealers licensed by the Securities
Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Self Regulatory Organizations (SRO) of the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
and National Association of Securities Dealers (NASD).
Recently the enforcement arm of the NYSE and NASD have combined to be known as the
Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA).
To become a registered representative, one must be sponsored by a broker-dealer firm and pass the
FINRA-administered Series 7 examination or another Limited Representative Qualifications Exam.
Some state laws and broker-dealer policies require the Series 63 examination to be passed, as well.
A registered representative (or simply "RR" or "rep" or "broker") is authorized to sell a large array
of securities such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, variable annuities, etc. and should not be confused
with the more narrowly licensed financial services representative, who is licensed by passing the
FINRA series 6 securities exam. The Series 6 permits the "rep" to sell only mutual funds and variable
annuity contracts. Variable products such as variable annuities or variable universal life insurance
policies typically also require reps obtain the appropriate state insurance department license(s) required
for such variable.
Continuous Net Settlement (CNS)
An automated book-entry accounting system. CNS centralizes the settlement of compared transactions and maintains an efficient flow of security and money balances.
Investopedia Says:
During the CNS process, there are reports that are generated which document the movements of money and securities. This system provides clearance for instruments like equities, corporate bonds, Unit Investment Trusts and municipal bonds.
average price account,
Average Price Account Identifiers
Broker-dealers often use their "average price accounts" as a mechanism to buy or sell large amounts of a given security for their institutional customers. Under this arrangement(约定, 商议), a broker-dealer‘s average price account may buy or sell a security in small increments throughout a trading session, and then transfer the accumulated long or short position to one or more institutional accounts for a volume-weighted average price after the market close.
As with transactions involving prime brokerage arrangements, there currently is no uniformity in how broker-dealers identify these transactions in EBS submissions. As a result, the Commission‘s trading analyses may inadvertently double-count such transactions -- once in the EBS submission for the firm‘s average price account, and again in the EBS submission for the institutional account receiving positions from the average price account. Two additional data elements in proposed Rule 17a-25 are designed to provide uniformity in identifying transactions involving average price accounts.
First, if an institutional account‘s transactions involved transfers from the broker-dealer‘s average price accounts, this would have to be reflected in one of the new data fields in the enhanced EBS format. This requirement is set forth in sub-paragraph (2) (i) under paragraph (b) of proposed Rule 17a-25. Similarly, if the account covered by an EBS submission were itself an average price account, this also would have to be reflected in a new field in the enhanced EBS format. This requirement is set forth in sub-paragraph (2) (ii) under paragraph (b) of proposed Rule 17a-25.18
成交量加权平均价, 英文Volume-weighted Average Price的缩写。VWAP是将多笔交易的价格按各自的成交量加权而算出的平均价,若是计算某一证券在某交易日的VWAP,将当日成交总值除以总成交量即可。VWAP可作为交易定价的一种方法,亦可作为衡量机构投资者或交易商的交易表现的尺度。英文亦称为dynamic time and sales。
<![if !vml]> <![endif]>
<![endif]>
Trade Reporting And Compliance Engine (TRACE)
A program developed by the National Association of Securities Dealers (NASD) which allows for the reporting of over-the-counter (OTC) transactions pertaining(与…有关) to eligible fixed-income securities. Brokers, who are NASD members and deal with specific fixed-income securities, are required to report their transactions by Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) rules.
Investopedia Says:
From 1998-2001, the SEC approved rules adopted by the NASD regarding the transactions in all U.S. corporate bonds and secondary OTC fixed-income transactions. These rules were developed to bring greater price transparency to bond markets. Subsequently, TRACE was brought into play in 2002 to comply with the newly approved rules. The program replaced the previous Fixed Income Pricing System (FIPS) used since 1994.
UIT 单位投资信托
An investment company that offers a fixed, unmanaged portfolio, generally of stocks and bonds, as redeemable "units" to investors for a specific period of time. It is designed to provide capital appreciation and/or dividend income.
Unit investment trusts are one of three types of investment companies; the other two are Mutual Funds and Closed-end Funds
Each unit typically costs $1,000 and is sold to investors by brokers. UITs can be resold(转售) in the secondary market. A UIT may be either a regulated investment corporation (RIC) or a grantor trust. The former is a corporation in which the investors are joint owners; the latter grants investors proportional ownership in the UIT‘s underlying securities.
<![if !supportLineBreakNewLine]>--------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2012-7-5
<![endif]>
Penny Stocks are any stock that trades below $5 per share. Most financial advisors and long-term investors tend to avoid them completely because of the extremely high risk that comes with owning them. They generally tend to fluctuate wildly in price, and although some report spectacular gains in a matter of a few days [or even hours], those who invest in them are generally surprised when they disappear altogether.
Generally, if a stock is trading that low, it is danger of losing its listing with an exchange. When this happens, a company is normally either in very bad financial shape, or on the brink of bankruptcy. Smart investors opt to avoid these.
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ECNB/p/4607138.html